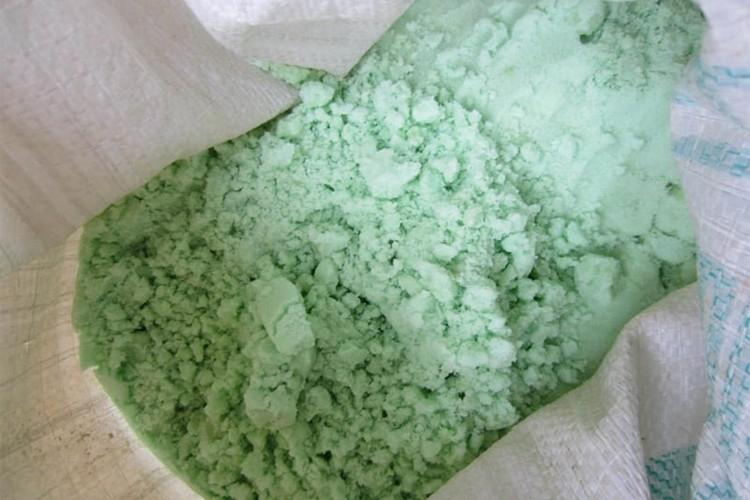
The blue-green powder that you have probably encountered in gardening is iron vitriol. Or ferrous sulfate, which is very versatile for the treatment of plants and the prevention of everything in the world. It is even introduced as a mineral supplement when feeding. Let's tell you more!
Fight against spring frosts
Treatment with a weak solution of ferrous sulfate before the appearance of buds helps to delay the beginning of the growing season by a couple of weeks. This is important for species that are sensitive to temperature extremes, such as grapes. After processing, they tolerate the first spring frosts much better after removing the winter shelter.

Iron vitriol from pests
An active and prophylactic insecticide is one of the main areas of application of ferrous sulfate, because it destroys not only insects, but also their masonry with larvae. Be sure to choose the concentration according to the situation: the minimum, if the kidneys are already forming. And more, up to 5% - in the fall, when the leaves have fallen.
When processing fruit trees with vitriol only, without other auxiliary preparations, up to 50% of the eggs of the honeydew can be destroyed. You need to process the trunk, all branches and the ground around the tree. Estimated dates are mid-April, but take into account climatic features, weather and type of culture.
Keep in mind that even a strong solution does not cope well with hibernating parasites. So you need to wait until they wake up and start laying eggs. But do not delay, otherwise the treatment will harm the plant and the crop, because after all it is a rather aggressive agent. Iron sulfate should not be combined with organophosphate insecticides.

Iron vitriol from fungus
The advantages of contact fungicides are their effectiveness and the fact that they do not accumulate inside. Ferrous sulfate is used for spring spraying when the above zero temperature is finally stabilized. The procedure can be repeated during flowering to protect the buds from fungus.
For the health of pears, apple trees and other fruit trees, treat them twice with a 3% solution with a week break. The same concentration and frequency is needed to protect rose bushes from spotting. For currants and raspberries, do not exceed the concentration of 2-2.5%, and for pome fruits, all 5% are suitable. In viticulture, vines are treated with 5% concentrate with an interval of two weeks against cancer, necrosis and anthracnose.
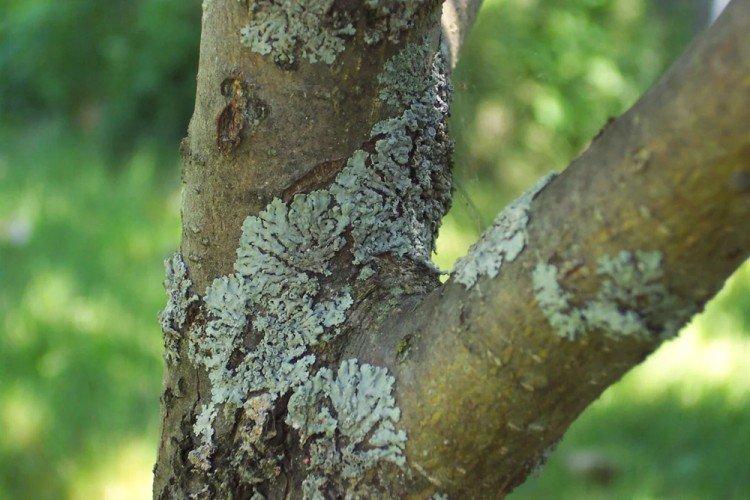

Moss and lichen control
A strong 3-5% solution of ferrous sulfate is very aggressive towards lichens and mosses. Spray trees as needed in the spring or fall, with a break of 1-2 weeks - and soon you will see how lichens and moss disappear on their own. Then treat the affected areas with an ash solution and the same 5% vitriol.

Treatment of wounds and sections with iron vitriol
A saturated solution of vitriol (100 g per liter) is a very good antiseptic, therefore it is used for fresh damage. It is also suitable for cleaning hollows, preventing the spread of infection and whitewashing trunks.

Iron vitriol from chlorosis
Pale leaves, stunted development, sluggish flowering and underdeveloped fruits are signs of chlorosis. It often affects apple, plum, cherry and other fruit trees. Chlorosis is usually directly related to iron deficiency, so treatment is likely to improve the situation.
Dilute 50 g of ferrous sulfate in a bucket of water and process the trees every 5-6 days until the symptoms disappear. For regular preventive treatment, a weaker solution is needed: 10 g per bucket of water. This procedure is carried out a little less often: about once a week.

Fertilizing with iron vitriol
Vitriol is often used together with top dressing, because the iron in it is in the most convenient and well assimilated form for plants. The sure signs of deficiency are the dying off of shoots, yellowness of leaves and wilting flowers without other obvious reasons and symptoms. Fruit trees are especially affected, because in their life, iron is indispensable for breathing.
For foliar dressing, iron vitriol is diluted in a proportion of 5-10 g per bucket. They also treat the beds: especially cabbage, potatoes and tomatoes. Add 100 g of vitriol to 10 kg of organic matter and mix into the soil while digging.
Avoid contact of ferrous sulfate with lime, and even an insignificant concentration is important. Prepare exceptionally soft water for solutions. Otherwise, as a result of the reaction, compounds are formed that the plants cannot absorb.

Security measures
Work strictly with gloves and only take glass or plastic containers. Do not store iron sulfate with food and do not use utensils that you use in everyday life. Make sure that the solution does not come into contact with the skin or eyes, and if this happens, rinse immediately with water!