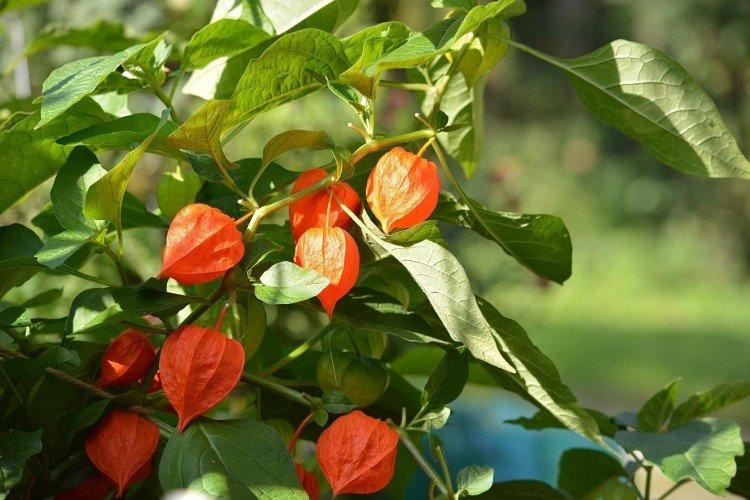
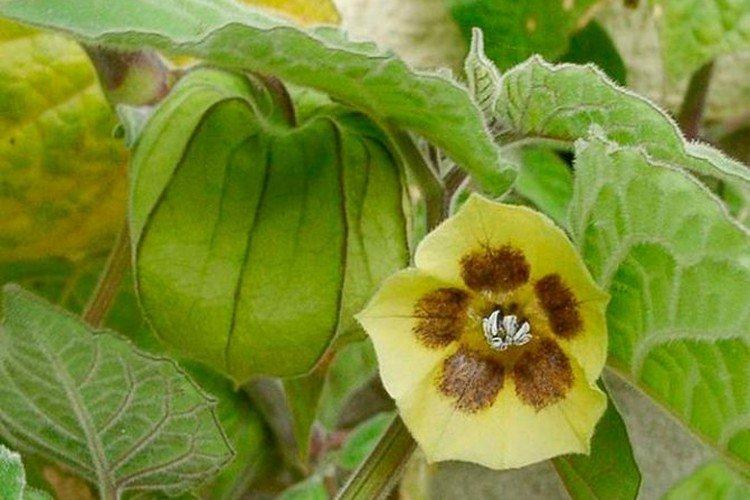
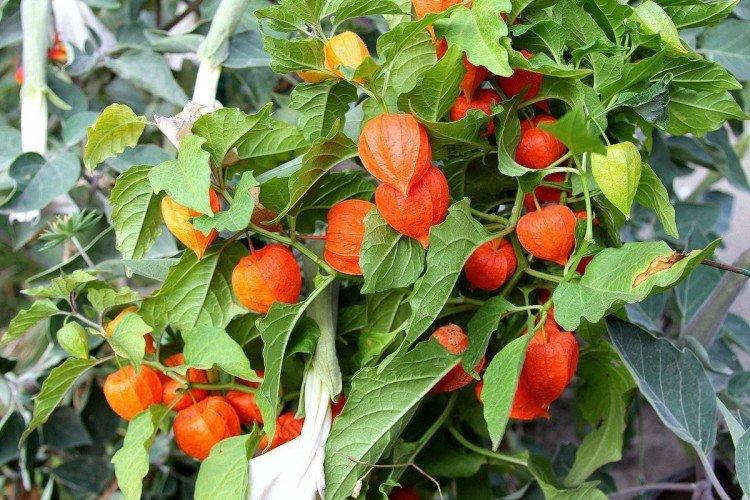
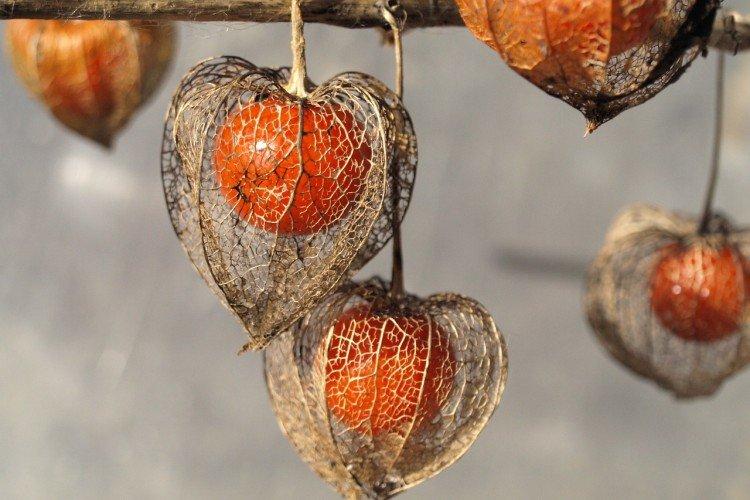
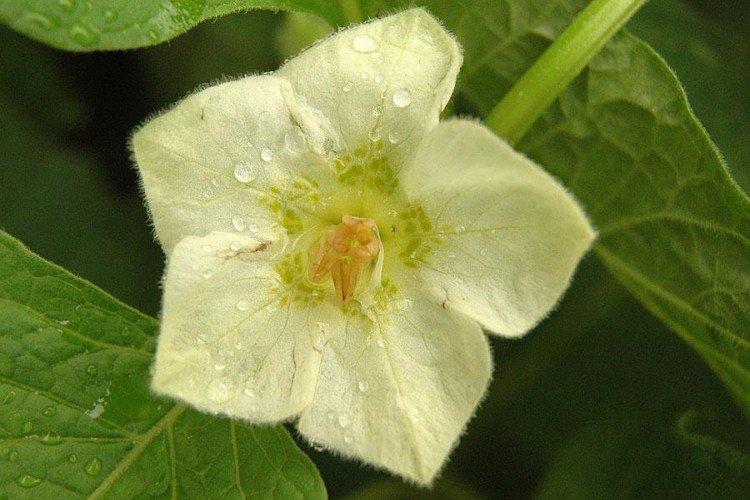
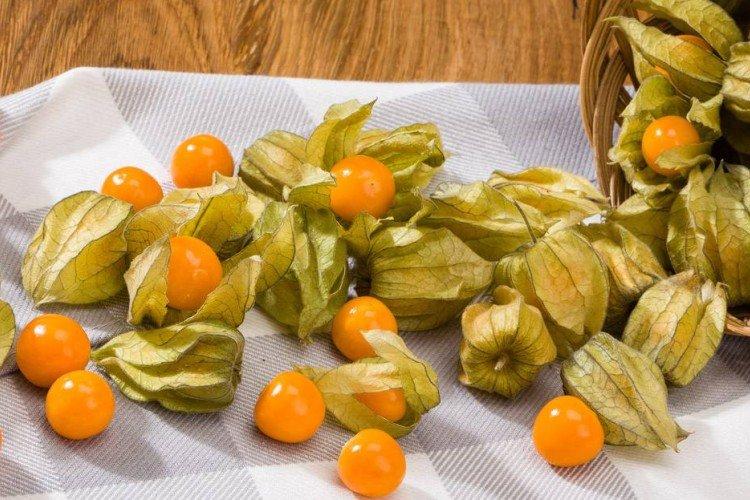
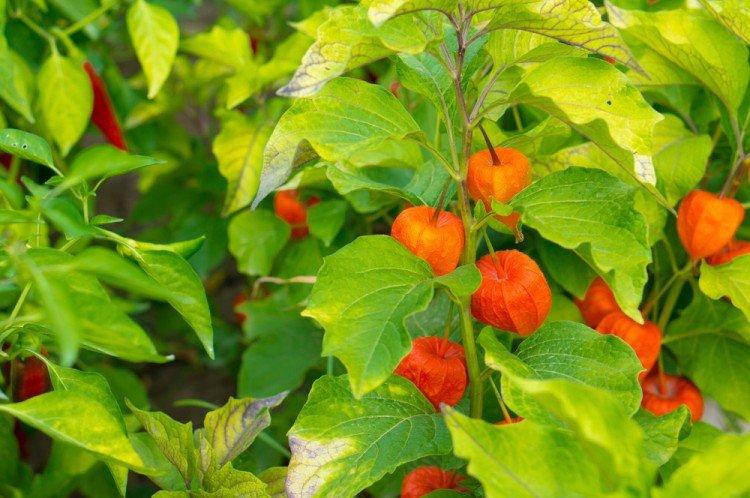
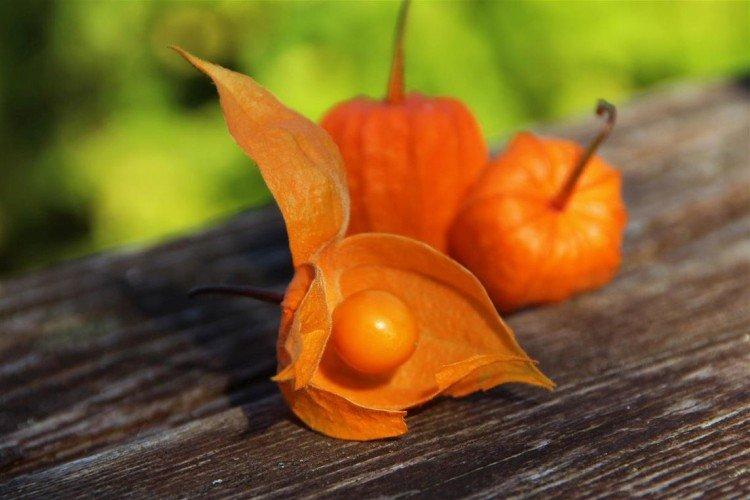
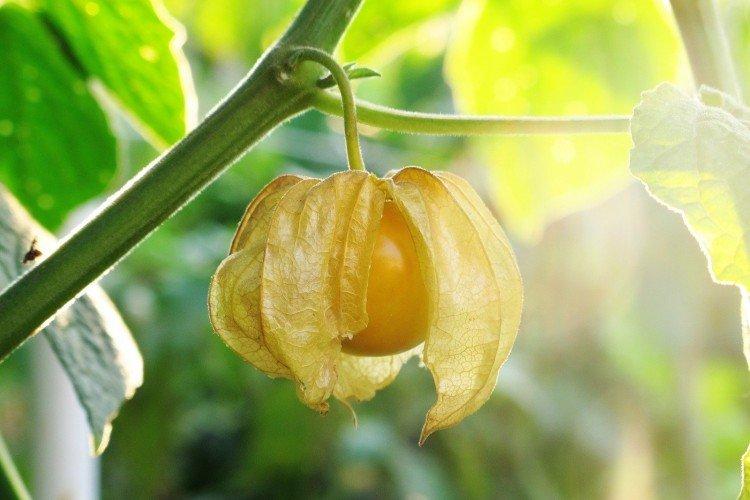
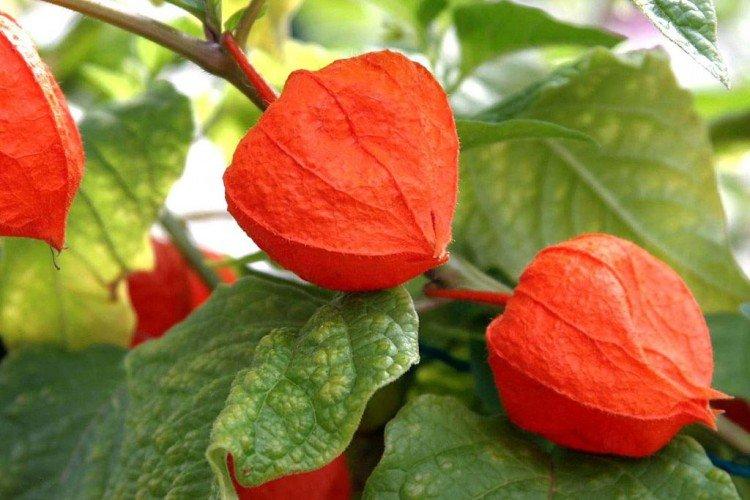
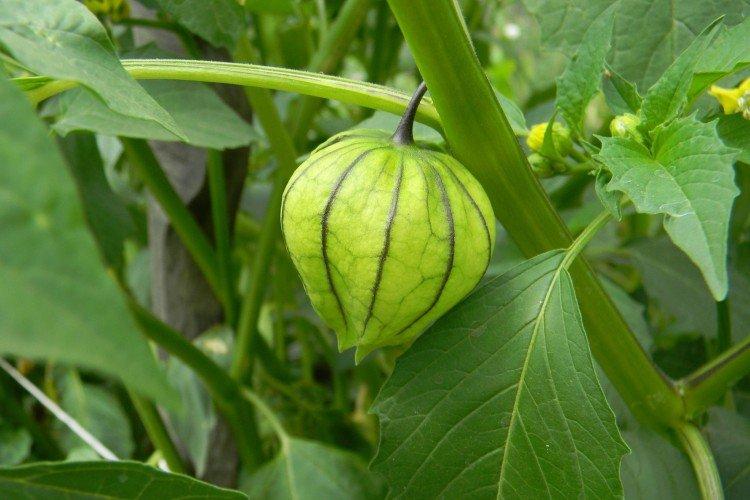
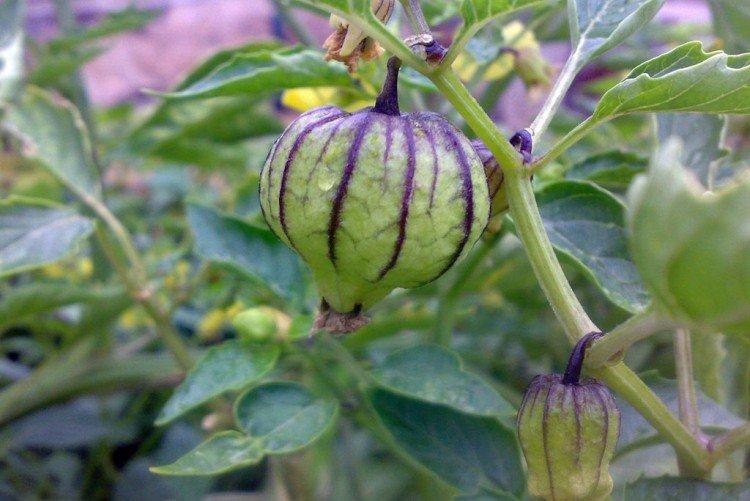
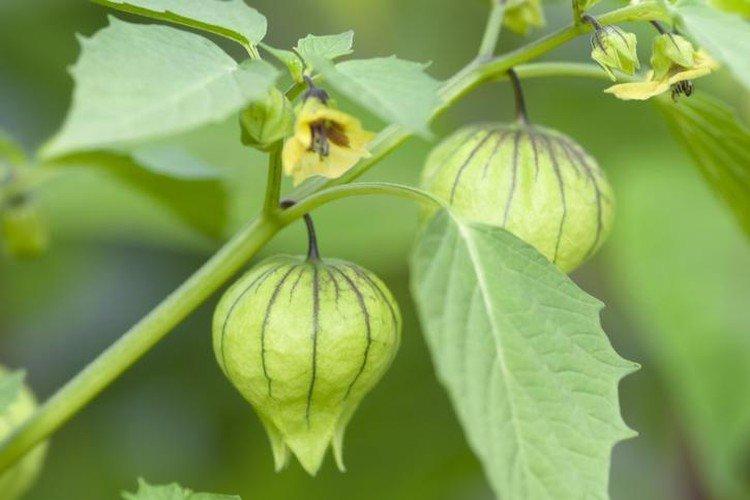
Beautiful leaves, beautiful flowers and fruits - all this is about physalis. Even edible varieties are very showy, not to mention the variety of ornamental varieties. By the way, do you even know that it can also be different? No? Then we'll tell you!
general information
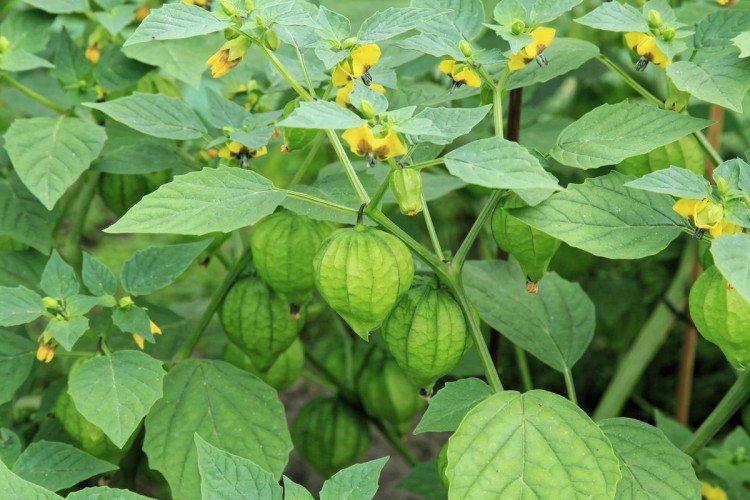
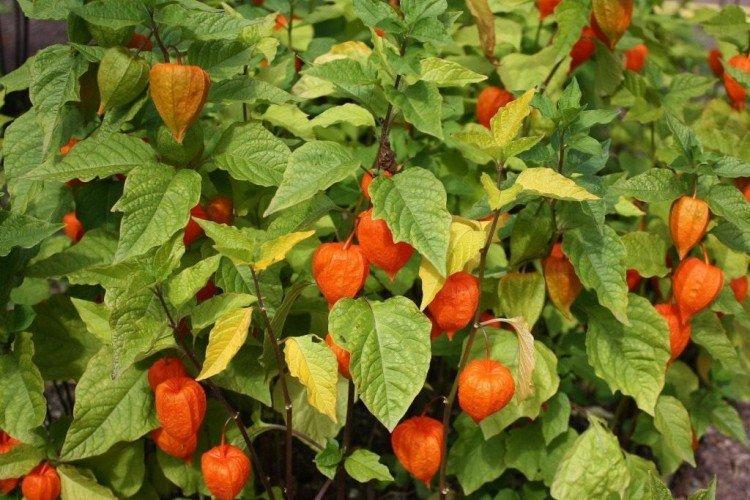
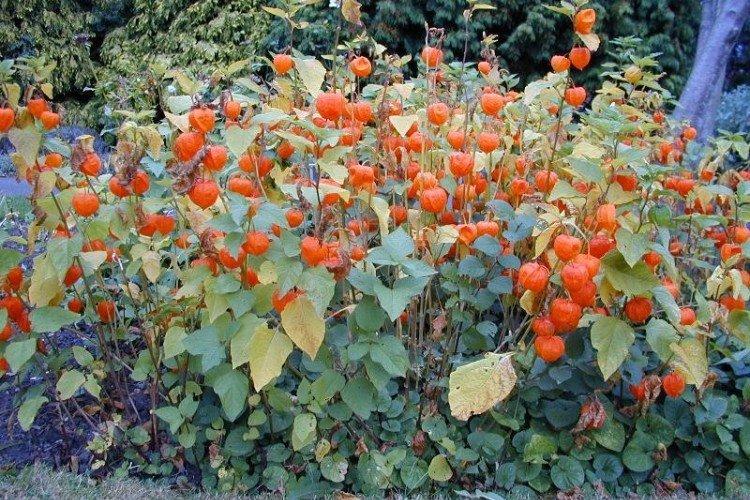
Physalis grows into a fairly large shrub thanks to its branching stems. At the same time, the average height ranges from 60 to 120 cm. Moreover, in 1.5 months one such bush easily gives up to 150 small fruits.
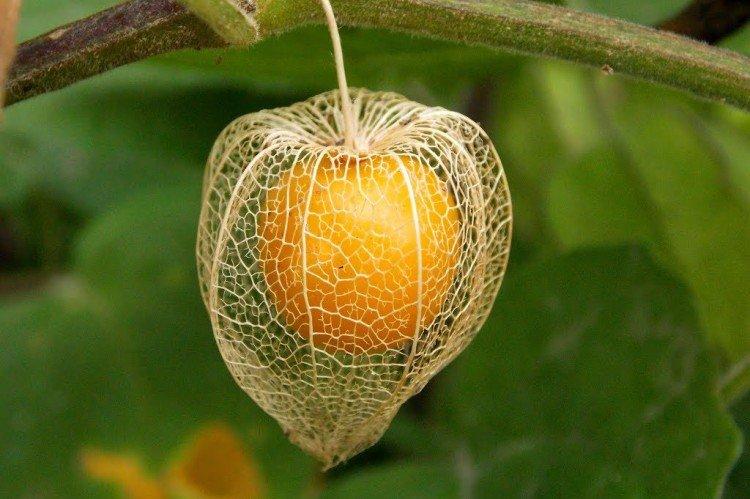
Physalis is the most extensive genus in its Solanaceae family. In nature, it is more common in South and North America, but it is already quite common in Asia and Europe. The name means "bubble" from Greek, which is easily explained by the shape of the fruit.
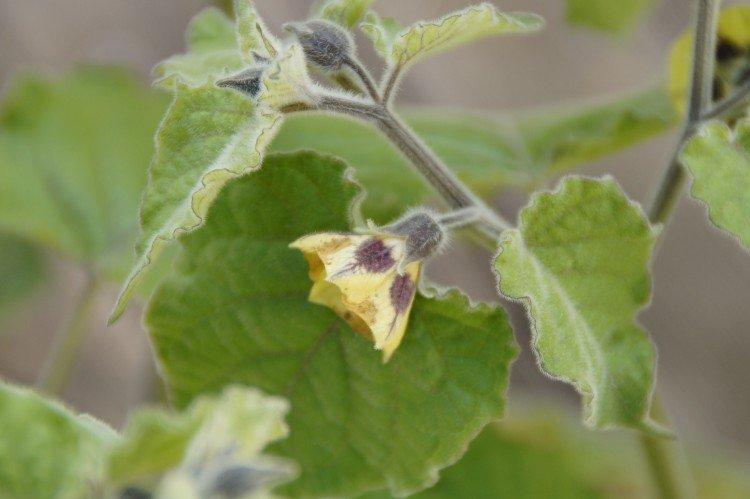
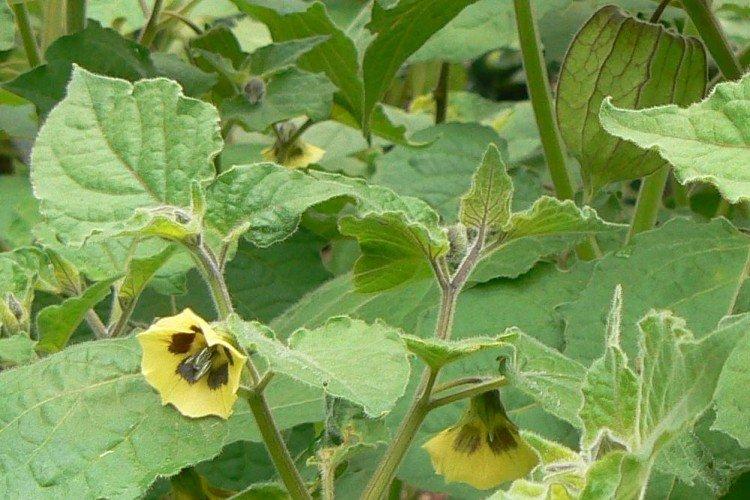
Among Physalis, there are annuals and perennials. As the shoots grow, they become woody, and the shrub resembles a real tree. In the flowering season, single flowers bloom along the entire length of the shoot, after which swollen spherical fruits with a characteristic aroma are formed.
In addition to its active use in cooking, physalis has many medicinal properties. And all thanks to the high content of beneficial acids and minerals. In folk medicine, even the leaves and roots of the plant are used to prepare decoctions.
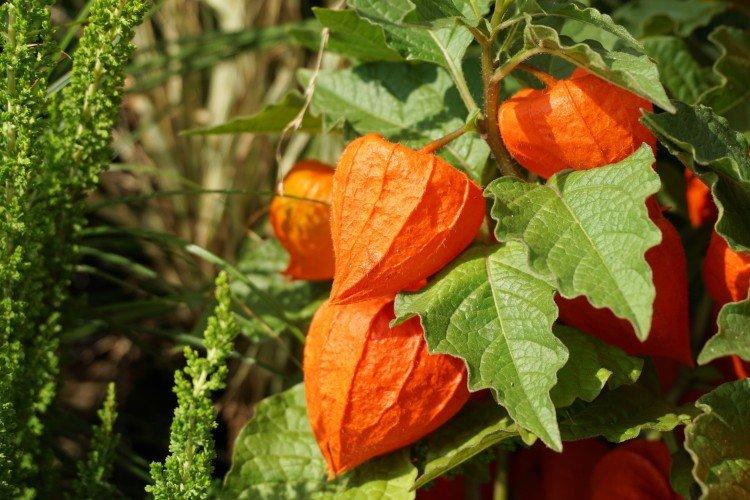

Physalis types
All types and varieties of physalis can be divided into two broad categories - decorative and edible. Their purpose is obvious, and they are all good in their own way. Here are some of the most popular varieties!
Alkekengi
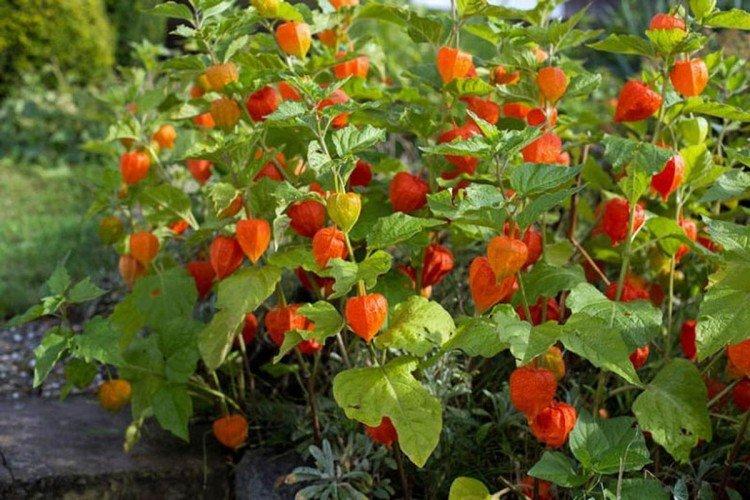
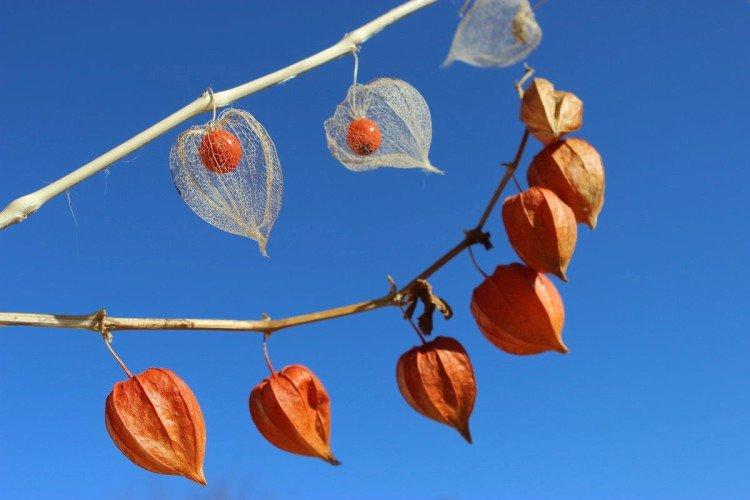
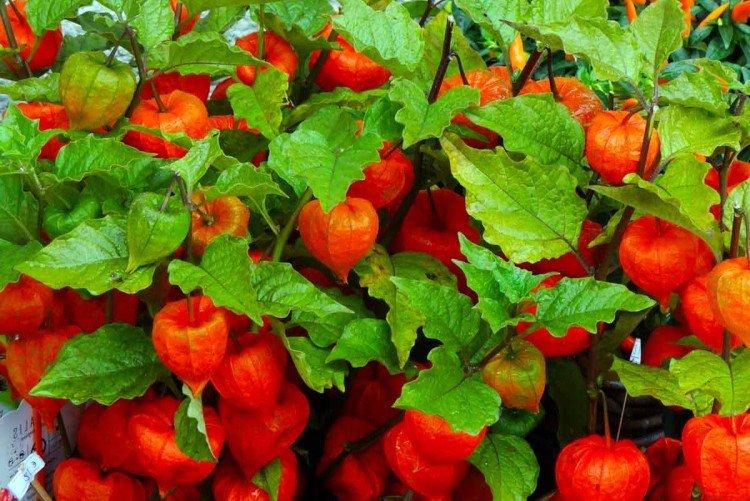
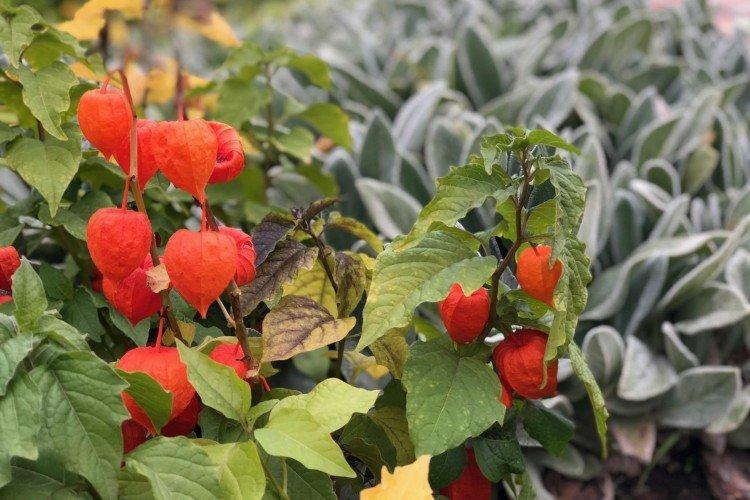
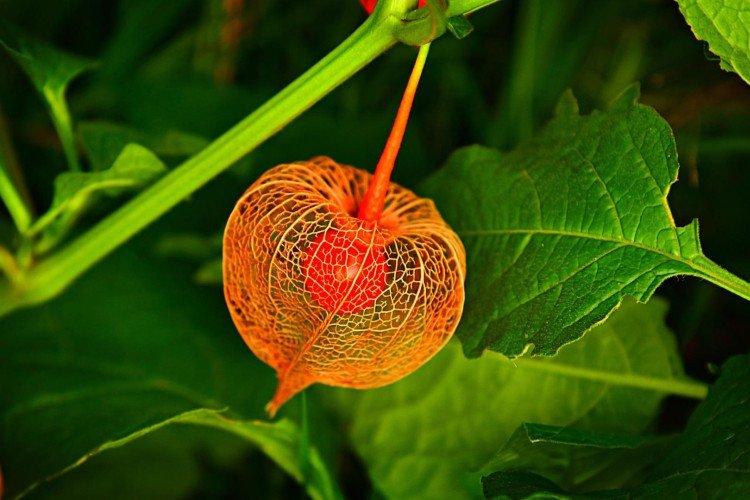
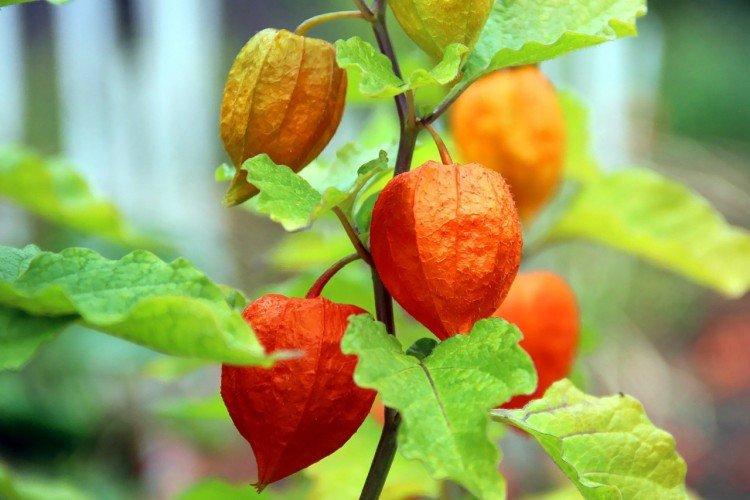
Decorative physalis, which is also called a red lantern. But in fact, the fruits are not only red, but also yellow or orange.
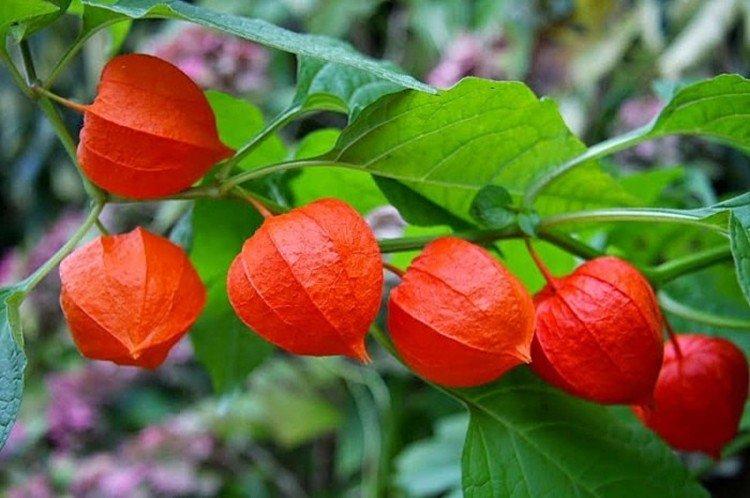

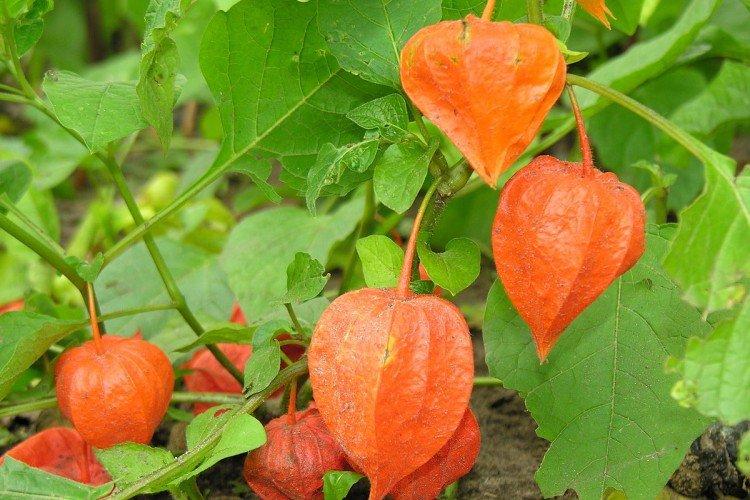
Franchet
A very effective decorative variety. The bright orange cup hides no less bright cherry fruits. This shrub is often used for landscape decoration.

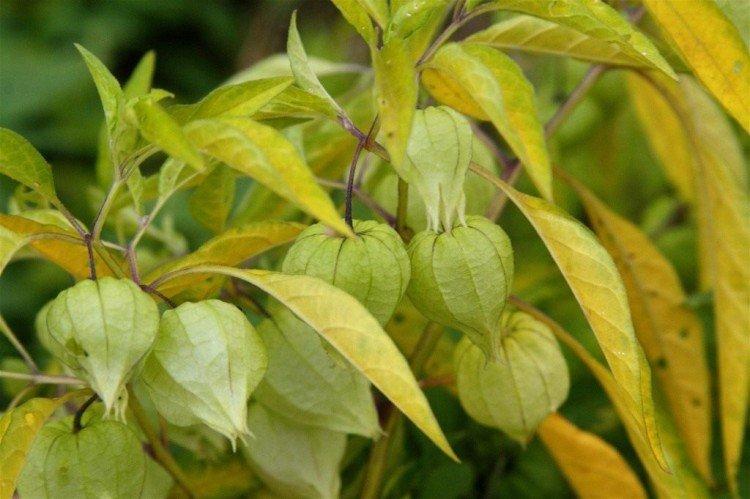
Longifolia
A tall ornamental shrub stretches up to 2 m. The fruits of this physalis are light, delicate cream shade, with ribbed edges.

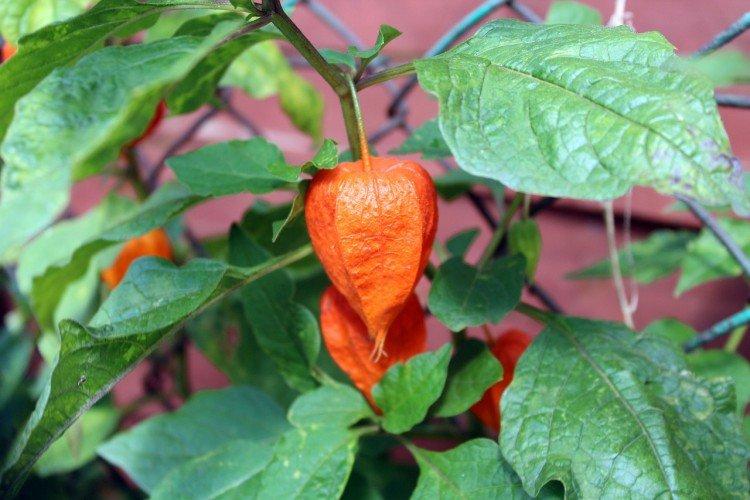
Vegetable physalis
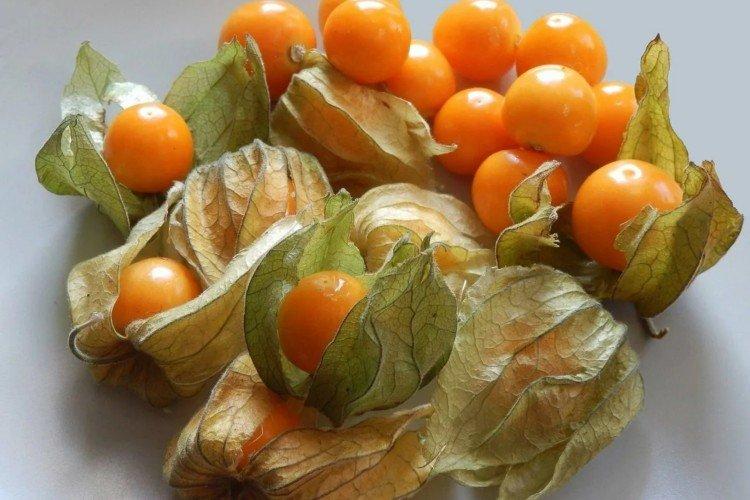
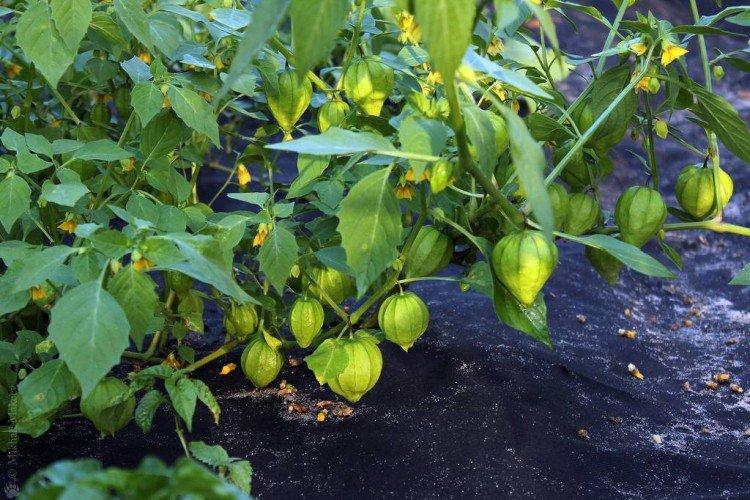
This is the main edible species that came to our latitudes straight from Mexico. Its fruits are fleshy and juicy, which is why it is called tomatil in its homeland.

Strawberry Physalis
It is also Peruvian, and it is a vast dessert species. In texture and taste, its fruits are more similar to the berries we are accustomed to than to the same tomatoes. The fruits of berry physalis are several times smaller than those of vegetables.
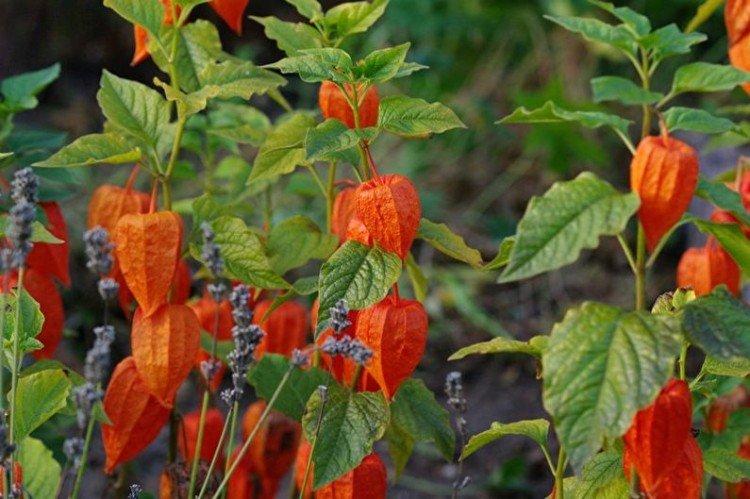

Physalis care
It doesn't matter for what purpose you plant physalis. All of its varieties are very similar in requirements, so we share the basic subtleties of care!
Temperature
Physalis is a frost-resistant plant that does not require a special temperature regime. The best conditions for active fruiting are 15-20 degrees. For fast germination of seeds, you need 10-12 degrees, and only for berry varieties - from +15.
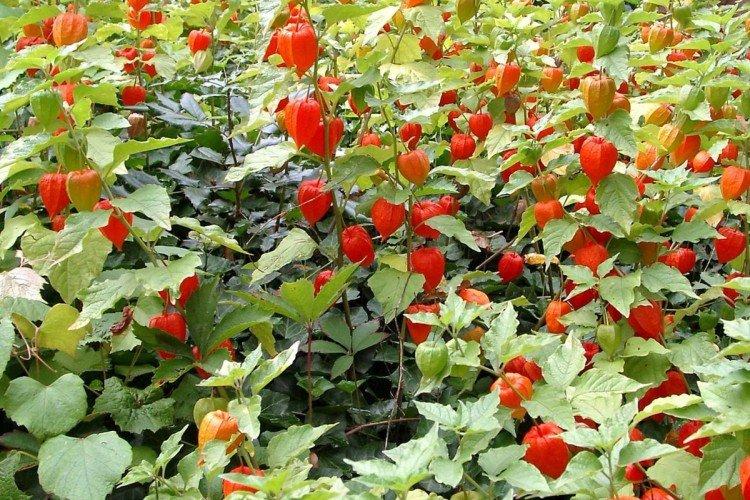

Lighting
Physalis loves good lighting, but is not too keen on direct sunlight. Ideally, there should be light shade on the site during peak hours.
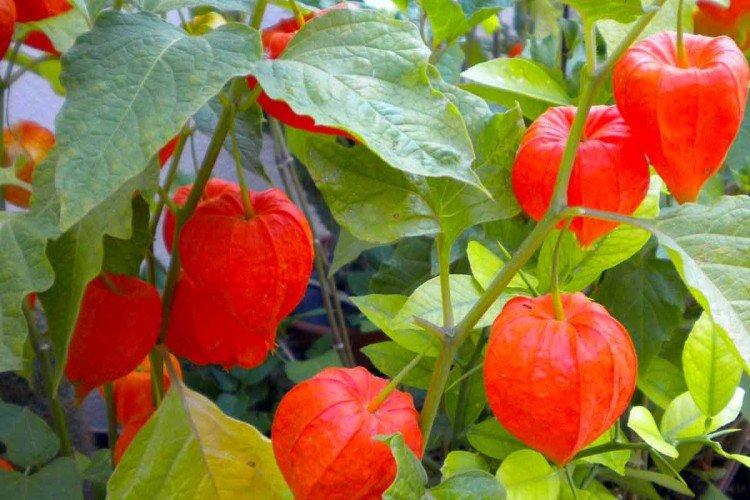

Watering
Physalis needs frequent intensive watering, especially young plants. Overgrown seedlings are even planted in holes with water for better rooting.
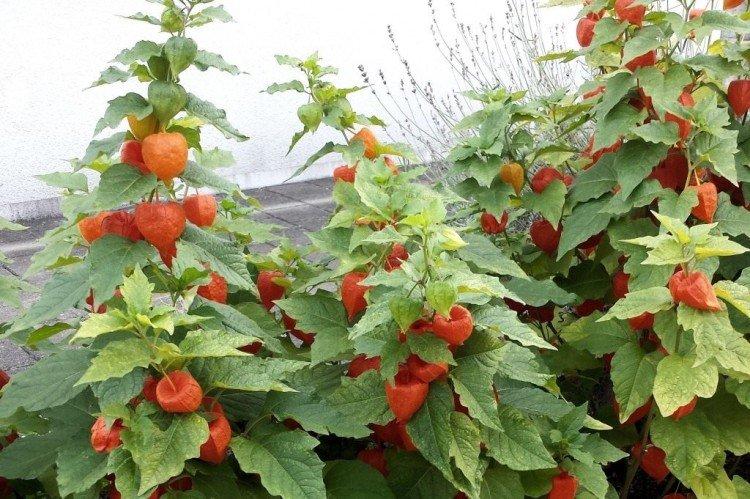

The soil
For all its exotic origin, physalis is completely unpretentious to the composition of the soil. But if you want the bush to bear fruit abundantly, you still need fertile soil. Physalis should not be planted after other nightshades, but it is possible after cabbage or cucumbers.

Fertilizers and feeding
Physalis needs to be fed regularly, and organics are great for this. You can prepare mineral fertilizers yourself from nitrate, superphosphates and potassium salt in equal proportions.

Trimming and pinching
Physalis does not need to be shaped, trimmed, pinched and pinned.The more and more actively it branches in a natural way, the more magnificent the flowering and the more impressive the harvest will be.

Harvesting
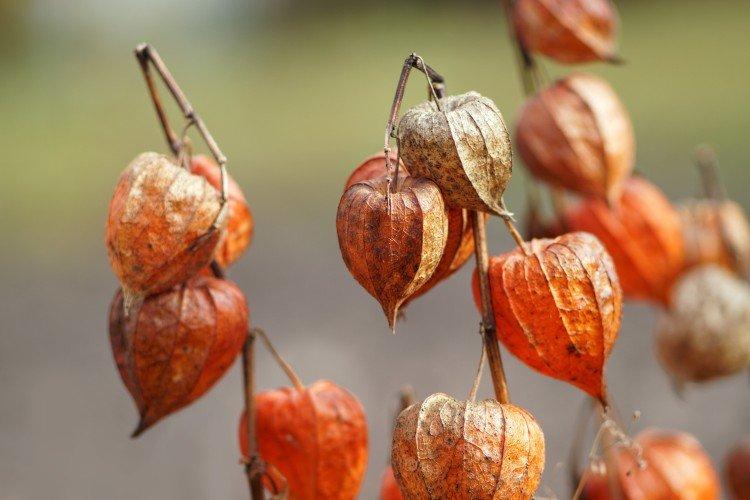
Physalis fruits can be safely left on the bush until the end of autumn. Together with the plant, they normally tolerate cold snaps and night frosts. It is more convenient to harvest when the cup is already dry. But if you plan to keep the fruits for a long time, they should be slightly unripe.

Wintering
The entire above-ground part of perennial decorative varieties for the winter can be safely cut off and used for bouquets. After that, cover the area with peat until spring. But after harvest, annual varieties are recommended to be completely destroyed by the roots.
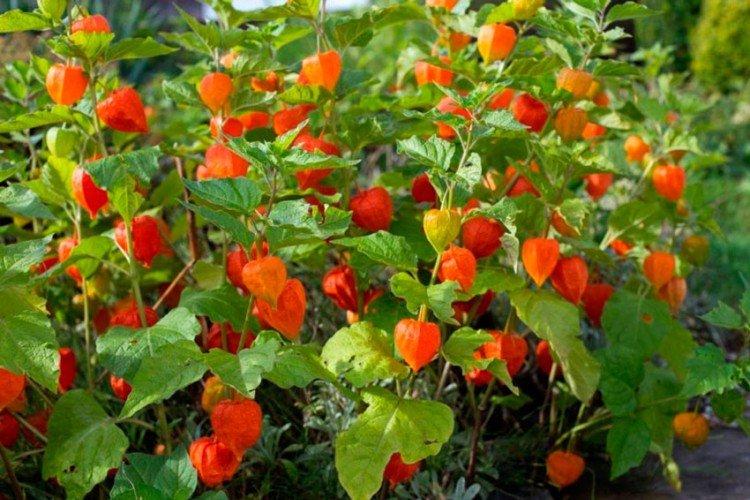

Planting and breeding
In warm regions, physalis can be planted directly into open ground closer to the beginning of May. The seeds are simply laid out in the furrows, and then thinned out after the seedlings appear. And you can plant them before winter - in October, but then it is better to mulch the site.
In middle latitudes, physalis is planted only through seedlings, but it will begin to bear fruit earlier. 1-1.5 months before transplanting into open ground, the seeds are planted in separate pots and left warm until the seedlings appear.
Keep humidity levels low because small sprouts are often prone to blacklegs. And regularly air the seedlings. If you plant physalis in containers, you can dive with the appearance of 2 leaves.
After the formation of 5-6 leaves, physalis can be transplanted into open ground in cloudy weather. It is best to plant the bushes in a checkerboard pattern with a distance of at least 0.5 m, because they will branch intensively. The depth of the planting hole is up to the first true leaf.

Physalis pests and diseases
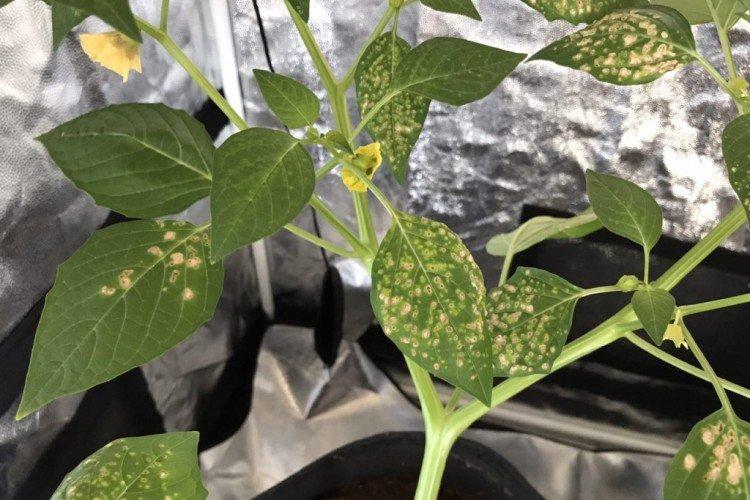
Chaotic yellow spots on leaves and shoots may indicate a viral mosaic. Diseased plants must be destroyed, but drug treatment can help in the early stages.
Penicillosis manifests itself as foci of rotting on fruits when damaged or cracked. To do this, the fruits must be collected in a timely manner, and at high humidity, the seedlings must be sprayed with potassium permanganate or fungicides.
Different fungal diseases can manifest themselves in different ways - in the form of spots, watery patches, plaque. The treatment is always the same: remove damaged plant fragments and treat the seedlings with fungicides.
The most common physalis pest is slugs. They need to be caught mechanically using traps. You can sprinkle the aisles with tobacco or phosphates, and also use special prophylactic drugs.

Physalis - photo
And if you still have a bad idea of how physalis really looks in the garden - this selection is especially for you!