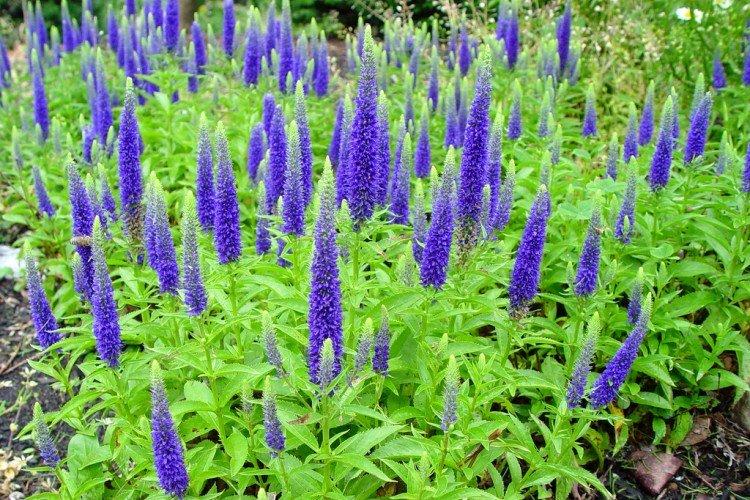
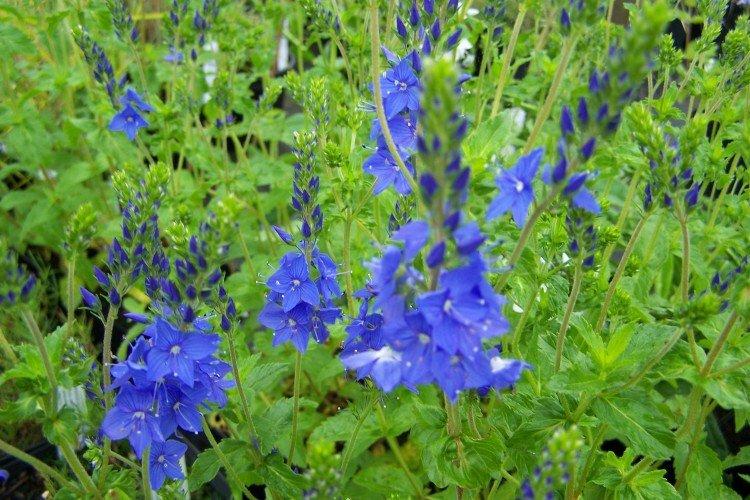
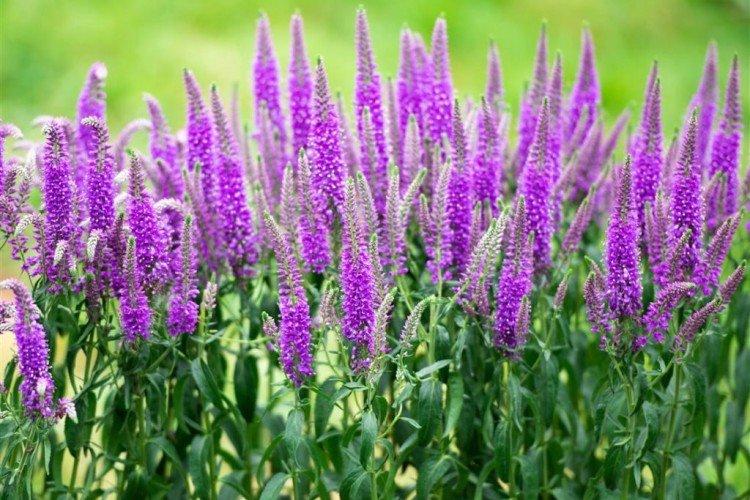
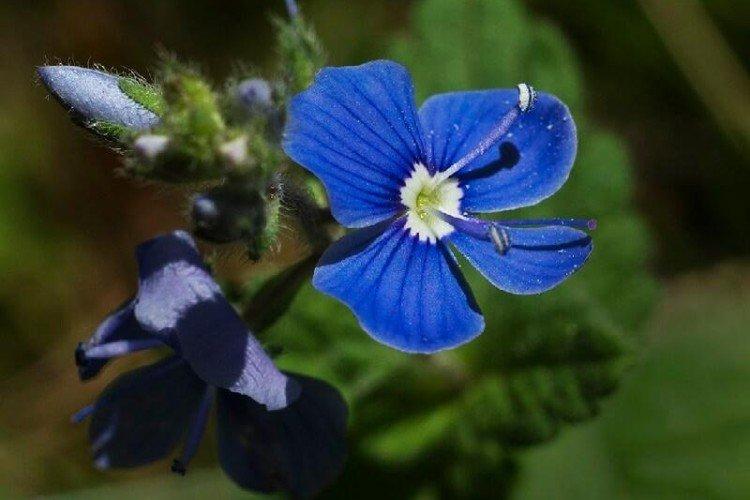
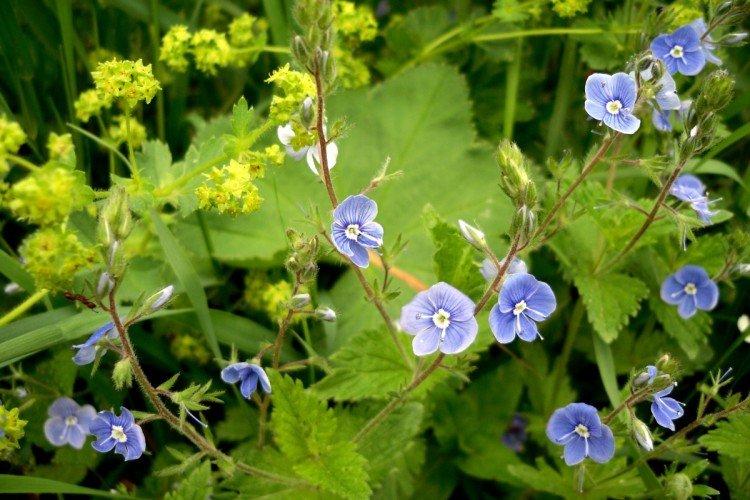
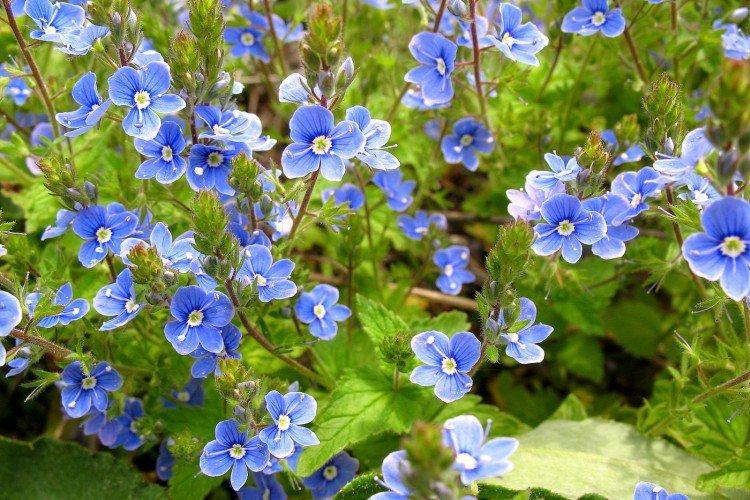
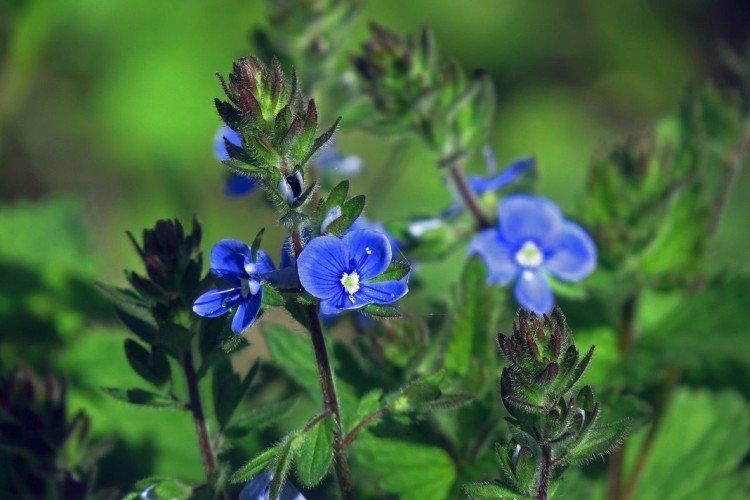
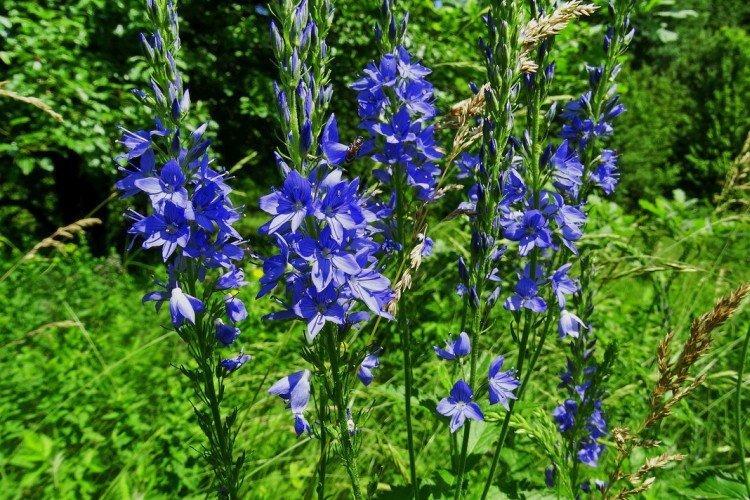
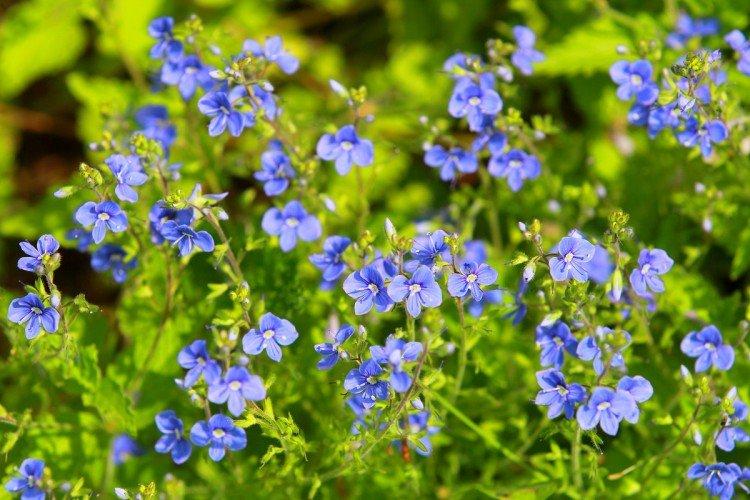
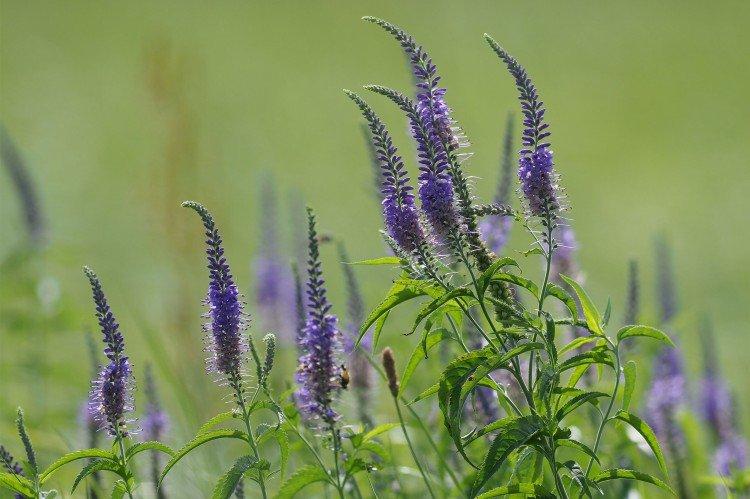
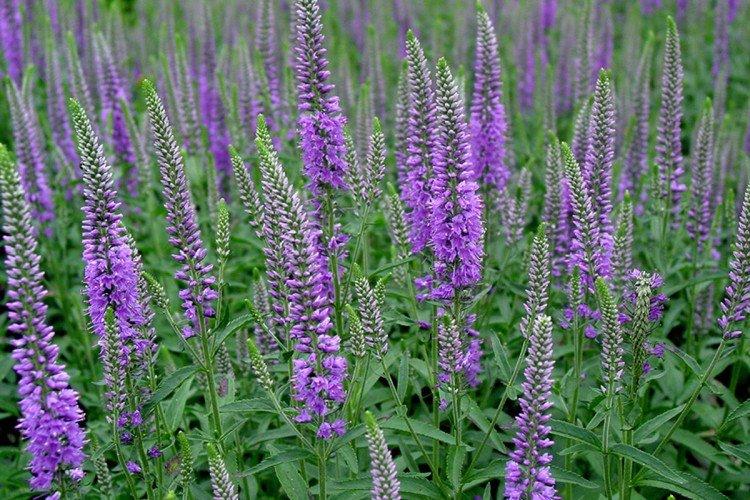
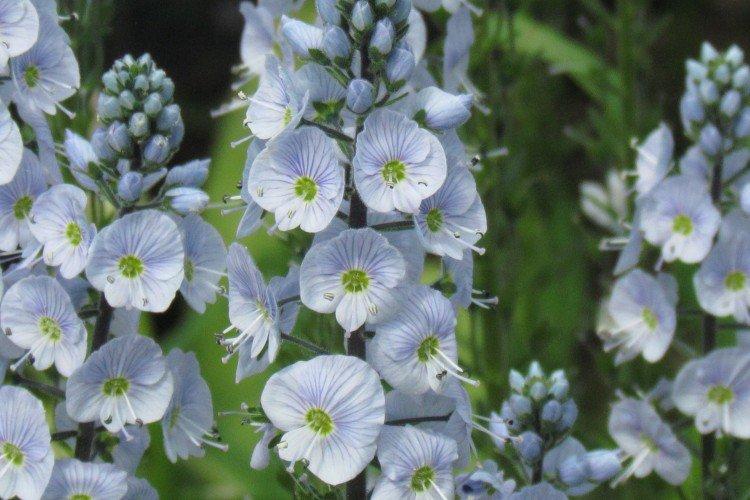
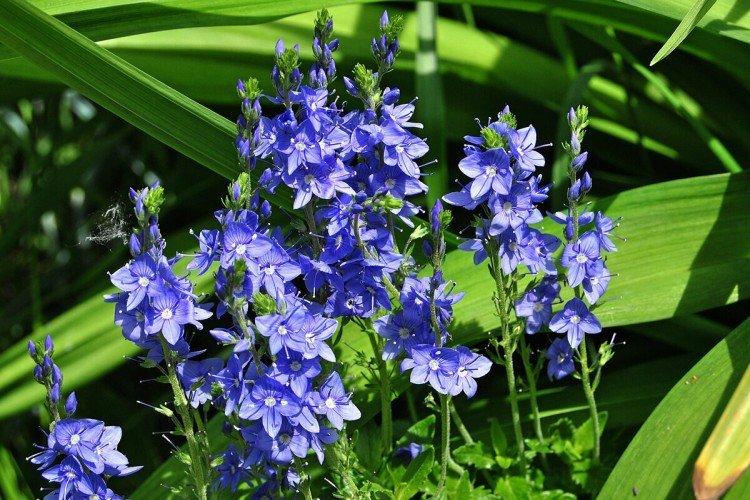
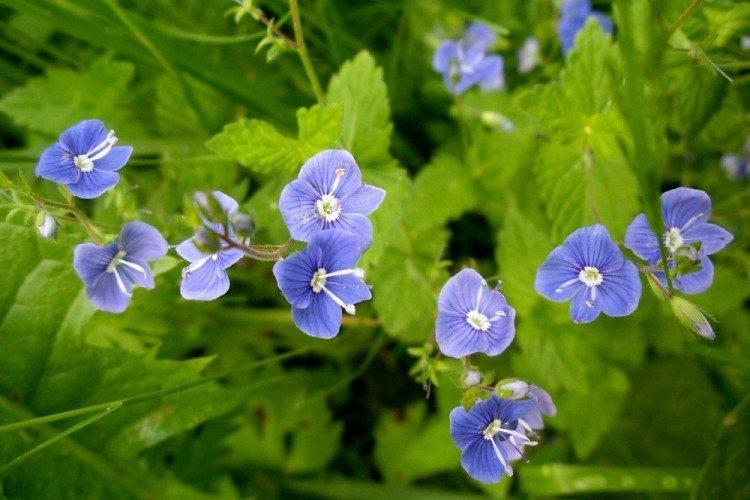
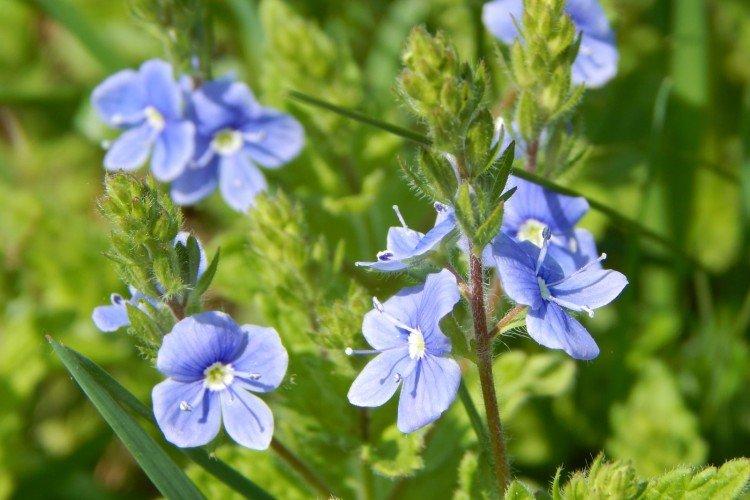
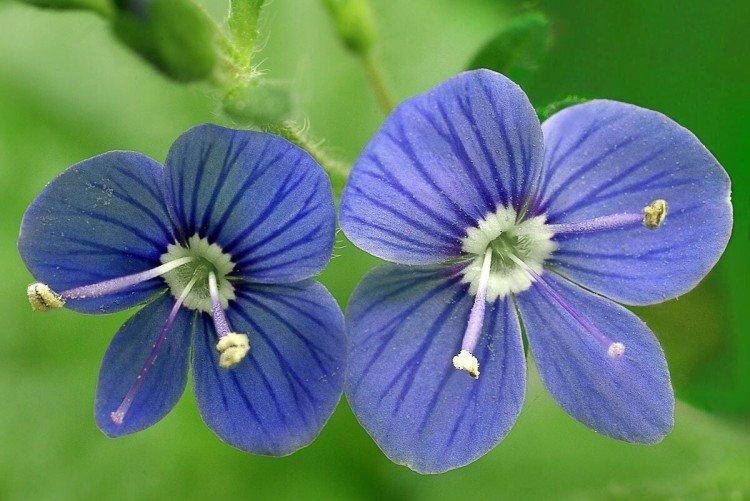
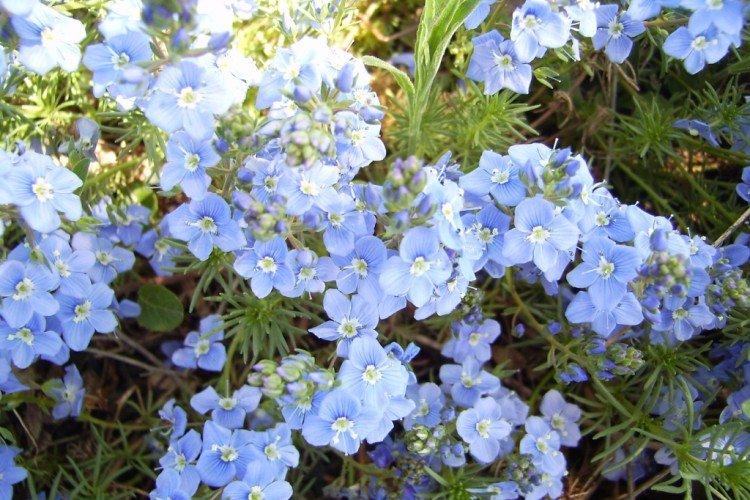
Such a simple, but such a cute flower Veronica simply does not leave anyone indifferent. In addition, its miraculous medicinal properties and a wide variety of species are appreciated. Let's tell you more about them!
general information
Previously, Veronica was separated into a separate family, but now it has been proven that she belongs to the plantains. Moreover, this is the most numerous and varied representative of them. In the garden, Veronica is good in monoplants and together with other bright flowers.
It is simply impossible to collect a single general description of this kind. There are small herbaceous annuals, and there are tall shrubs with lignified shoots. Leaves and shoots are most often narrow and pubescent, with a grayish tint.
Small delicate buds are collected in long spikelets, and less often in panicles and umbrellas. Graceful pointed petals look very nice and neat. The structure of the rhizome depends entirely on the growing conditions - on fertile soils, near water or in rocky terrain.
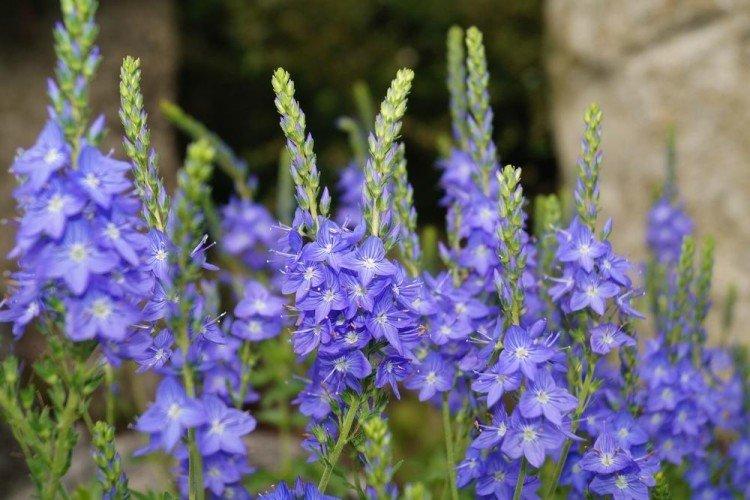

Types of Veronica
The Veronica genus is truly huge: more than 300 species of this plant. They are common all over the world, and almost half of them are found in Russia. Let's consider the most popular!
Dubravnaya veronica
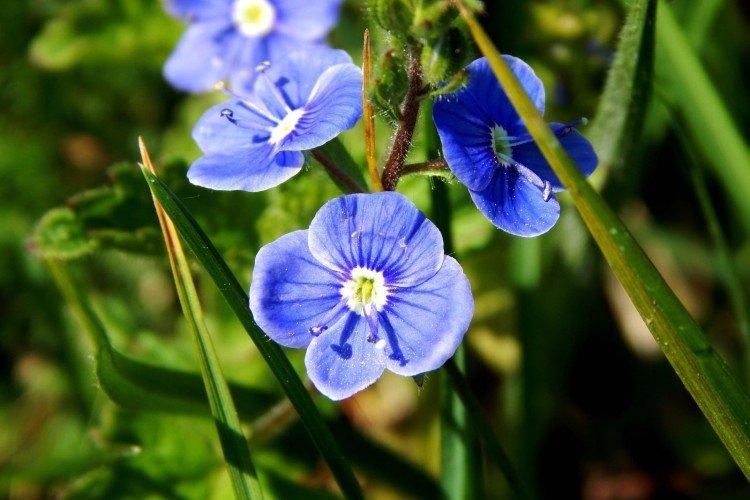
Found in forests and fields. Bushes up to 40 cm tall are covered with loose inflorescences with rather large blue buds - up to 1 cm each.
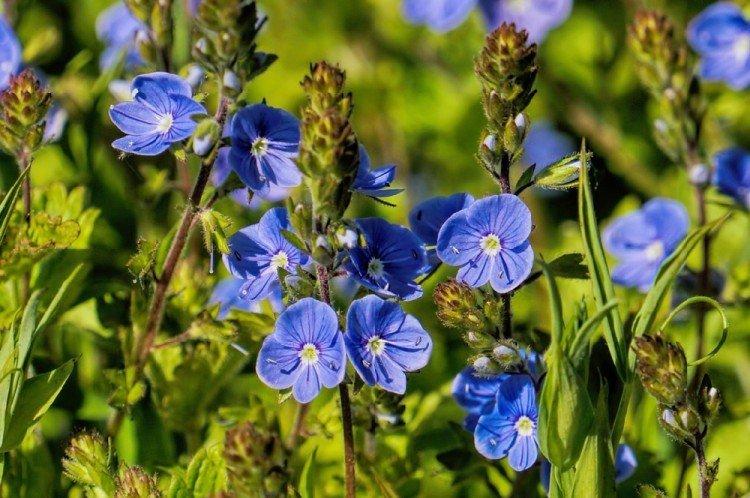

Medicinal veronica
It is it that is traditionally used in folk medicine, and also spectacular ground cover rugs are obtained from it. Medicinal Veronica grows on the most sparse sandy soils.
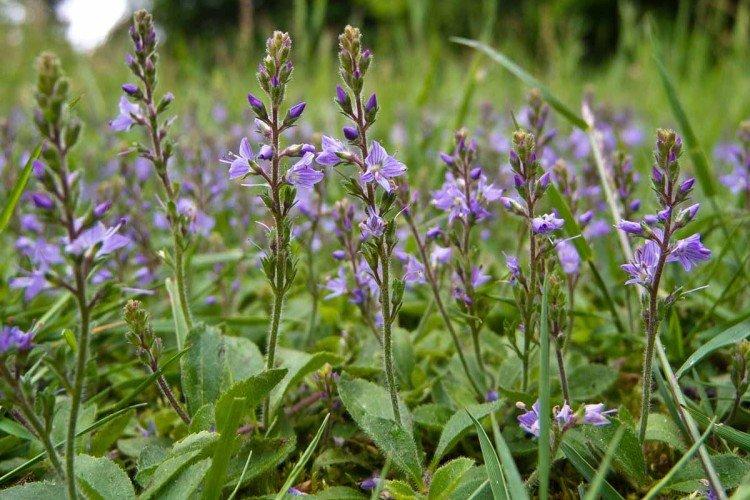

Armenian veronica
A dense but compact perennial with numerous recumbent shoots up to 10 cm in length. It has feathery, dissected leaves and purple or blue buds.
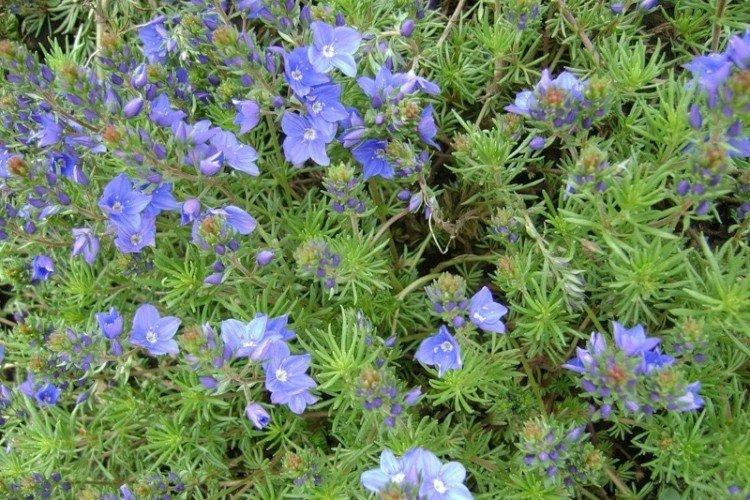

Gentian veronica
Medium-sized variety up to 45 cm with beautiful leafy rosettes. The peduncles themselves are almost twice as high, with multi-flowered spike-shaped inflorescences of white color.
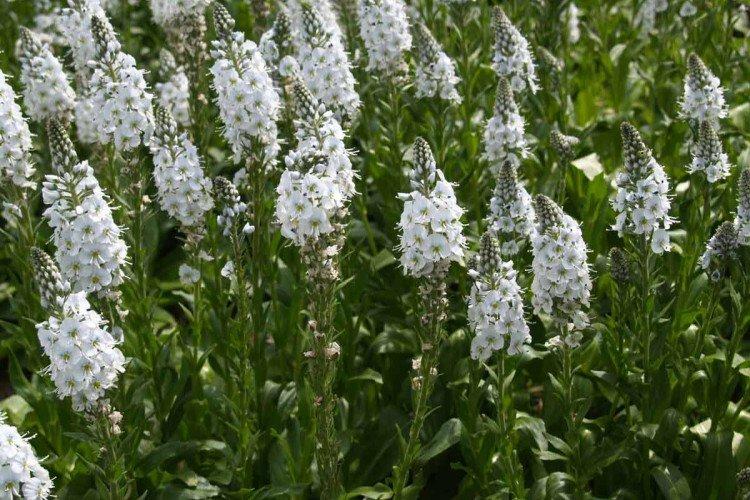

Filamentous veronica
One of the most aggressive species that can easily grow throughout the garden. It takes root with all of its parts simply by touching the ground.
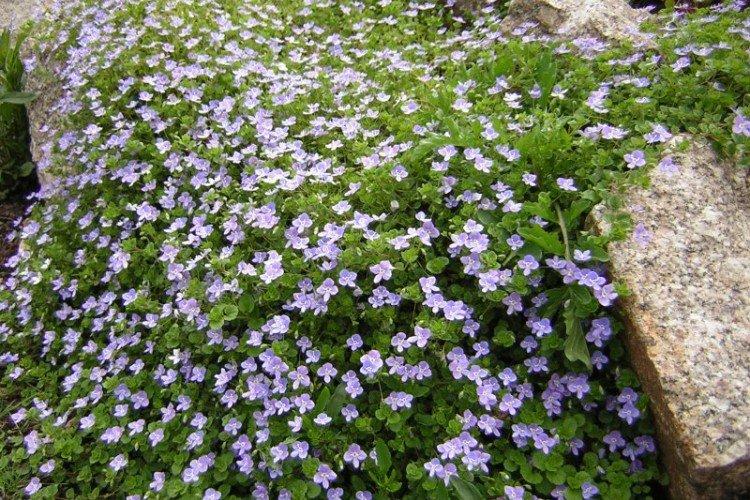

Big veronica
A tall variety up to 70 cm high with fleecy single shoots and a powerful rhizome. Great Veronica has spectacular spikelet inflorescences, and it also winters beautifully even in Siberia.
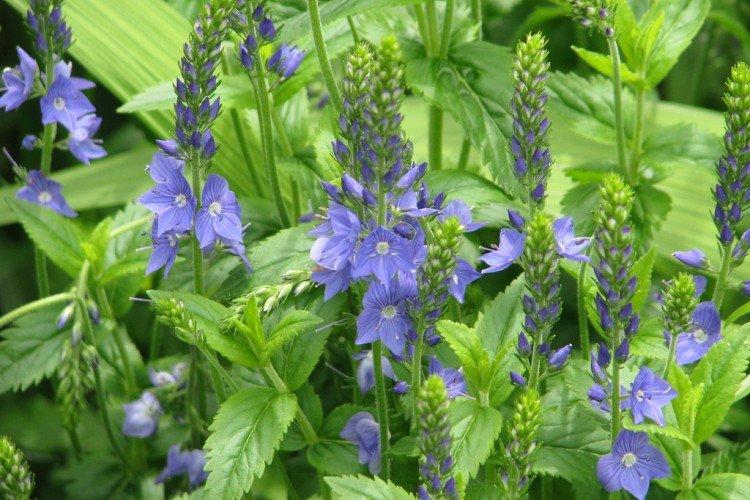

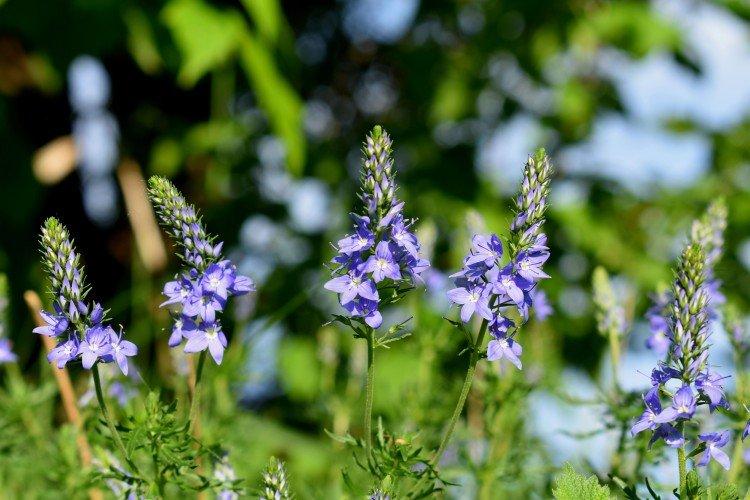
Spikelet veronica
This species has an amazing variety of colors. In addition to blue and blue varieties, white, pink and purple are very common. The spikelet height is up to 40 cm.
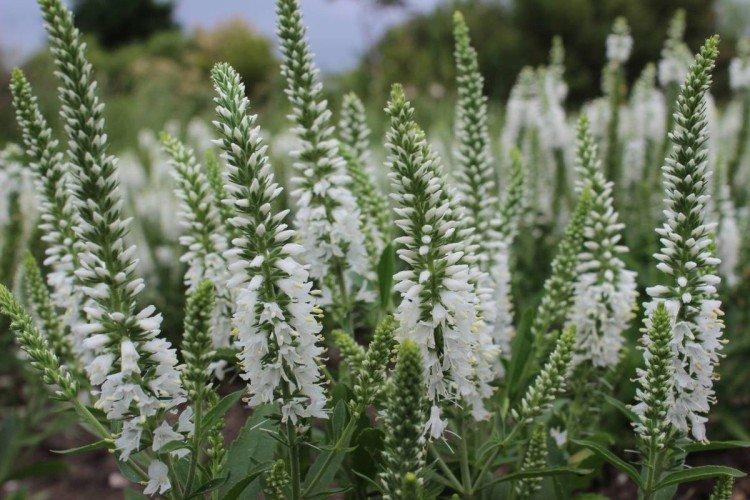

Caring for Veronica
The specificity of caring for Veronica completely depends on the specific species, or rather, on the conditions of its growth in nature. But we tried to systematize the information and bring out general recommendations!
Temperature and lighting
Spikelet and great Veronica prefer the sun, and forest and oak forest species grow better in partial shade. Almost all of them are equally resistant to heat and frost. In nature, Veronica prefers a temperate or cool climate.
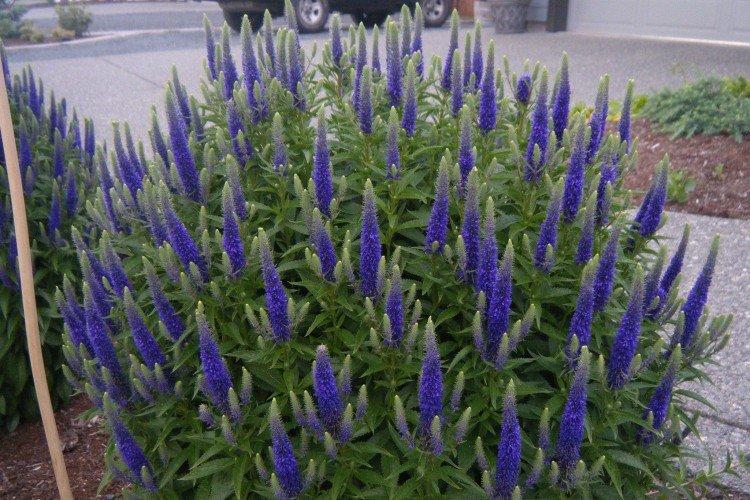

Watering
Veronica does not need additional watering and easily tolerates drought. Only if the dry season is too long can you water the planting a little several times. The water-loving species include species that live in water, as well as spikelet and gentian Veronica.
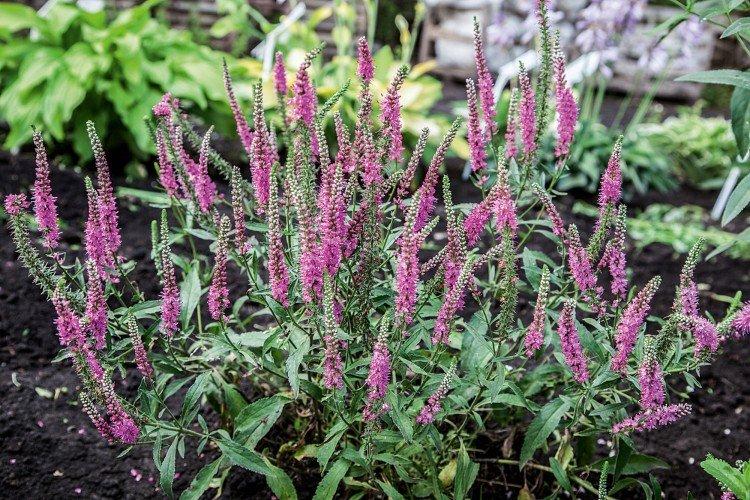

The soil
Mountain and rocky species grow best on rocky ground. Medicinal and long-leaved plants prefer fertile soil. Oak and forest ones need good drainage and low acidity. Sandy sands and loams are also fine.
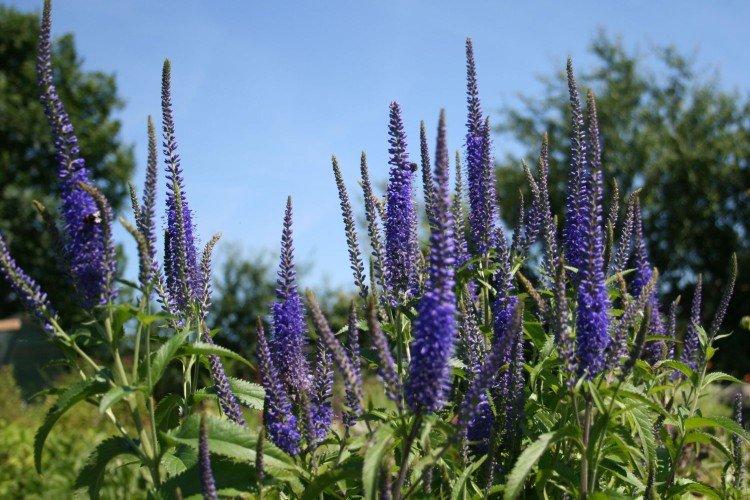

Fertilizers and feeding
Top dressing for Veronica, with the right choice of the site, is not needed at all. If the soil is too poor and scarce, you can apply fertilizer literally once a season.
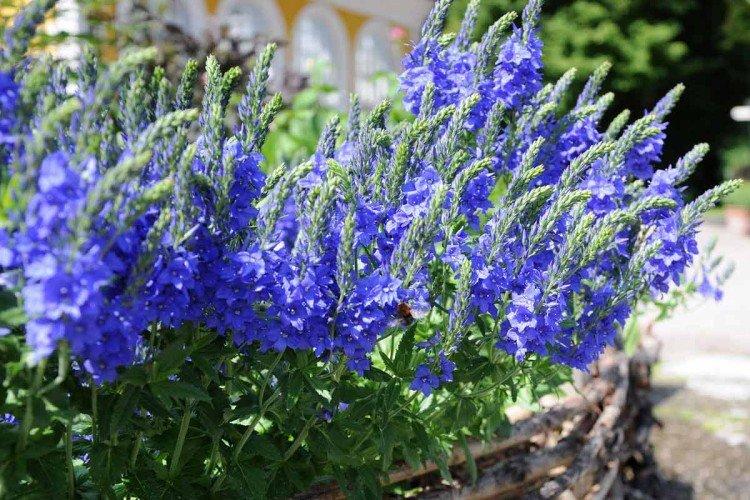

Wintering
Perennial Veronica does not need shelter for the winter, even in our latitudes. She easily tolerates frosts down to -30 degrees, and generally feels great in the northern hemisphere.
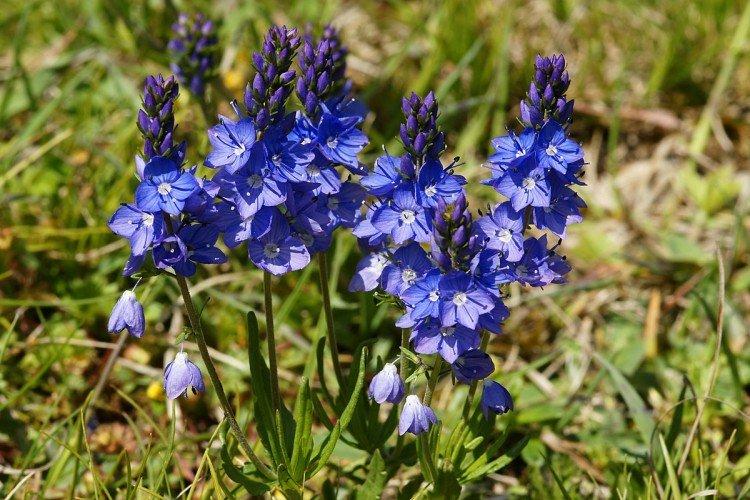

Planting and breeding veronica
The easiest way to propagate an adult healthy shrub is by dividing in early spring. Young delenki are rooted in sand or peat under a jar, and then transplanted into the garden at a distance of 30-50 cm.
Young tops take root in moist soil in partial shade. This is done in the summer, and the length of the cuttings is 10 cm. The seeds are sown in open soil in late autumn, but such bushes will bloom in a year. Otherwise, there are no more tricks and secrets at all.
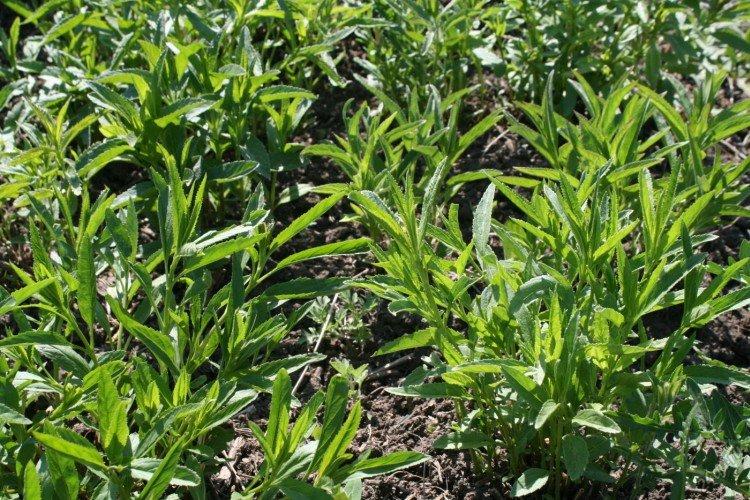

Pest and disease control
Sometimes Veronica suffers from powdery mildew, but here fungicides cope. It is more difficult with ring spot, which is transmitted to certain species from raspberries. This is a virus and the affected plant must be removed as soon as possible.
Veronica leaves are eaten by different types of caterpillars - scoops, moths, garden moths. But more dangerous enemies are aphids and nematodes, which multiply rapidly. For nematodes, special nematicides are used, and complex insecticides help against all other pests.
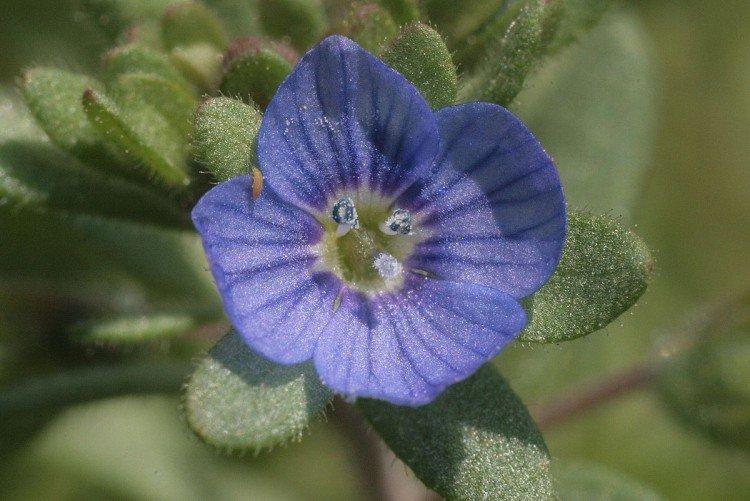

Veronica flower - photo
We advise you to first decide what you need flowers for, and then choose the appropriate type of Veronica. Different varieties are good for rock gardens, rockeries, flowering carpets, ponds, and even tall vertical accents.