The garden rose is prized for its excellent decorative qualities. And that is why it is so unfortunate when she is suffering from diseases, fungi or viruses. In order to detect and fix the problem in time, regularly examine the leaves of the rose garden. And we will tell you what to look for!
Bumps and bumps on the leaves
Irregularities on the leaves of the rose remain due to insects, which equip their masonry from the back side. Sometimes the fungus leads to swelling of individual spots and areas.
- Small aphids leave pimples and tubercles on the surface of the leaves. She lays eggs on the back side, and in these places the plates swell;
- Thrips in the process of life can also damage the leaf plates, but they are much less likely to settle on roses.
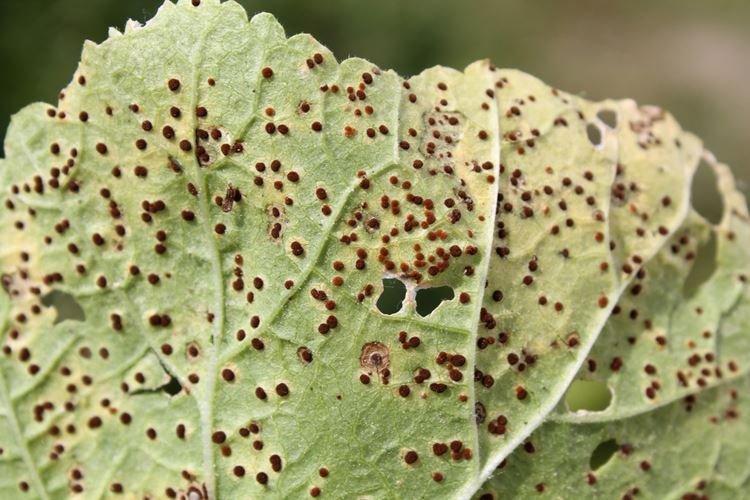

Leaves turn yellow and dry
This is the most common problem and can be literally anything from a heat wave to an incurable virus. In this case, we recommend observing the rose for several days in order to track changes in dynamics.
- If the rose is too dry and hot, it is the leaves that will react first, because the shrub is trying to preserve a valuable resource. Monitor the temperature and vary the irrigation regime according to the weather and season;
- Yellow and dry burns on the leaves remain if you water or wash the rose in the midst of a sunny day;
- Chaotic yellow patterns are a classic symptom of a viral mosaic. She does not heal and even seems pretty, but in the future she will destroy the bush;
- Deficiency of iron or potassium causes the leaves to turn bright yellow, but with green or purple streaks.
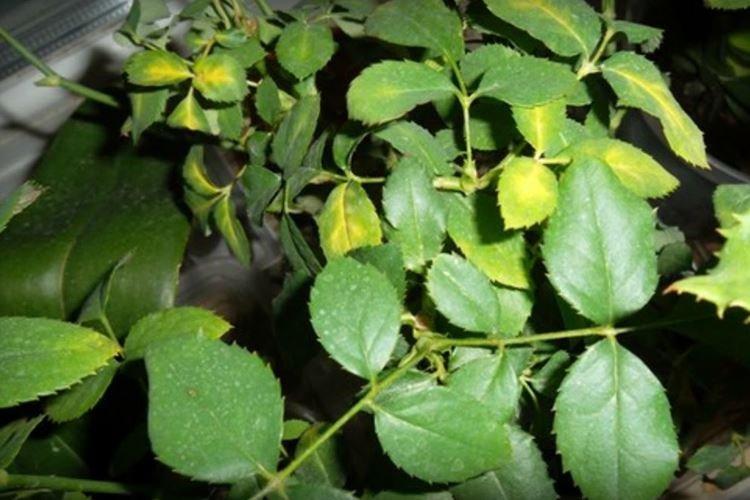

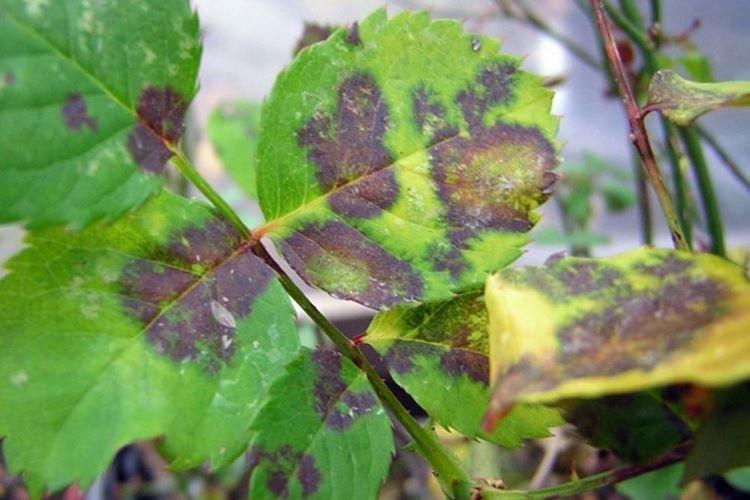
Brown spots on the leaves of a rose
Unlike yellow spots, brown spots are more likely to indicate serious fungal or bacterial diseases. Here it is important to take action as soon as possible before the infection has covered the entire rose garden.
- If the rose is constantly poured, the leaves will gradually darken and rot. Therefore, it is important to control soil moisture;
- Bright red spots are a characteristic symptom of fungal rust. But it only looks frightening, but in fact, a common disease is perfectly treated with fungicides;
- Dark spots spread over leaves and shoots from top to bottom when affected by gray mold. A fluffy grayish bloom from spores gradually appears;
- Chaotic red-violet spots - an indicator of peronosporosis. Later, it leads to cracking and death of the buds, so that the rose may not bloom;
- Brown spots are left behind by cercospora, because this is literally the brown spot of a rose. The fungus loves heat and high humidity;
- Brown spots with a white center - a symptom of septoria. Phyllostictosis and pestalotia are manifested in approximately the same way, but the same fungicides help from them.

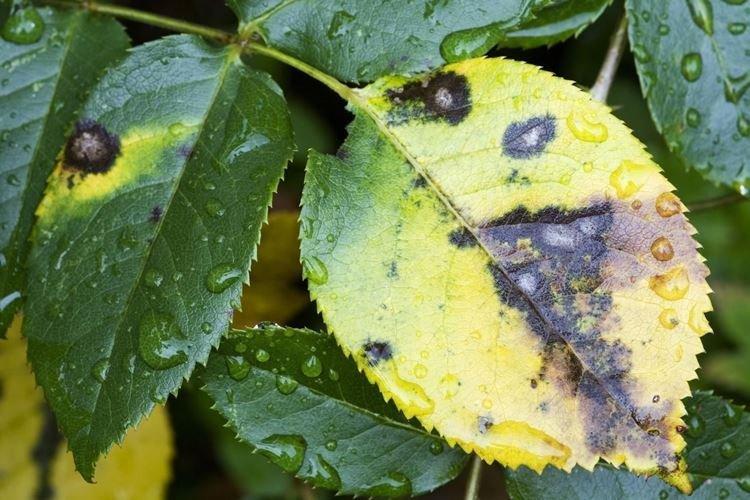
The leaves of the rose turn black
Leaves begin to rapidly turn black due to irreversible damage or dangerous diseases. Sometimes the problem is with improper care, but this is more common in sensitive young seedlings.
- Black spots on leaves and shoots are formed due to bacterial burns;
- Stem cancer also leaves tumors with ulcers, and in the future it can destroy the rose completely. Most often, it penetrates into open wounds, so all sections and injuries must always be processed;
- Due to the black spot, the rose becomes covered with rapidly spreading dark spots. Leaves fly from top to bottom;
- Downy mildew, in terms of symptoms on roses, is more reminiscent of black spot than white fungus. Although sometimes the spots can be reddish or purple.

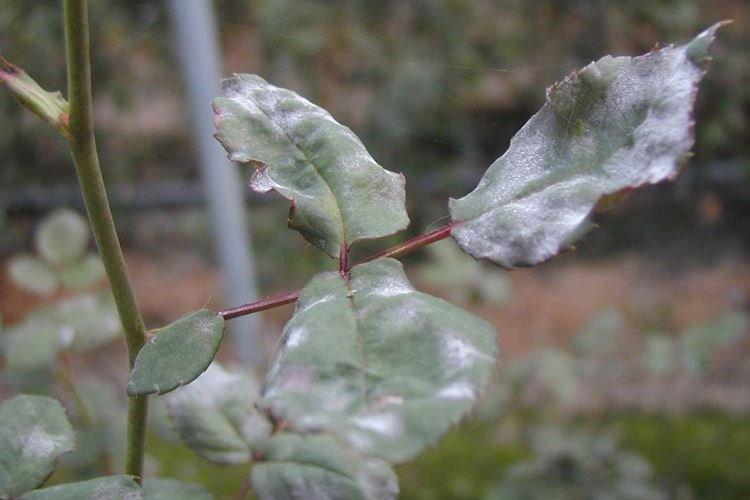
White bloom on rose leaves
A velvety white bloom at first glance may even seem beautiful until you know that these are fungal spores. Although sometimes you can confuse with them the weightless cobweb that some insects leave.
- Powdery mildew leaves that very white velvety bloom after prolonged rains;
- Among the branches and leaves, spider mites are hiding, which braid the rose with whitish cobwebs;
- Small white spots remain when the leaves are attacked by the rose leafhopper. It is easy to notice visually from the reverse side along the veins.

Pale and light leaves
Healthy and young leaves should not fade for no reason. This means that there is a violation in agricultural technology or the rose has already begun to develop a disease.
- If the roses lack nutrition, the leaves will turn pale and wither. Do not forget nitrogen in early spring and complex feeding during the season;
- Young shoots grow painful if the bushes are planted too close to each other. They are cramped, and they absorb all the elements from the soil;
- A rose will always be light and pale if it constantly lacks the sun. This disrupts the process of photosynthesis, therefore, varieties adapted to such conditions are needed for planting in the shade.

The leaves of the rose are curled
Leaves curl into boats, tubules and other strange shapes due to severe viral lesions. Although sometimes the problem is not so radical, and it is enough to get rid of pests and fungi.
- Leaves can deform because they lack light and air. Therefore, roses need regular sanitary pruning and thinning;
- Deficiency of individual trace elements also leads to deformation, because roses need a lot of nutrition for abundant flowering;
- The curl virus is little studied and incurable, but it rarely infects roses. Although it is also worth keeping in mind in order to preserve the healthy part of the rose garden.