Unfortunately, even round-the-clock and daily care is not able to completely save your favorite flowers from problems. That is why it is better to know in advance what you may face and how to deal with it. So today we want to tell you more about diseases of indoor plants!
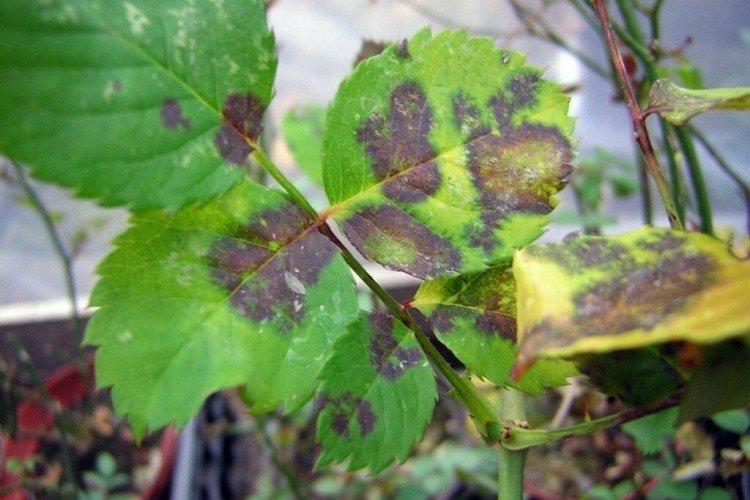
1. Wet rot
If unpleasant smelling and as if oily spots appear on the leaves or shoots, then this is it. Most often, plants with fleshy juicy leaves suffer from the disease. The main reasons are an excess of moisture or nitrogen. It is necessary to remove damaged fragments, dry the soil and use special preparations.
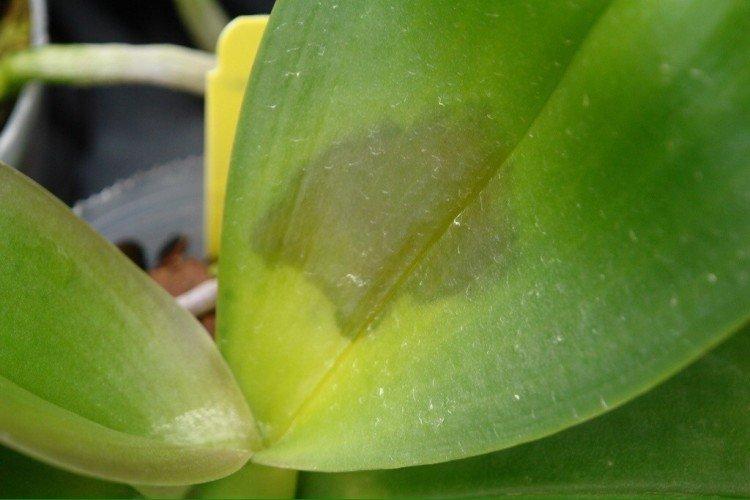

2. Mosaic
There are several varieties of the puzzle, but they all have one thing in common - this is a rapidly spreading virus that cannot be cured. First, the plant becomes covered with whitish or yellow chaotic spots, then development slows down, and it dies. The damaged flower must be isolated and destroyed as soon as possible.
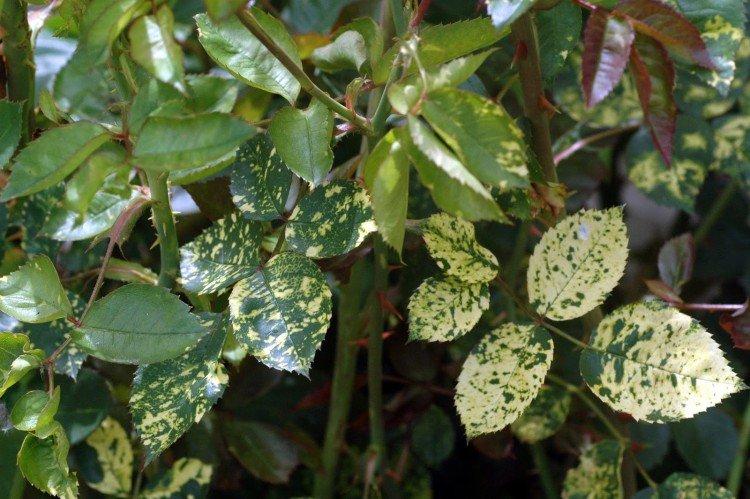

3. Powdery mildew
The leaves of plants are covered with whitish spots that resemble flour plaque. They gradually turn gray and change their structure. It is a bacterial disease that most often manifests itself in warmth and high humidity.
It is necessary to adjust the care, reduce the introduction of nitrogen, regularly ventilate and spray the plant with sulfur, special preparations or a solution of soda ash and copper sulfate according to the instructions.
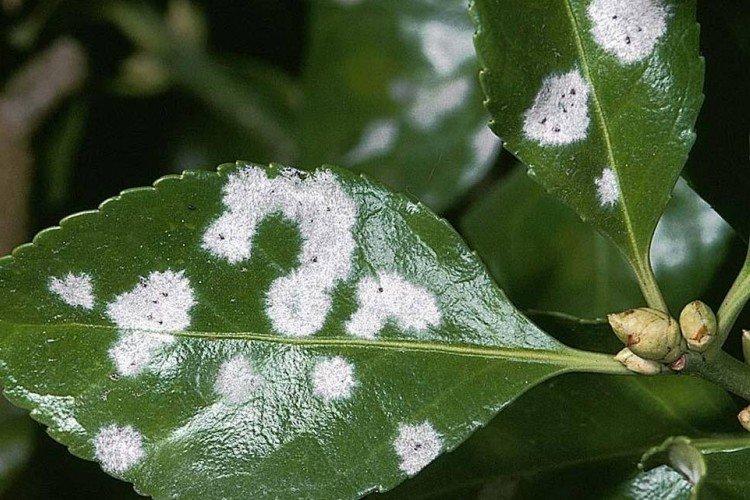

4. Late blight
The leaves of the plant change color and wither, new shoots do not grow, and over time, the root system begins to rot. In the early stages, you need to remove the plant from the flowerpot, rinse the root, remove rotting areas, soak the root system in a fungicide according to the instructions and transplant the plant into disinfected soil.
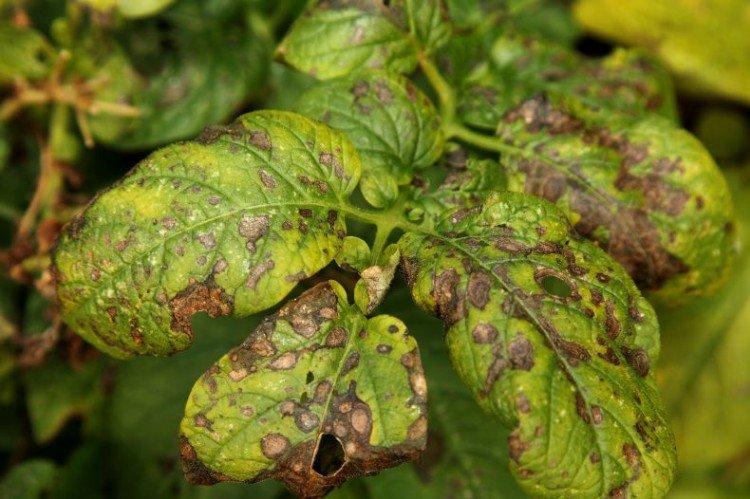

5. Rust
It is one of the most easily recognizable diseases, because the leaves are covered with characteristic rusty spots, and bumps appear on the back. You can try to remove the damaged areas and treat everything with fungicides, but more often than not, rust does not heal.
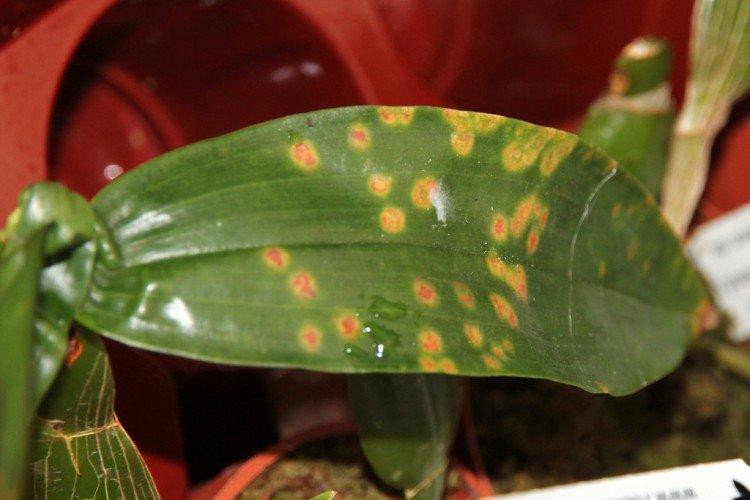

6. Black leg
When affected by this fungus, the base of the cutting turns black, and gradually the plant dies off. The main reason is too dense soil, so always use loose enough soil. The affected stalk must be removed immediately.
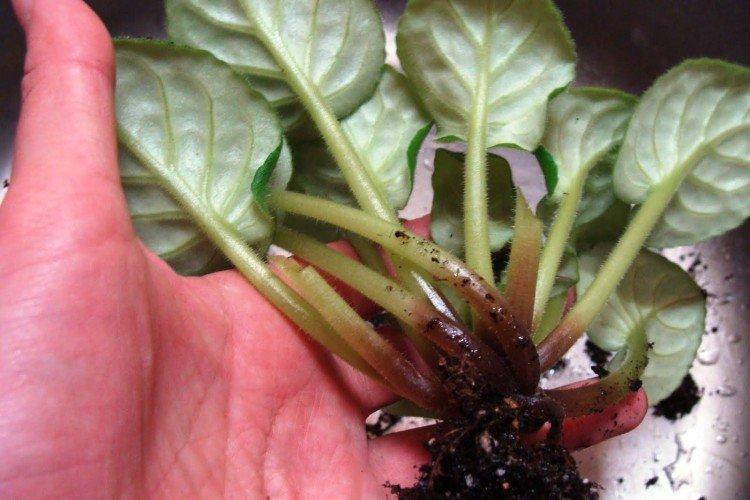

7. Gray rot
When affected by gray mold, the plant becomes covered with grayish mold, which gradually diverges in wide rings. If rot has already formed, you need to remove the damaged areas, treat the cut with charcoal or ash, dry the soil and adjust the care. For prophylaxis, it is necessary to observe the temperature, humidity and light conditions, remove the dying parts of the plant in time and disinfect the soil.
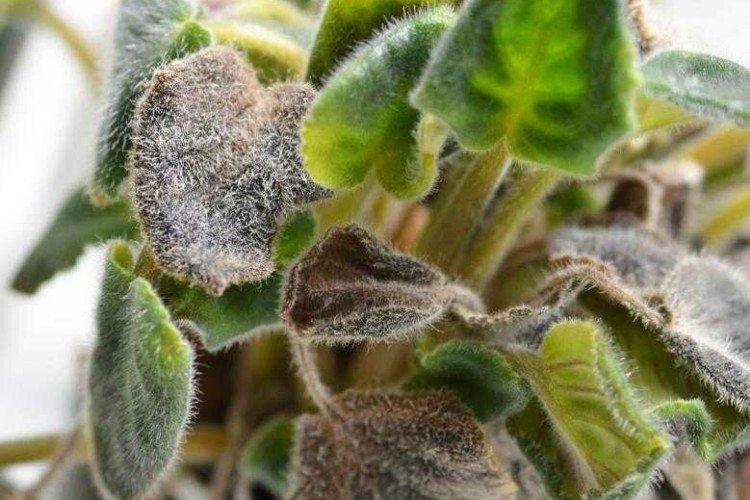

8. Leaf spot
It is rather not a specific disease, but a whole category of fungal and bacterial lesions. The spots may be brown, black, gray, white, or dry. In most cases, there is no particular need to determine which fungus has settled on the flower. It is important to remove the spoiled leaves as soon as possible, treat the flowerpot with a complex fungicide and stop spraying until the situation stabilizes.
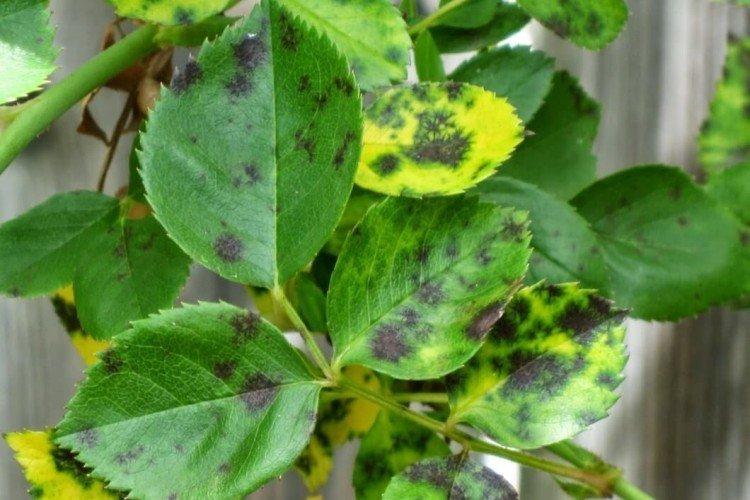

9. Dropsy
On the back of the leaves, dense growths appear, which gradually grow. This is most often associated with an excess of moisture with a lack of light. Remove affected leaf blades, reduce watering frequency, and move the plant to the sun.

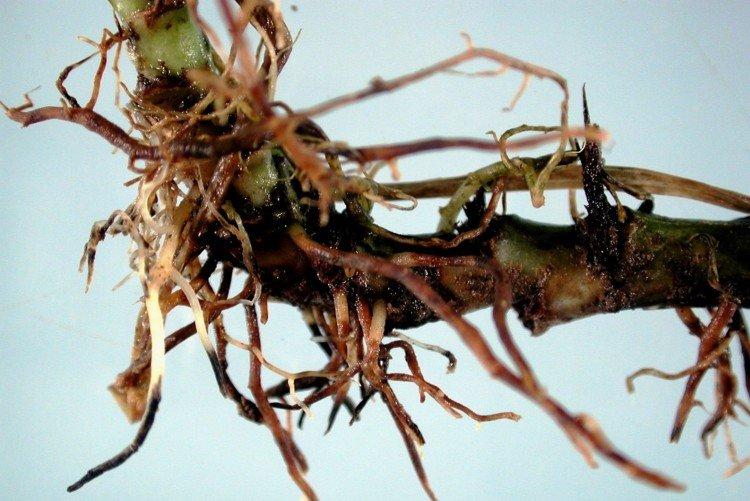
10. Root rot
The main cause of root rot is soil that is too wet, especially when combined with low temperatures. Most often, the disease becomes noticeable when the ground part of the plant deteriorates and withers.Sometimes an emergency transplant can help, but most of the plant dies.

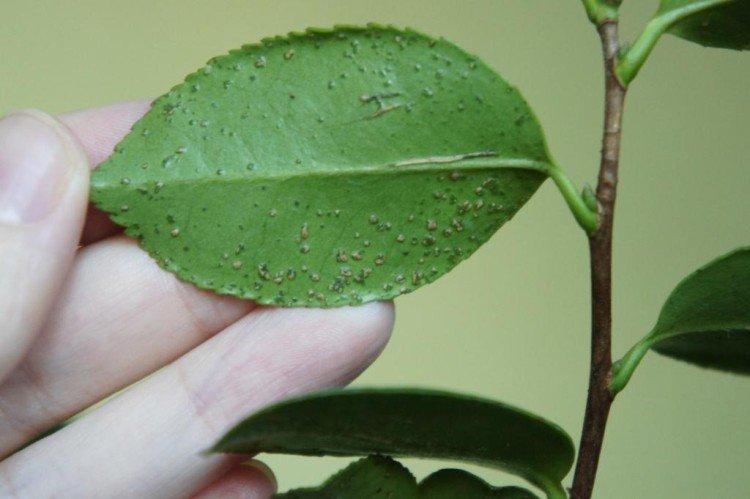
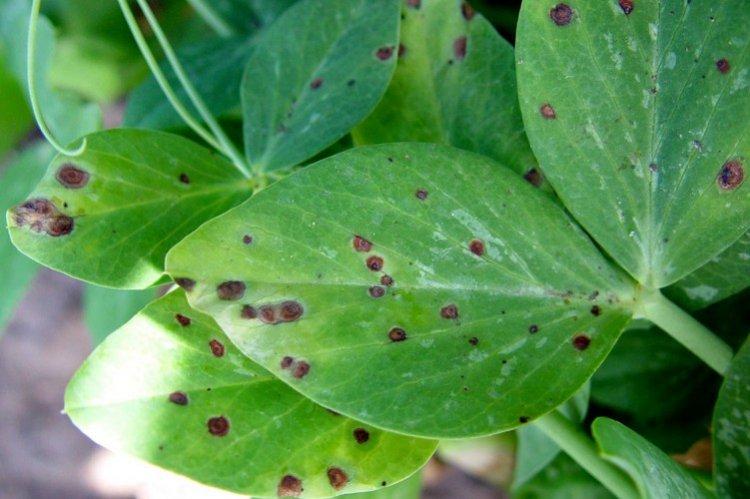
11. Ascochitis
Ascochitis is rare on indoor plants, but it is somewhat different from other fungal infections. Small brown spots on the leaves gradually grow, acquire a wide yellow border and crack. Sometimes the first signs can be confused with a lack of moisture, so it is important to control the situation. It is better to carry out preventive treatment with a complex fungicide.

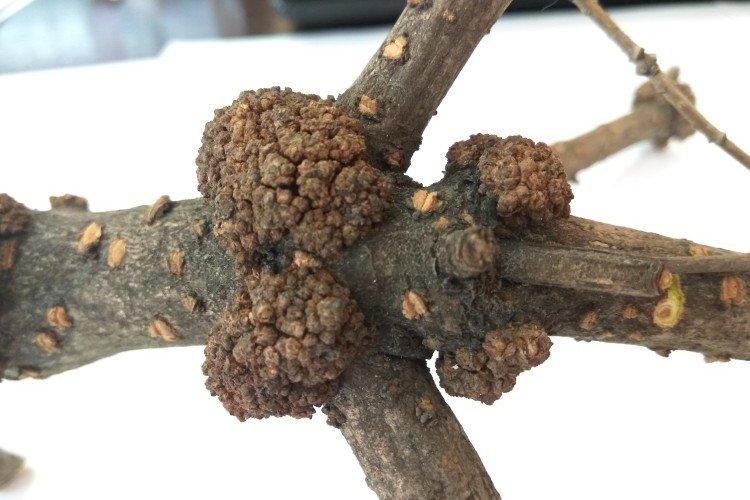
12. Bacterial cancer
Large bumpy growths appear on the root system, which become more and more. If it was possible to detect bacterial cancer at the very beginning, it is enough to remove the damaged areas, treat the plant with drugs and transplant. There is no treatment in the later stages.

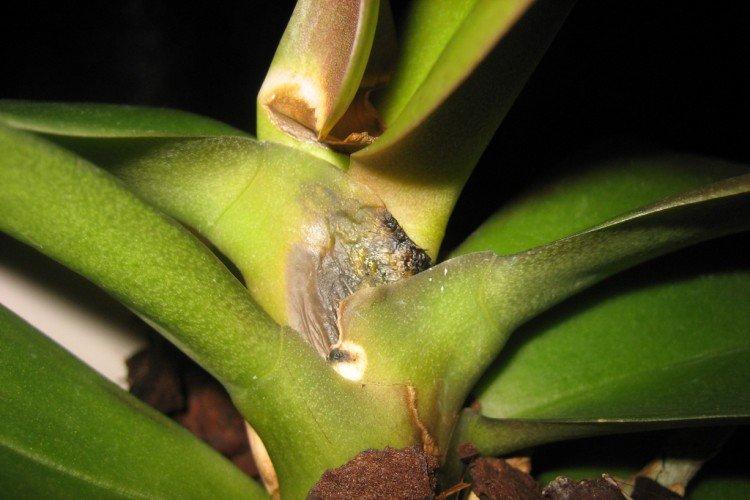
13. Fusarium
Plants wither, stems become thinner, and leaves turn brown. Weaker shoots are attacked first and the rate of attack increases with high humidity. At the beginning, the flower can be treated with fungicides, but if the process is already clearly active, it is better to destroy the plant along with the earthy clod, and be sure to disinfect the flowerpot.

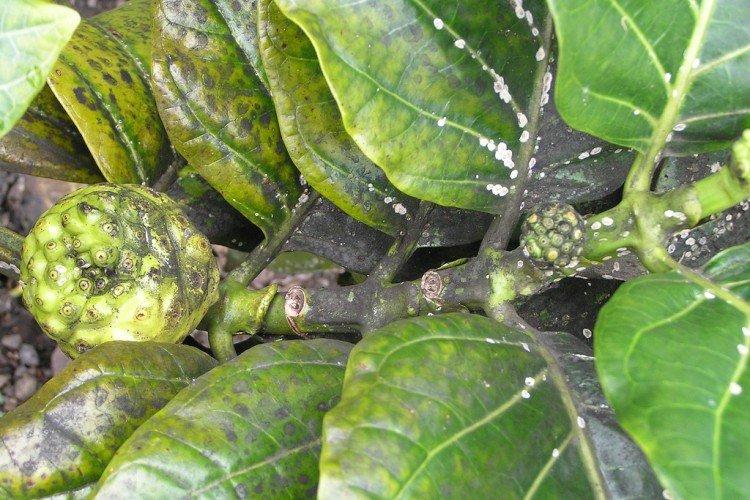
14. Verticillary wilting
With this type of wilting, the lower leaves first fade and turn gray. Old plates twist and dry, while new ones lag behind in growth and development. The main preventive method is disinfection of soil for indoor plants, especially if you are using garden soil. Fungicides only help in the early stages.

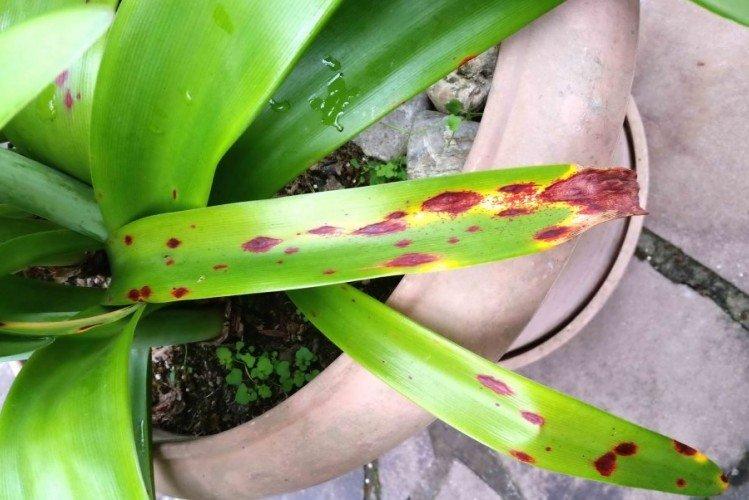
15. Red burn
On the peduncles and leaves of bulbous plants, red spots appear, which are gradually covered with a crust. The scales on the bulbs turn red, and the whole plant is deformed. Soaking in a fungicide helps, but keep in mind that aggressive drugs can injure nascent peduncles.