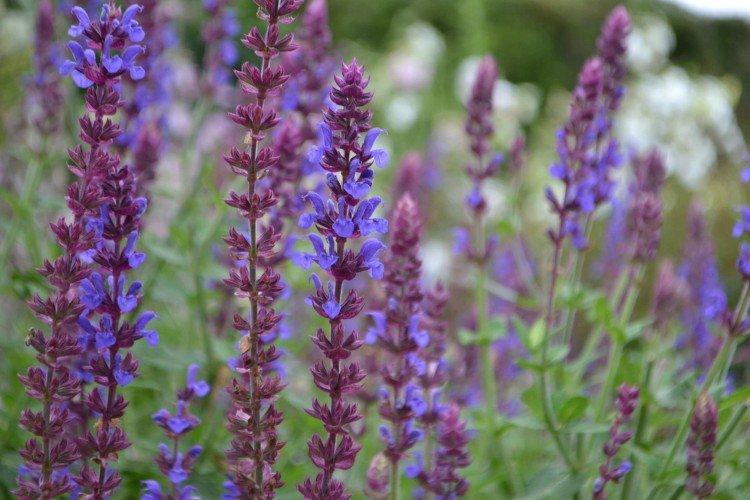
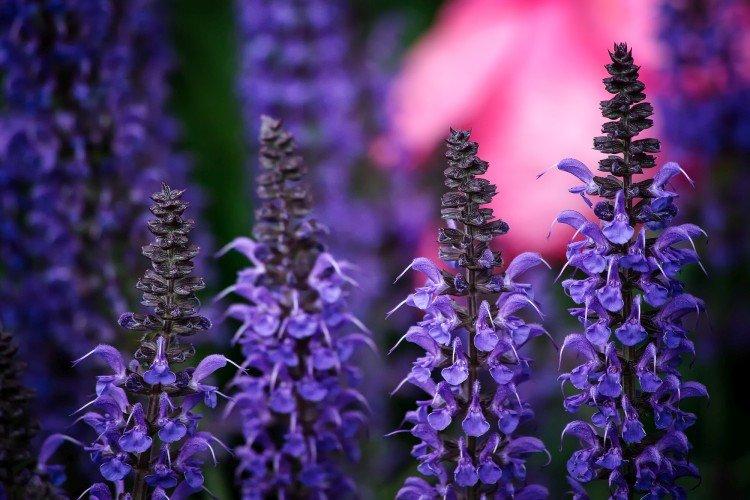
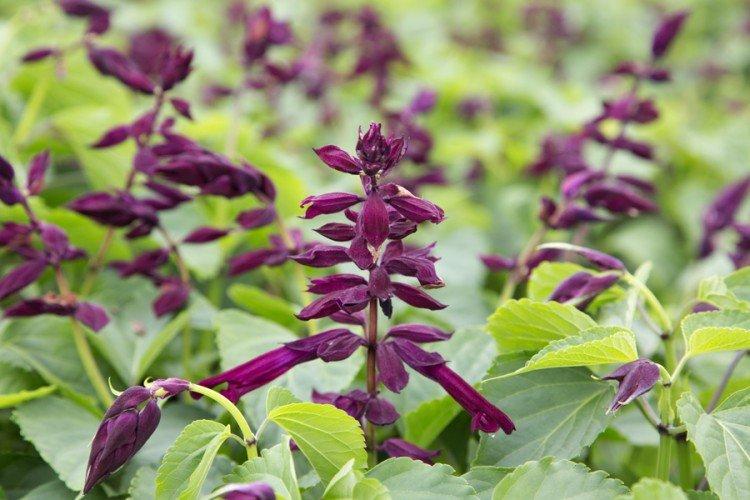
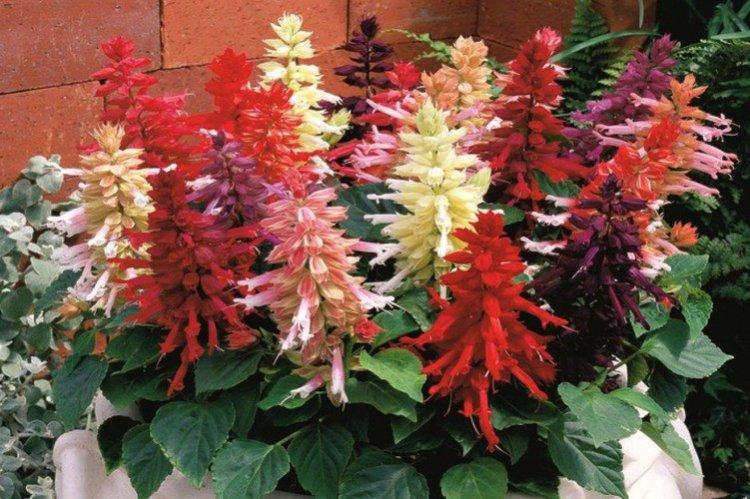
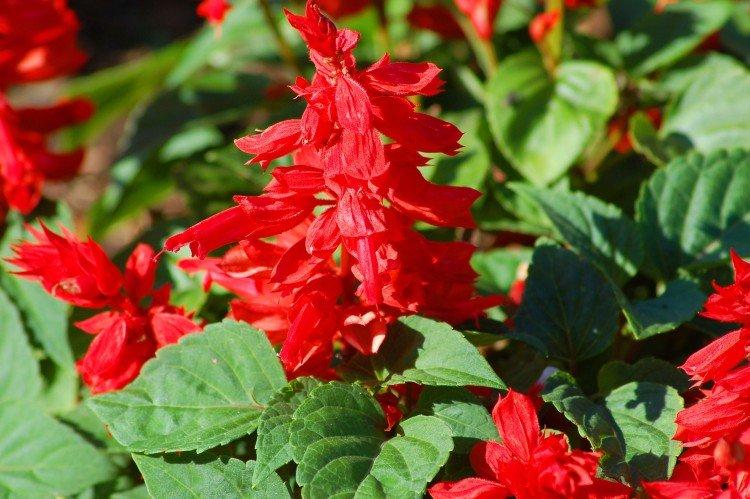
Sage, already well known to all of us, hides behind the outlandish name of salvia. This is not only a medicinal plant, but also a whole group of decorative species and varieties to decorate your garden. We will tell you more about them today!
general information
Salvia or sage is a perennial shrub or herb, depending on the species. In its natural environment, salvia lives in temperate and tropical climatic zones. The name from Latin is closely related to the concept of "health", and it is not surprising, because the healing properties of sage were known in ancient times.
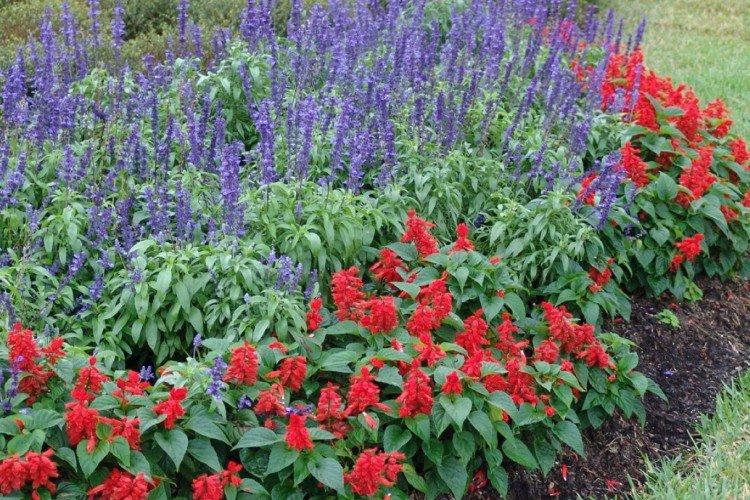
Basically, in everyday life, sage is called just medicinal varieties, and salvia - decorative. In horticulture, the spectacular plant began to be used about 300 years ago, and since then, breeders have greatly succeeded in their creative searches.
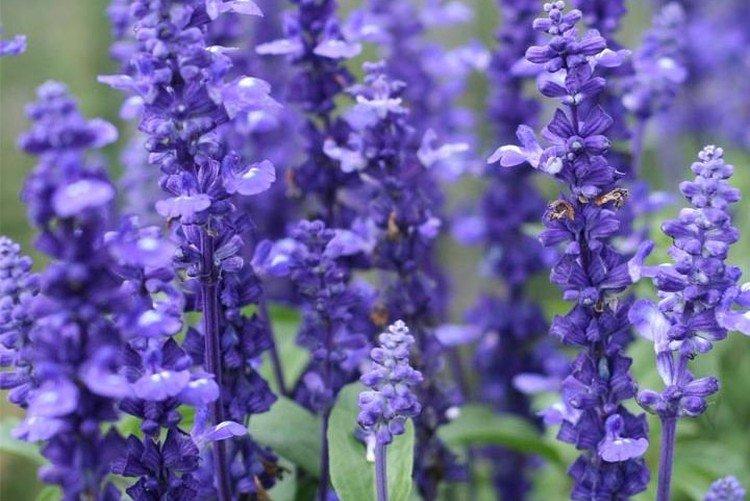
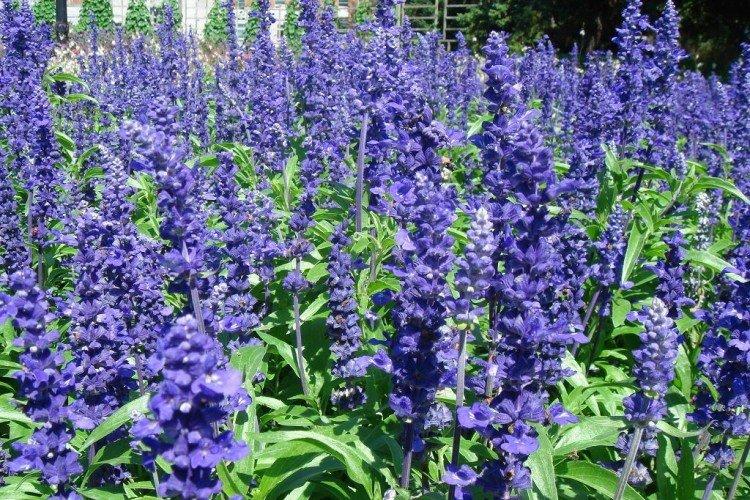
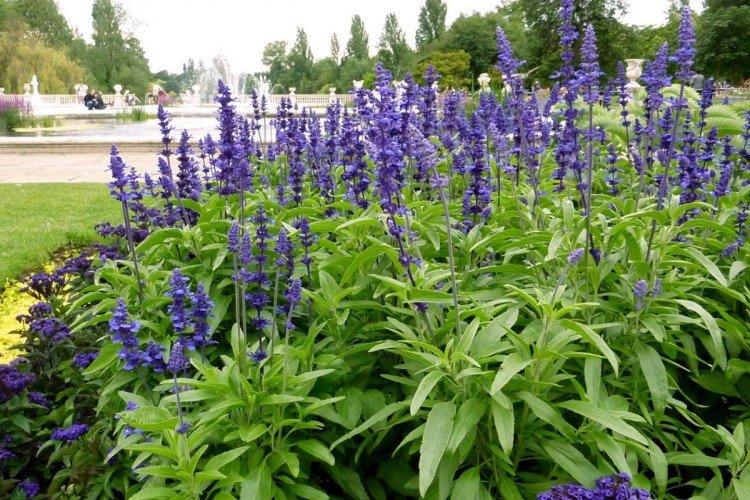
In mid-latitudes, salvia is most often grown as an annual, which makes it even less of a hassle. The plant has characteristic tetrahedral shoots up to 1.2 m tall with thin petioled leaves. Inflorescences are of a complex paniculate or spike-like shape, and their length reaches 20 cm. The flowers are small, all shades of white, pink and purple.
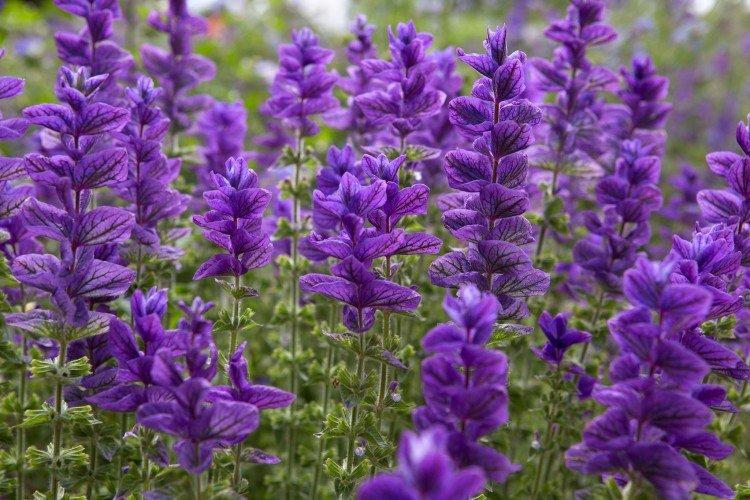

Salvia species
There are actually a huge variety of salvia species - almost a thousand. It is trite because it is very popular and widespread. Let's analyze the main ones!
Medicinal salvia
Even medicinal pharmaceutical varieties are actually very decorative. There are herbaceous and semi-shrub subspecies that grow up to 70 cm.
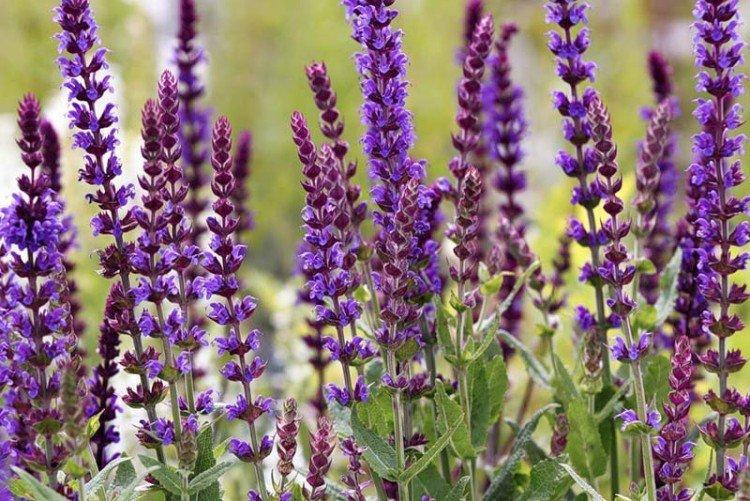

Meadow salvia
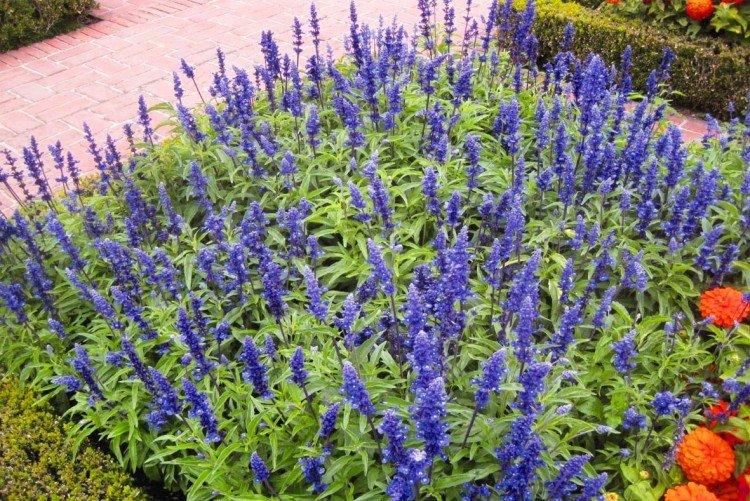
Meadow varieties are notable for very spectacular and beautiful flowering. The most common shades are white, blue and purple. The clusters of the inflorescences are very long, almost from the ground.
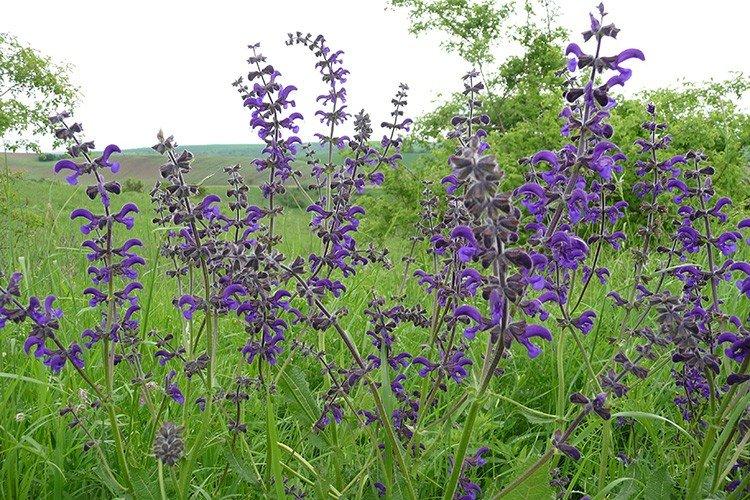

Forest salvia
Wild, but very decorative at the same time. Forest sage feels great in the middle lane, is not afraid of cold weather and blooms in early summer.
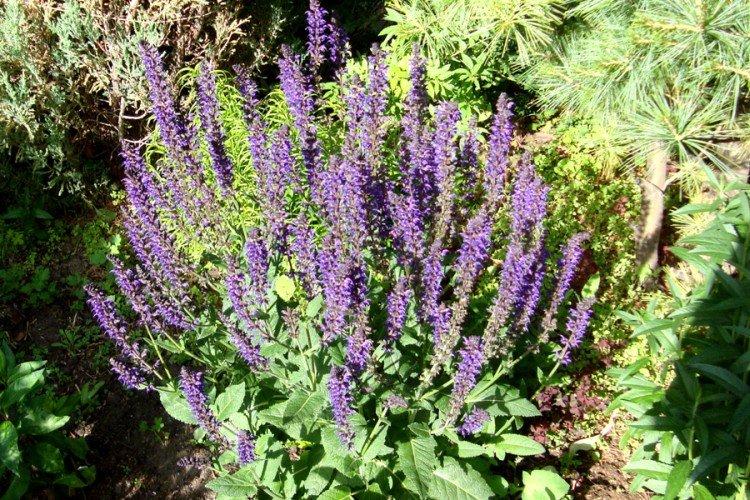

Marsh salvia
The South American guest prefers warmth and grows best in southern regions. But this is a real giant, because its shoots stretch out to an impressive 2 m.
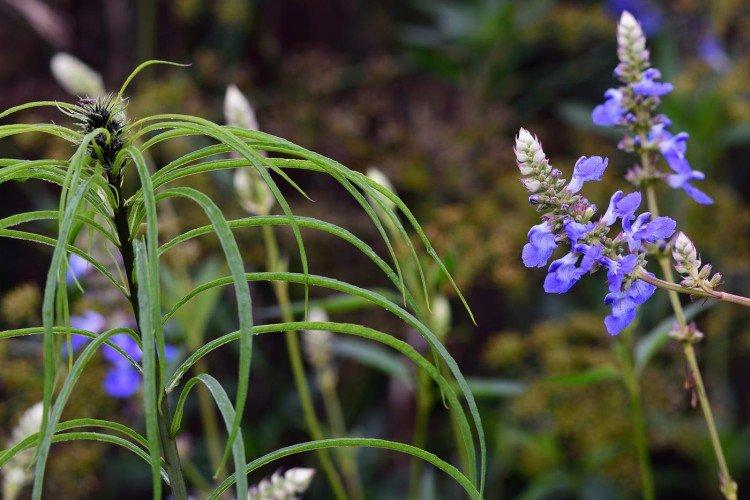

Whorled salvia
Possibly the most beautiful variety in the entire collection thanks to its lush bloom. In addition, the flowers are painted in a very bright and spectacular purple.
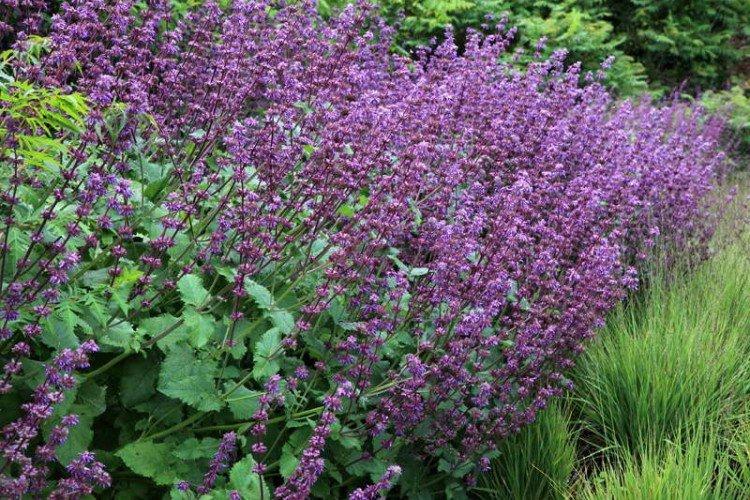

Oak salvia
This is one of the most frost-resistant and unpretentious species among all existing ones. Even complete beginners in gardening can cope with oak salvia.
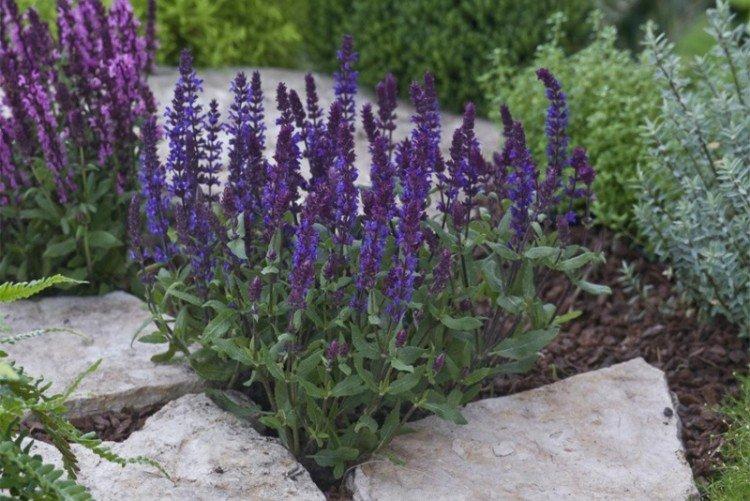

Sparkling salvia
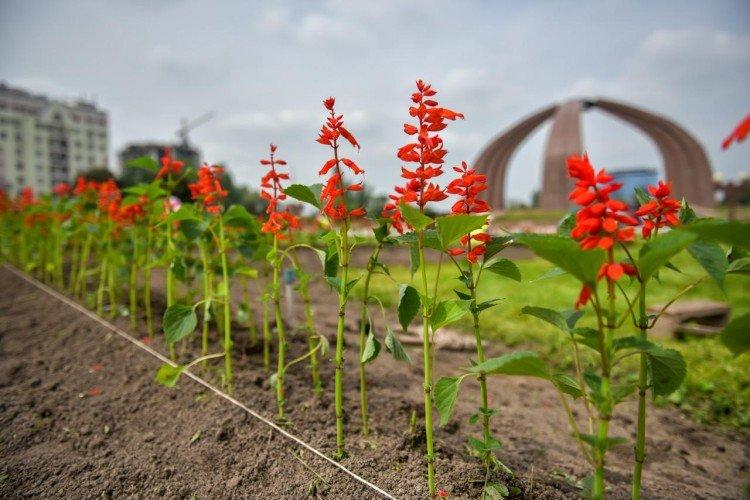
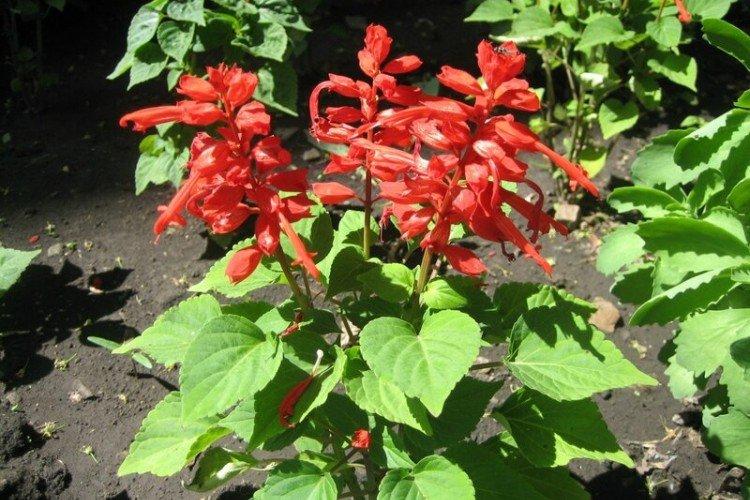
An insanely popular decorative perennial, which is especially loved by gardeners and breeders. She has very bright flowers of all shades from orange to burgundy and eggplant.
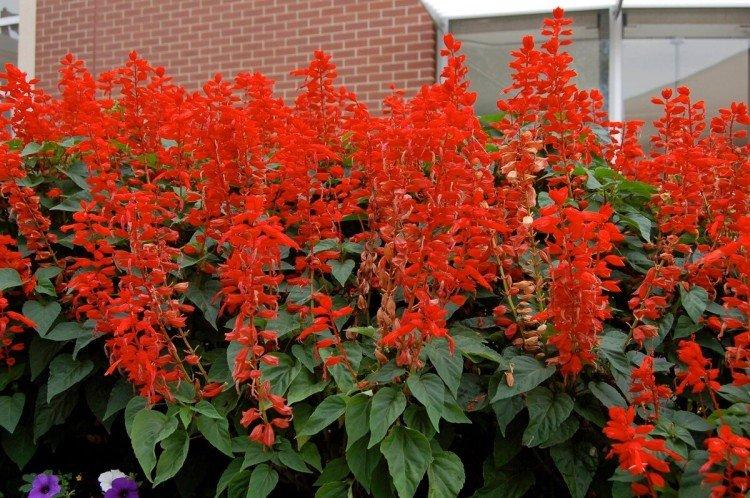

Transylvanian salvia
If you need a plant that is not afraid of frost and shady areas, choose this type. Even with a minimal amount of sun, the Transylvanian Salvia blooms all summer.
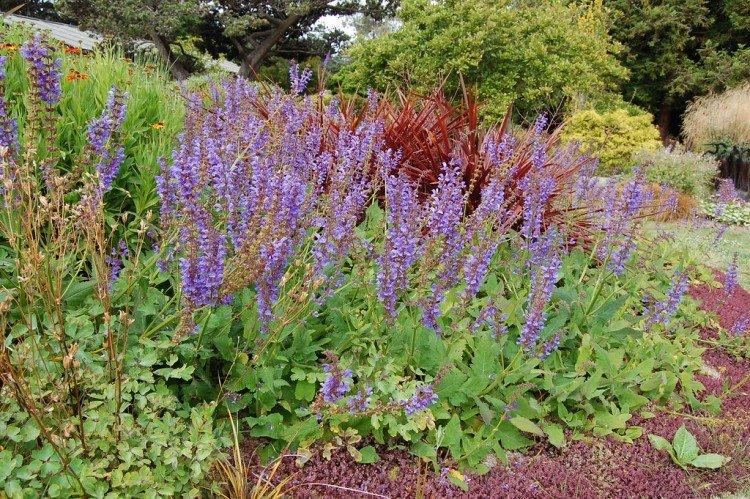

Salvia care
There is nothing specific about caring for salvia. Everything, as for other garden plants - a good choice of a site and watering with fertilizing according to the schedule.
Temperature and lighting
Salvia does not tolerate the cold, so you cannot plant it in the garden while the threat of night frosts remains. Most species prefer bright, bright areas, but, for example, the sticky salvia loves partial shade.
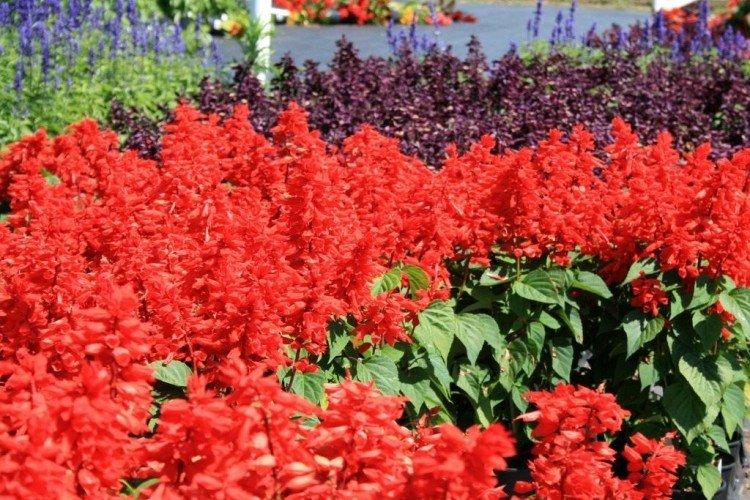

Watering
Salvia is watered only after the soil has dried and strictly in the evening. Do not pour too much water, as the plant's root system will rot easily. Be sure to loosen the topsoil and remove the weeds along the way.

The soil
Salvia needs light, sandy soil that allows air and water to pass through well. The reason is the same - the vulnerability of the root system to rot and fungus. Therefore, very good drainage is also needed.

Fertilizers and feeding
Salvia is fed with complex fertilizers in a minimum concentration, but at least twice a season. The first portion is added under the seedlings indoors, and the next one - at the beginning of budding.

Pruning
Pruning is relevant only for perennial varieties in warm regions, but we still could not ignore this point. Perennial salvia needs formative pruning to stimulate branching. The second time it is cut before wintering, leaving small areas of old lignified shoots with a pair of buds.

Wintering
Salvia does not hibernate in the open field in the middle lane, because it will simply die over the winter. Some varieties are able to overwinter under cover in warmer regions, but if frosts do hit, the flower will freeze. Therefore, it is easier to immediately grow it as an annual.

Planting and breeding
Annual salvia is grown directly from seed, but perennials can be propagated by cuttings or by dividing the rhizome. Sowing in open ground is carried out in early spring or by winter under cover.
Many ornamental salvia varieties can only be grown normally through seedlings. By the end of February, seeds are sown in containers in moist, loose soil. From it you need to lightly sprinkle on top and remove to a warm place with minimal watering by spraying or through a pallet.
After 2-4 weeks, the first shoots will appear, which can be dived after 2-3 adult leaves. Salvia also needs a second pick after about 20 days, already in separate pots about 10 cm in diameter. This is necessary so that she grows a strong rhizome.
After 4 leaves, it is recommended to pinch the salvia for bushiness. In April, gradually begin to harden the seedlings, keeping the temperature around 10 degrees at night. When the frosts have passed, the seedlings with an earthen clod pass into the holes in the garden at a distance of 30 cm from each other.

Pest and disease control
Salvia leaves are very fond of slugs and snails, and they will have to be collected mechanically. Often aphids and small thrips settle on plants, and in this case, insecticide treatment will already help.
Salvia is sensitive to root rot and blackleg. Therefore, you cannot fill the plant and it is important to periodically inspect the root part. These diseases progress very quickly, so it is better to simply remove the affected bushes.

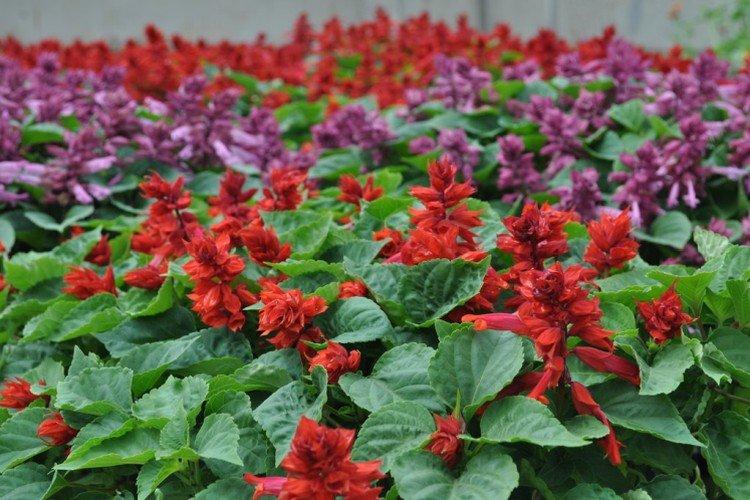
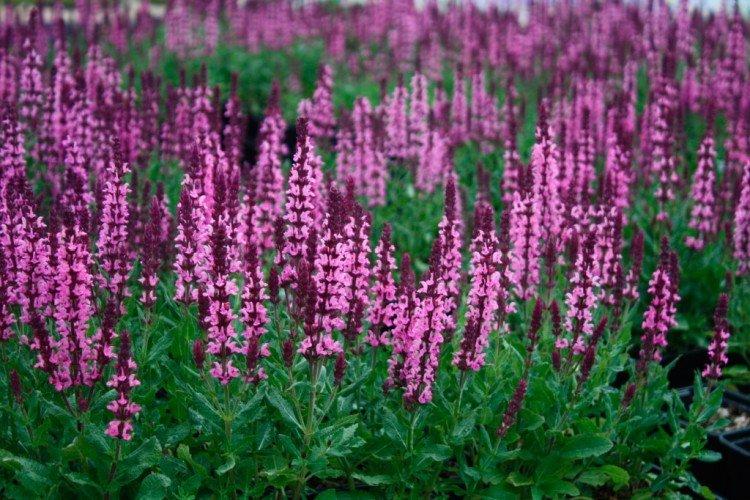
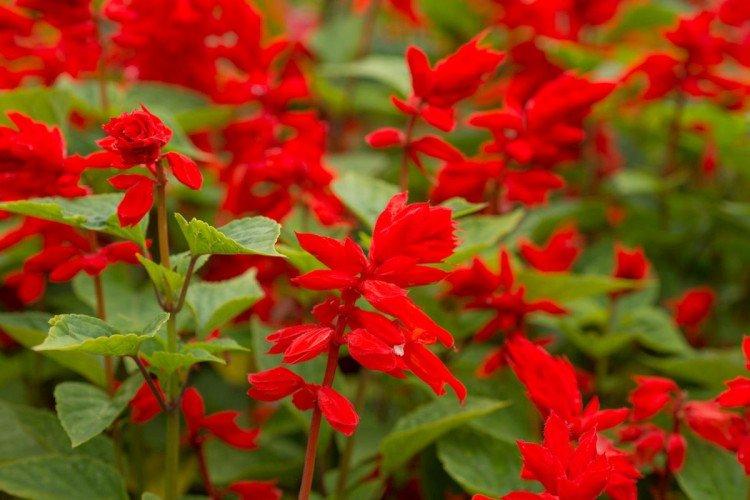
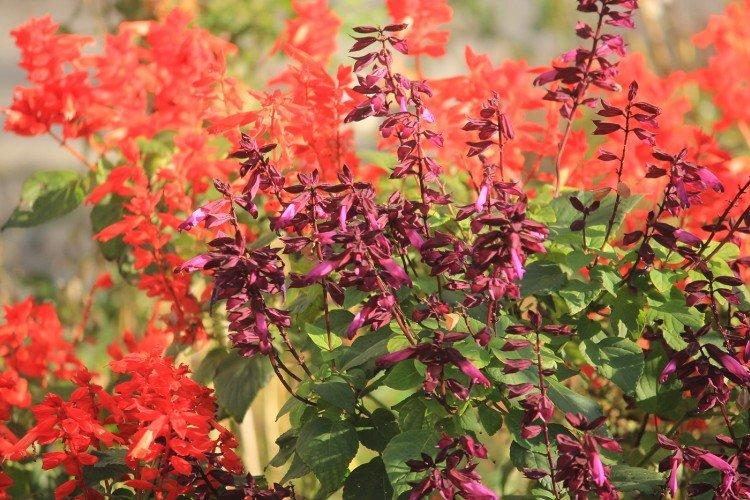
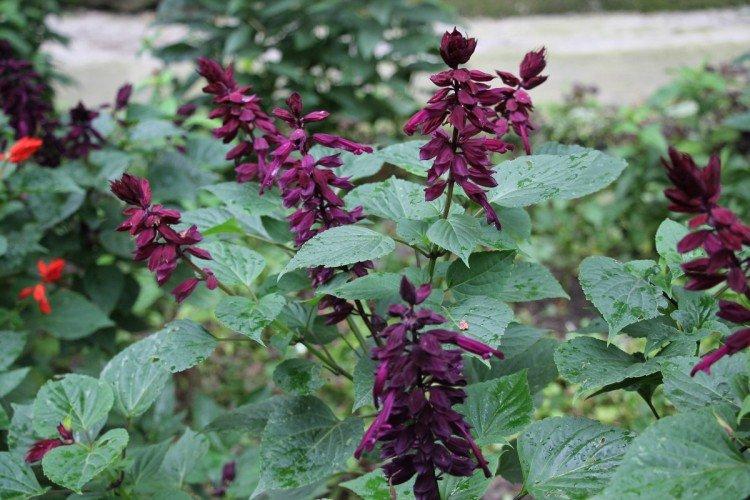
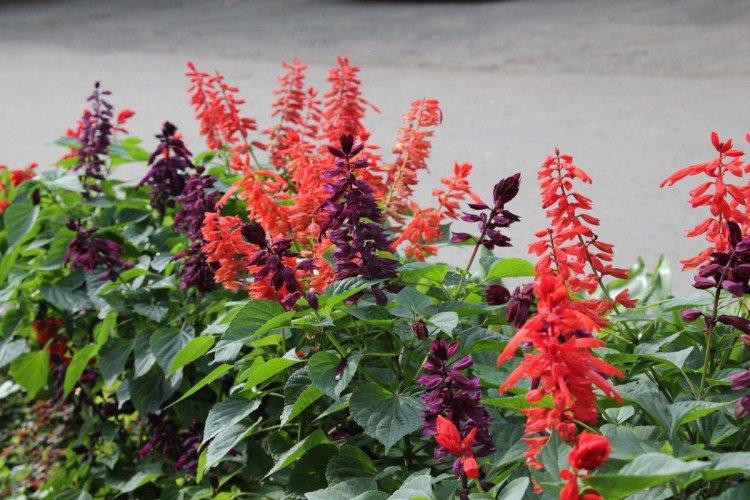
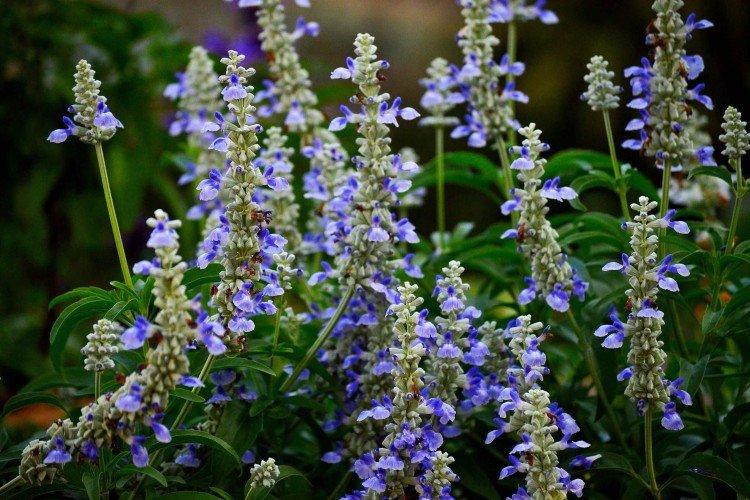
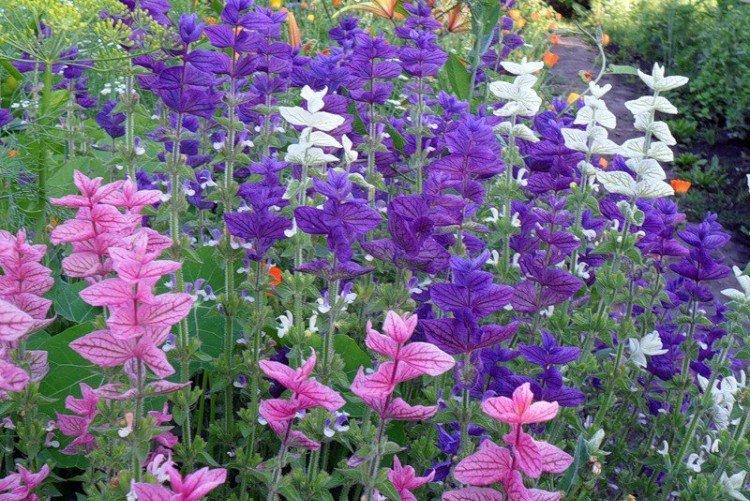
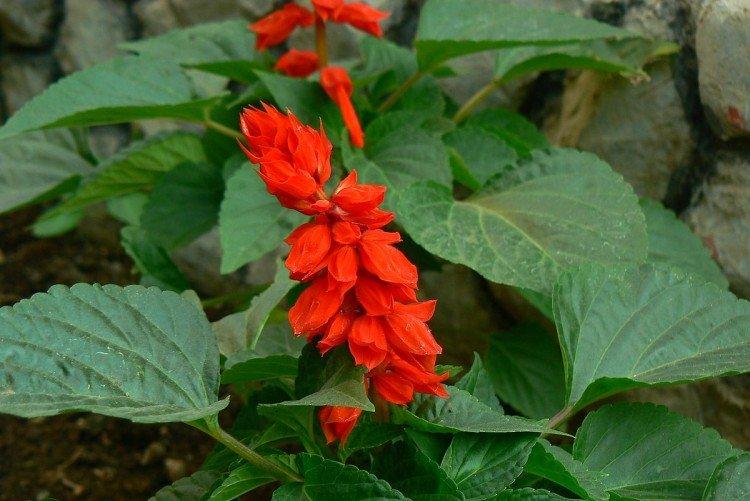
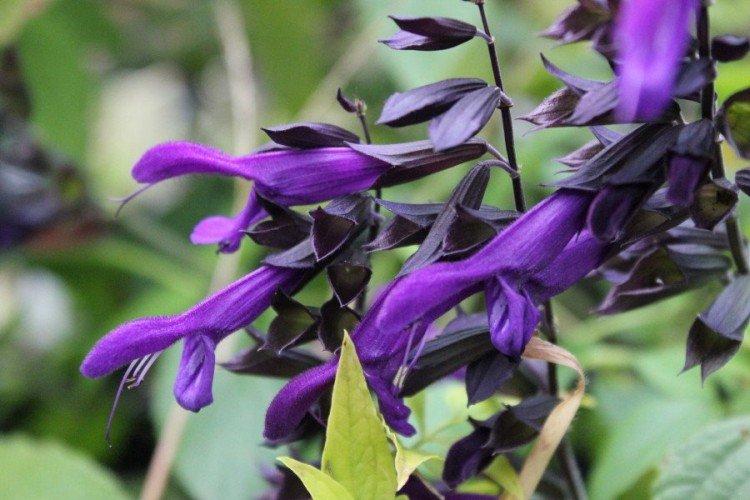
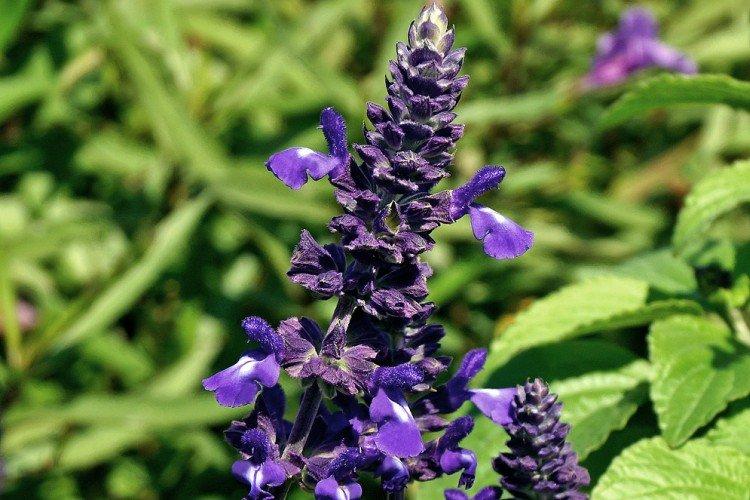
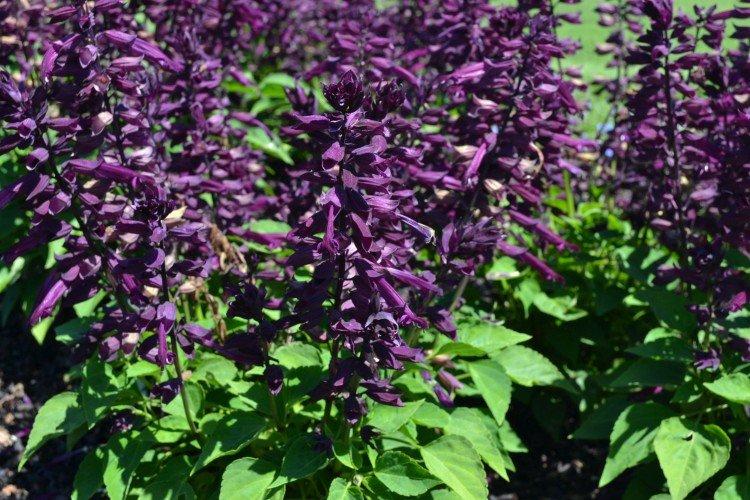
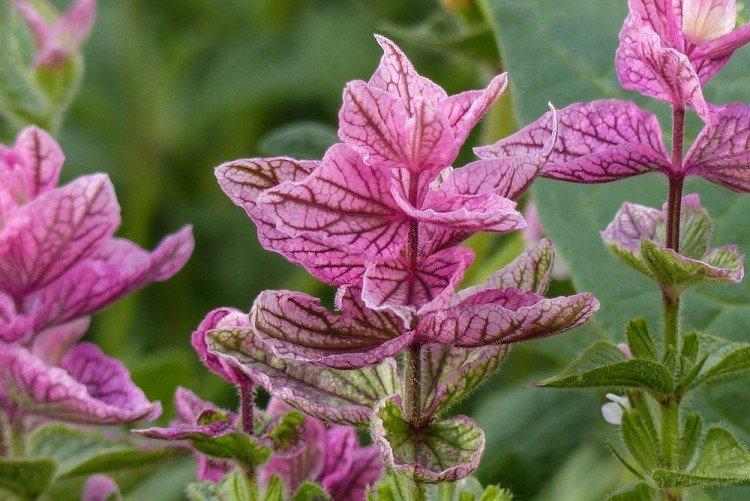
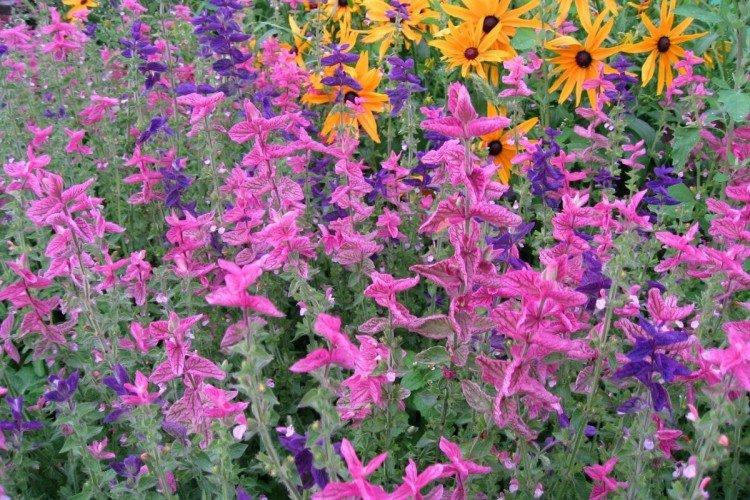
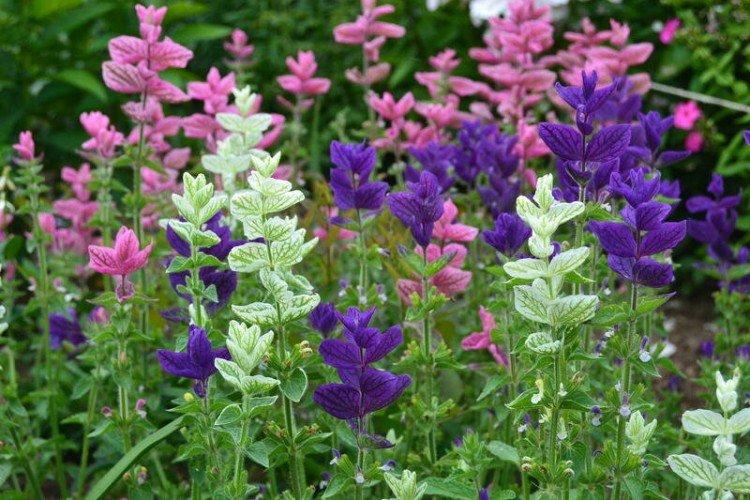
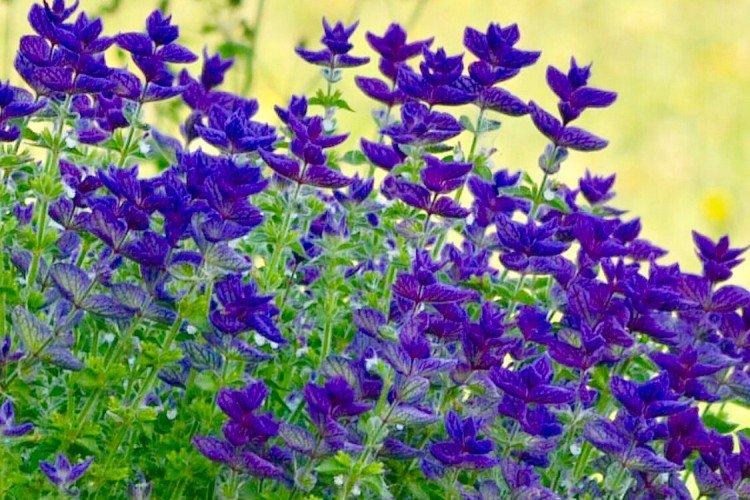
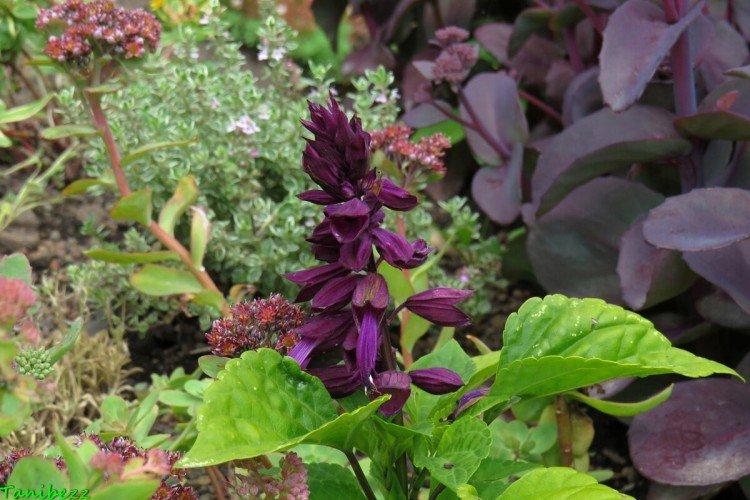
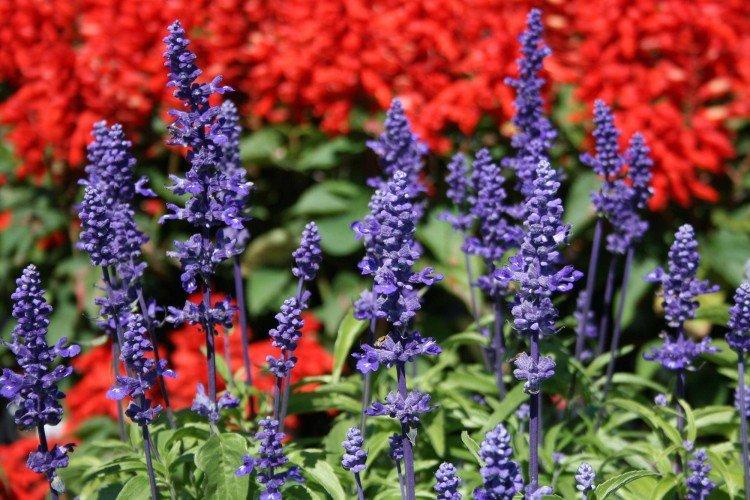
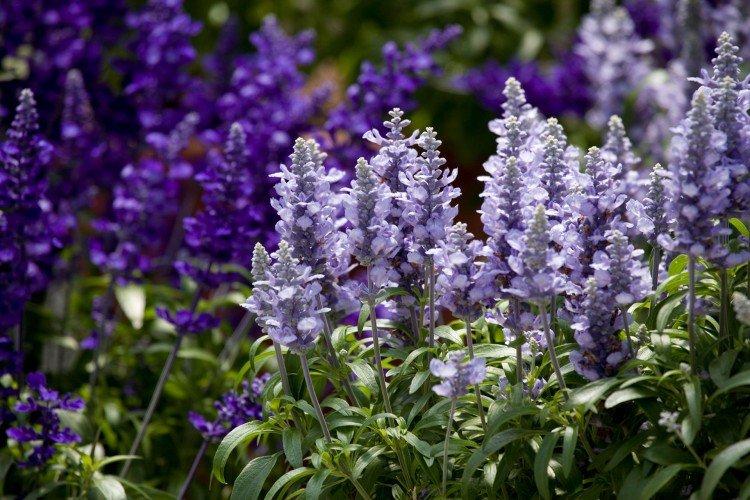
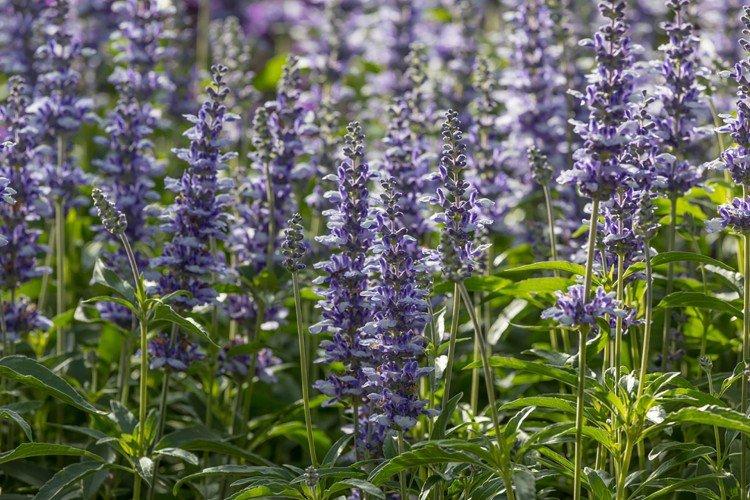
Salvia - photo
And now we invite you to take a look at this collection of photos! We have collected the most interesting and beautiful types of salvias so that you can fully appreciate them!