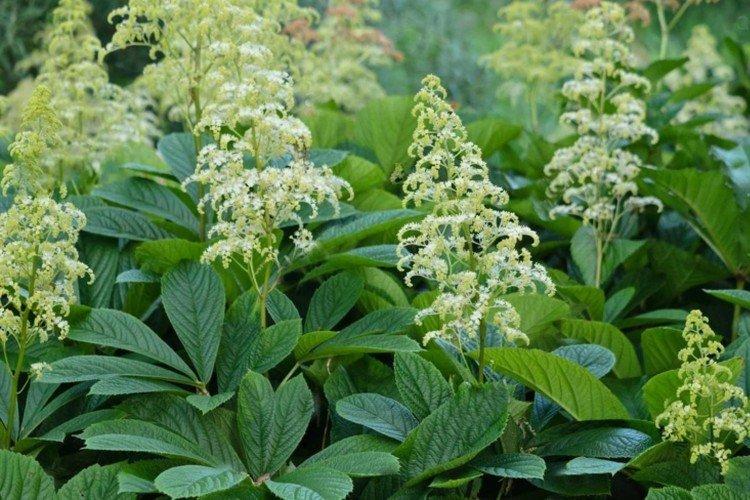
The huge leaves of Rogersia and its simple yet showy panicle blossoms fit perfectly into the modern green garden. The plant is completely unpretentious, very decorative and feels great in the shade. What else do you need? Let's talk more about Rogers!
general information
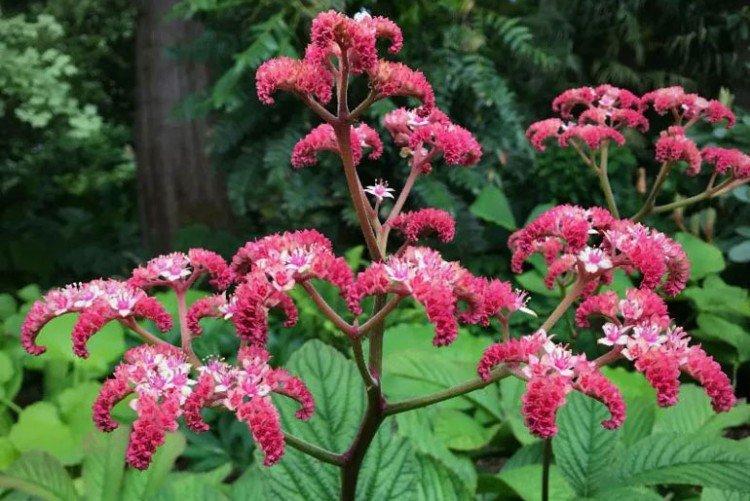
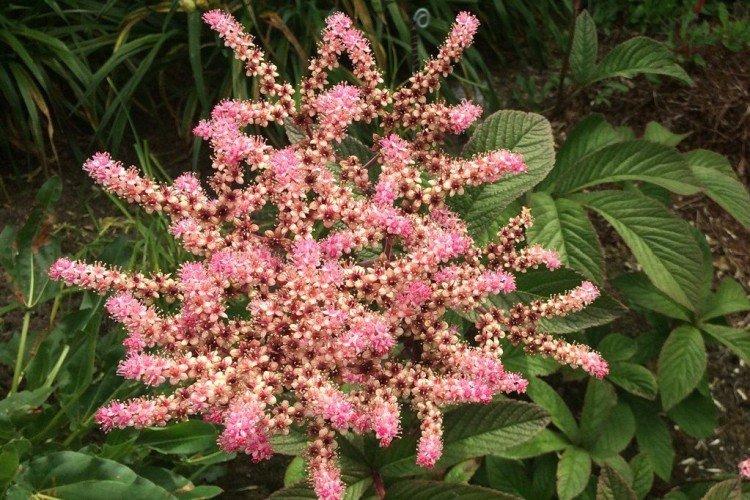
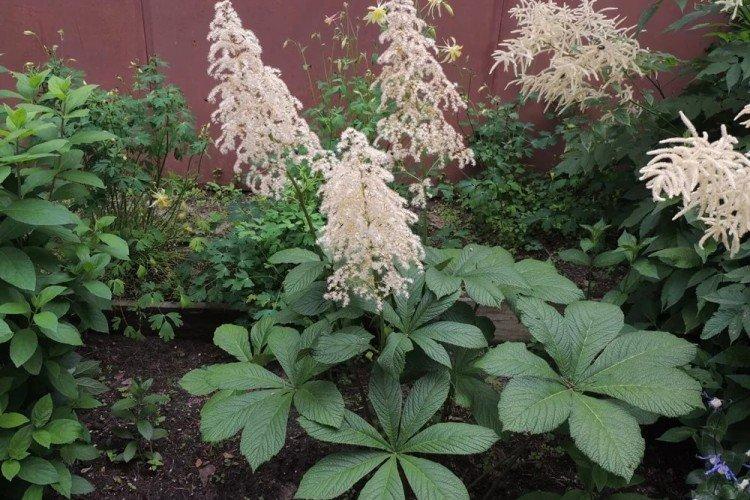
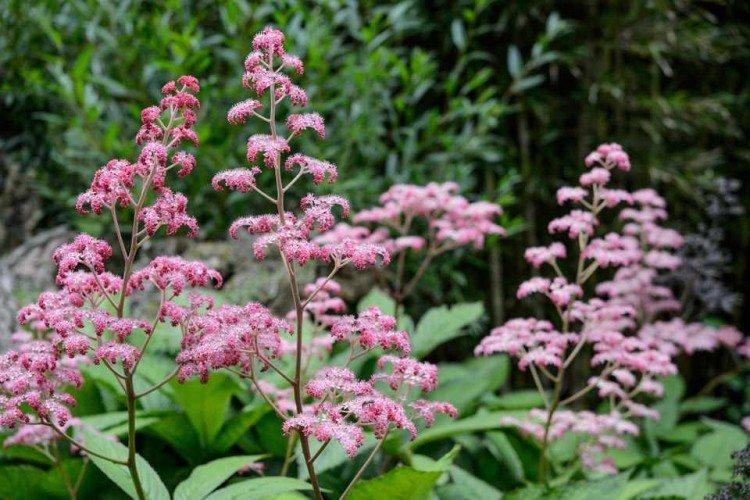
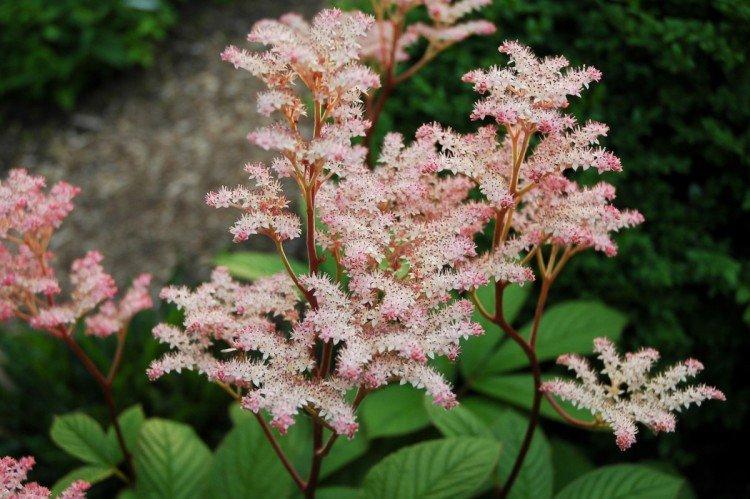
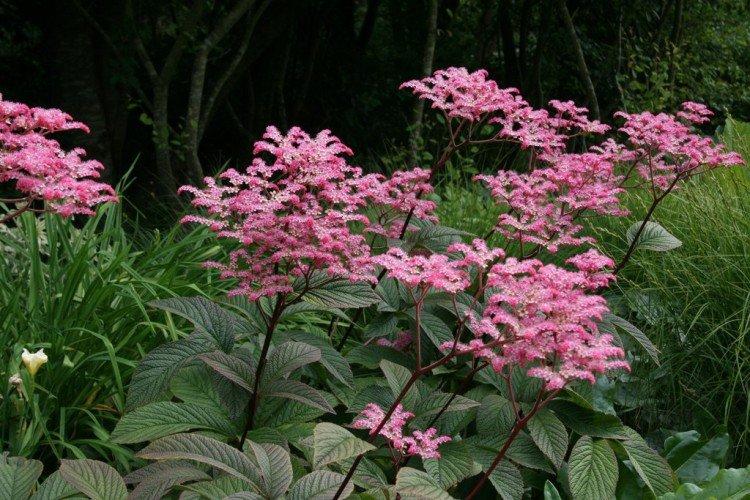
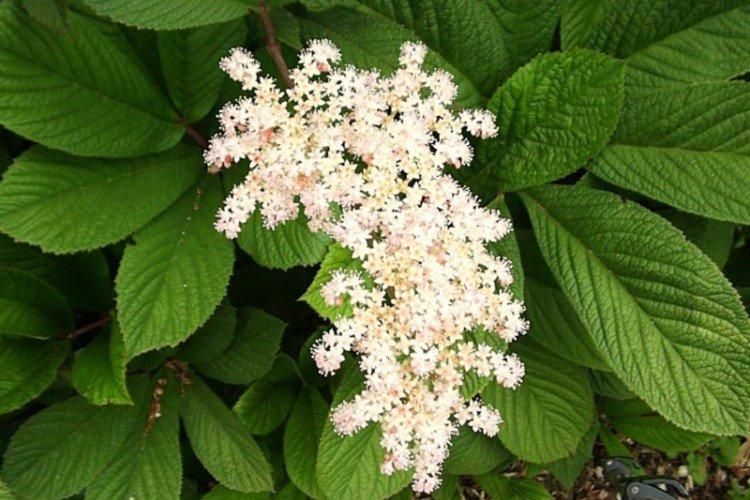
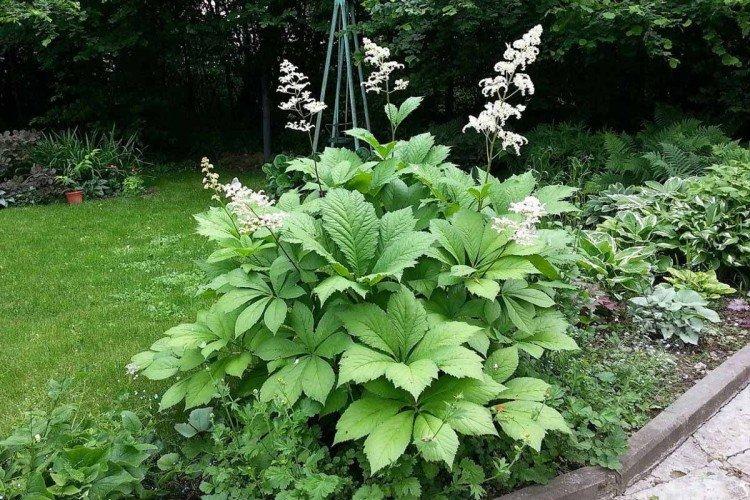
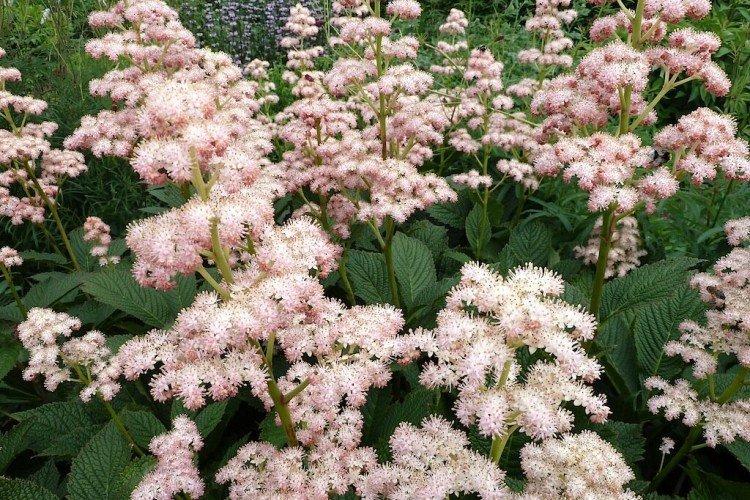
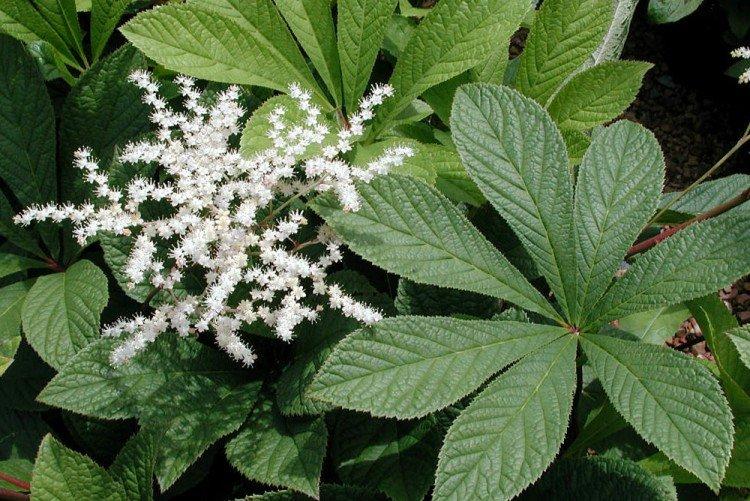
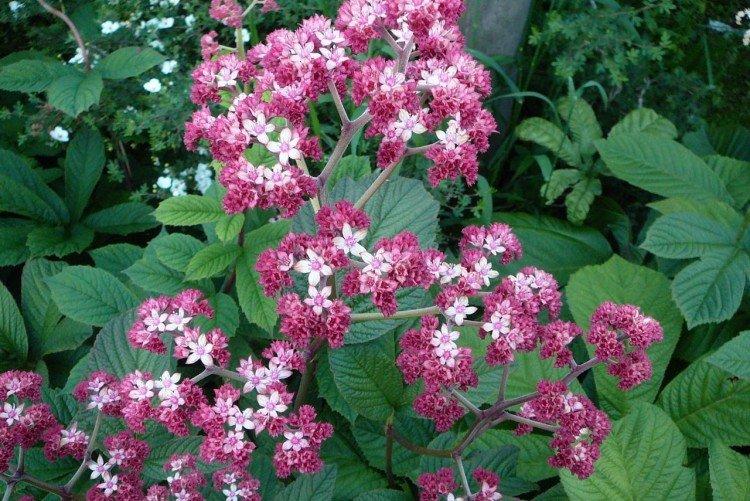
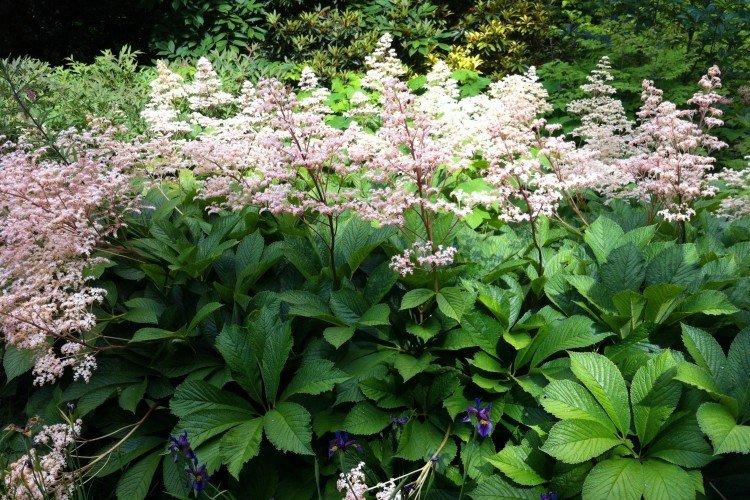
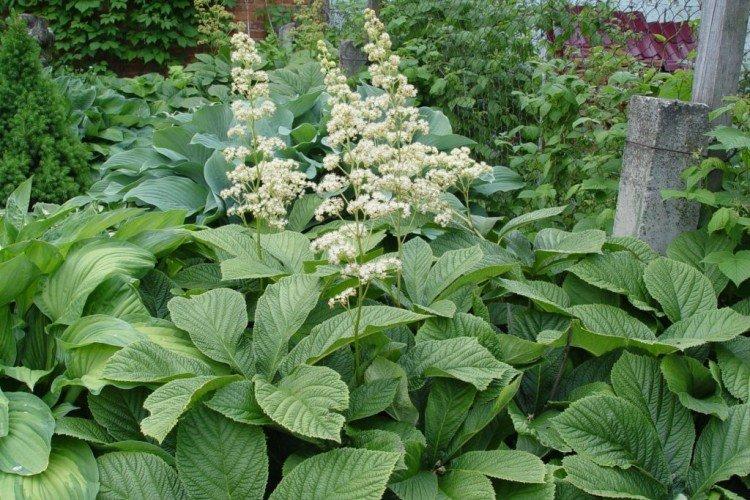
Rogersia is a moisture-loving and shade-loving plant native to the mountainous regions of Asia. It is appreciated for its large carved leaves, the ability to grow quickly and take up all the space. By the flowering season, the lush green crown is complemented by tall inflorescences.
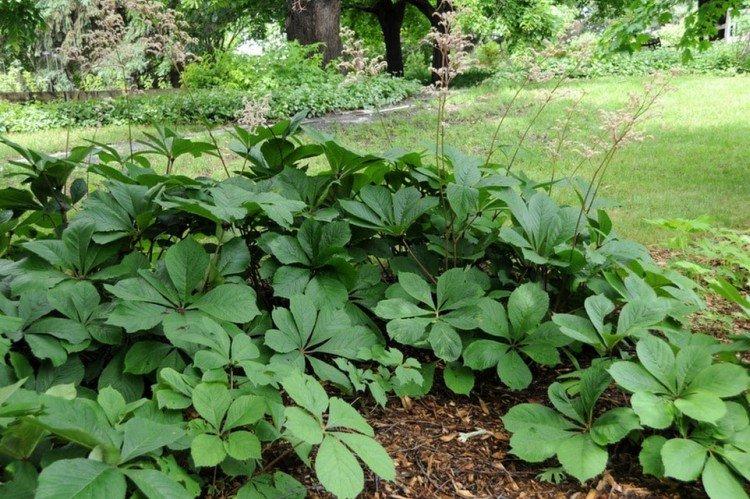
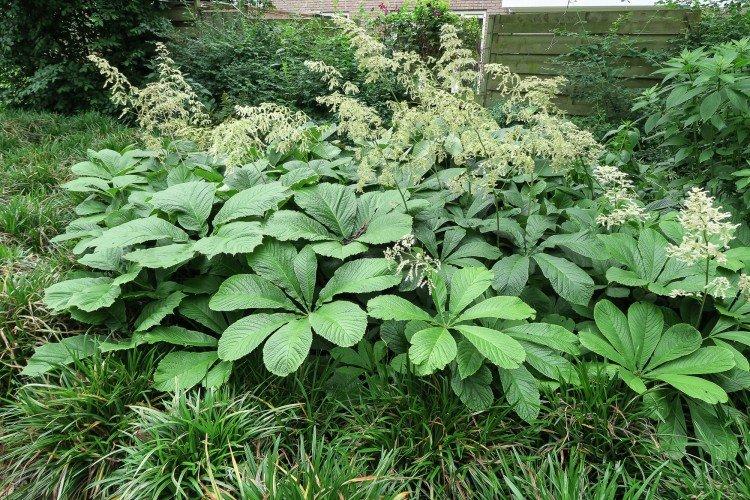
Rogersia has a strong core rhizome, which gradually grows to the sides with age. The average height of inflorescences is up to 1.5 m, but branches with leaves are usually lower. Erect branched shoots form a dense shrub.
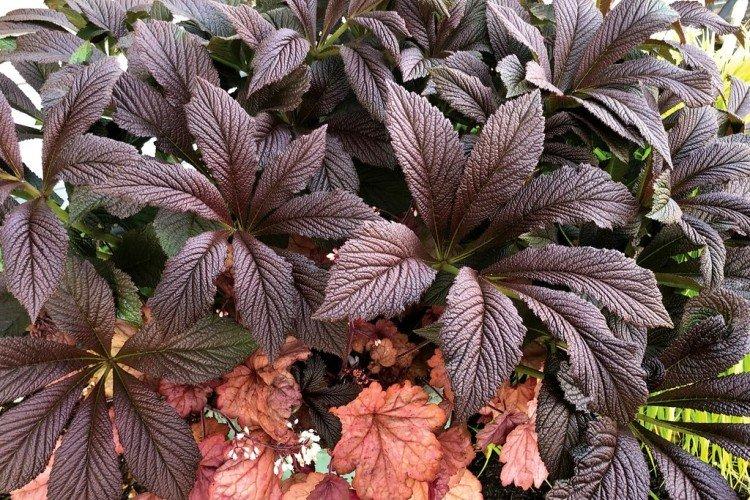
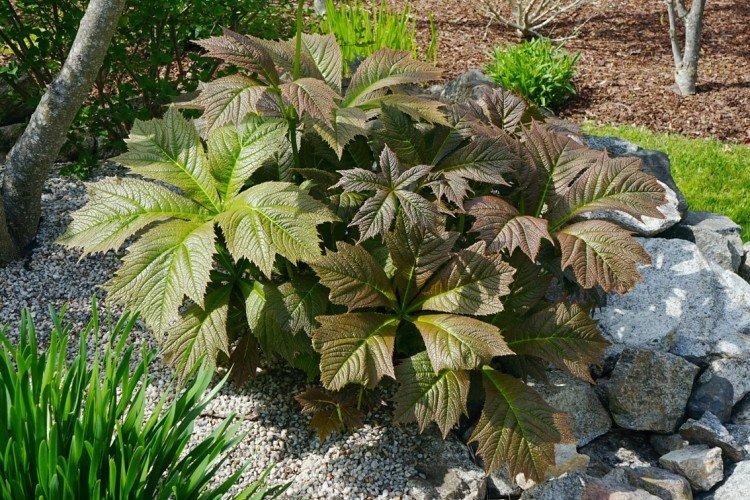
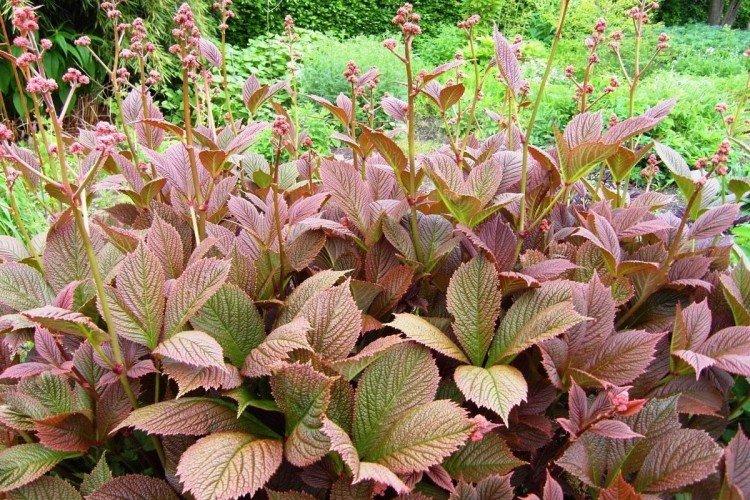
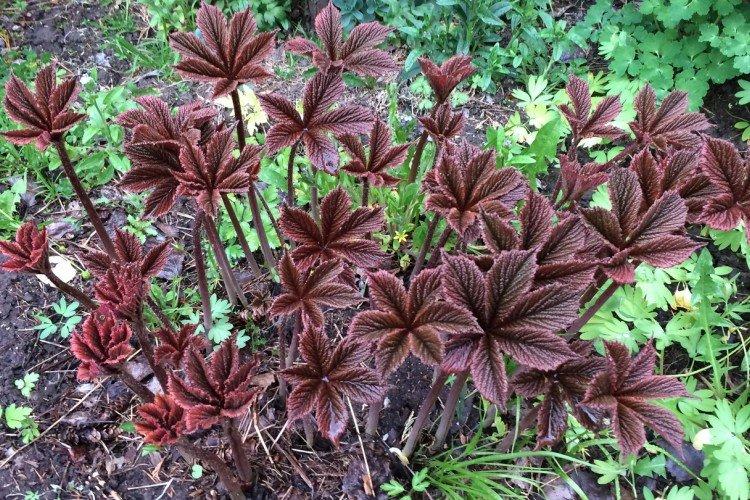
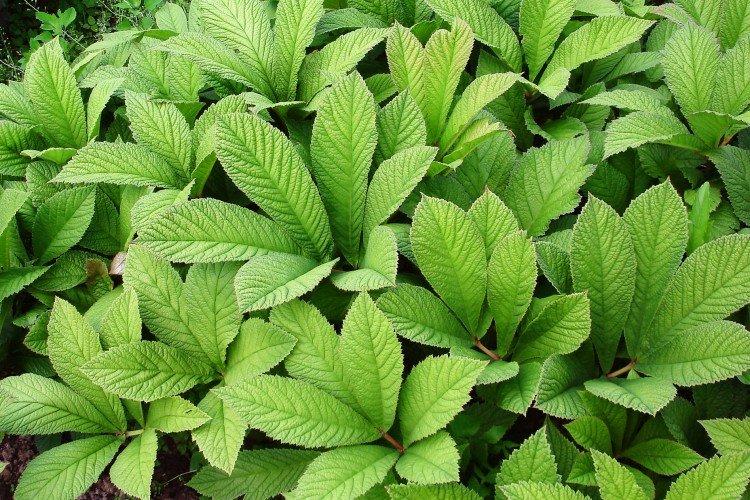
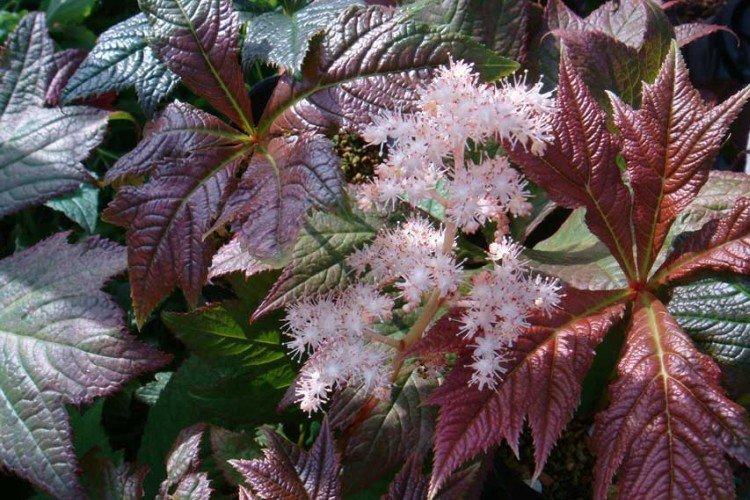
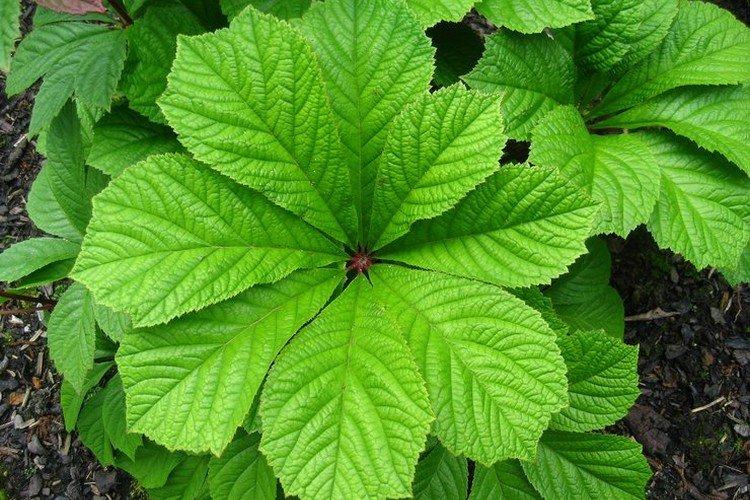
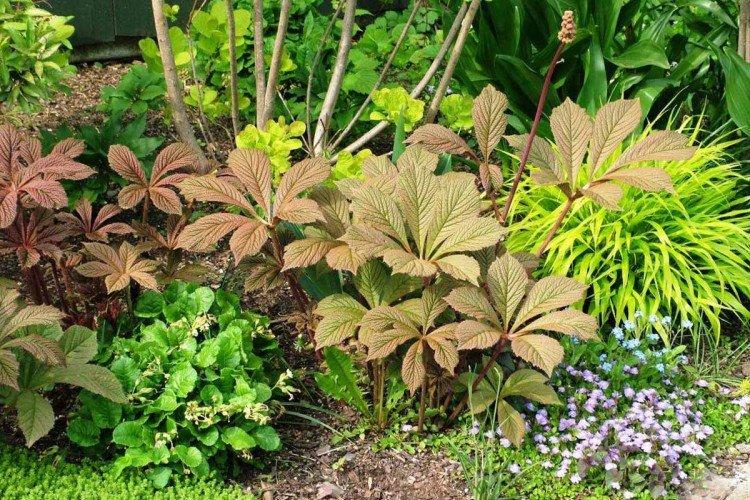
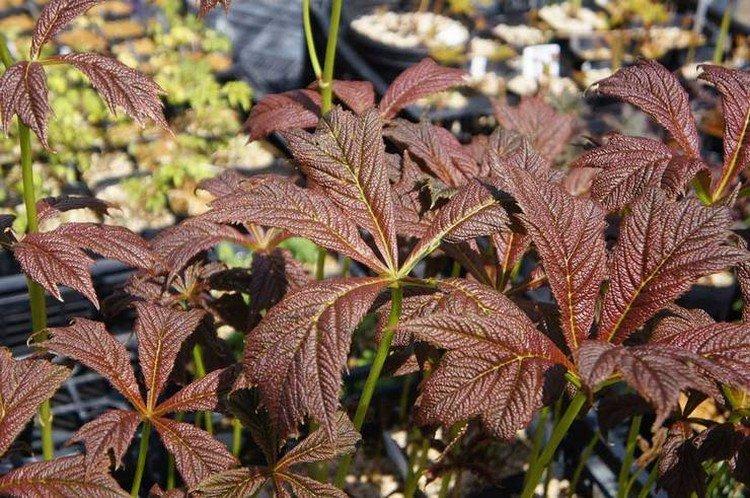
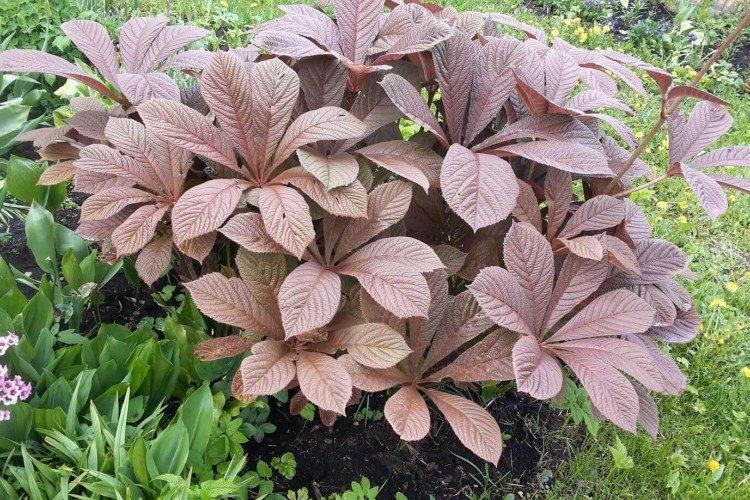
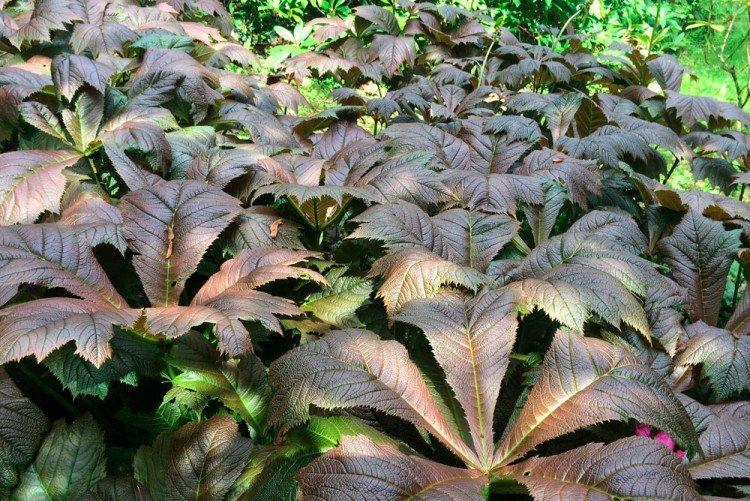
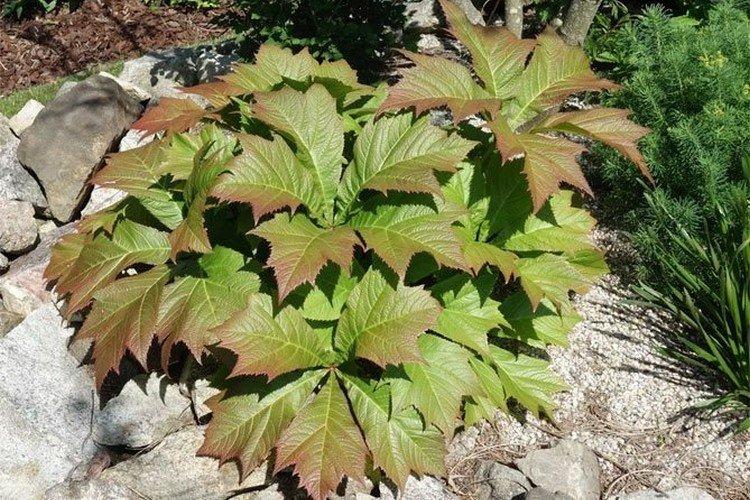
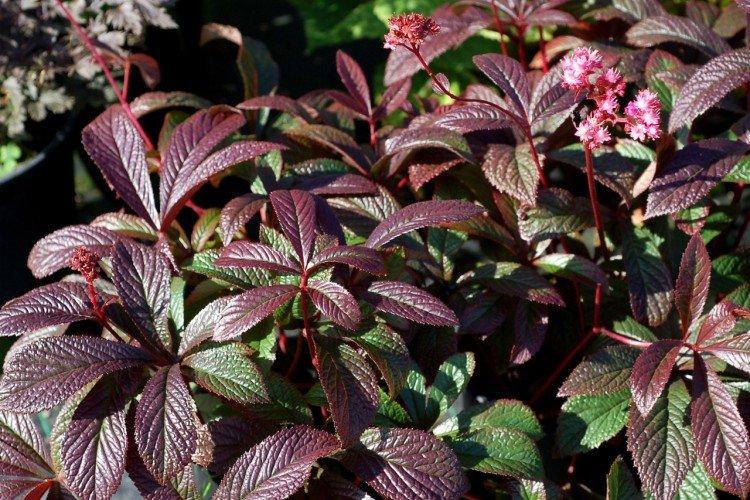
The diameter of the rogersia leaves easily reaches 50 cm. They can be of different shades - from green to red and bronze. There are varieties that change color during the season. Rogersia blooms in the middle of summer, and after wilting, the leaves begin to grow even more actively.
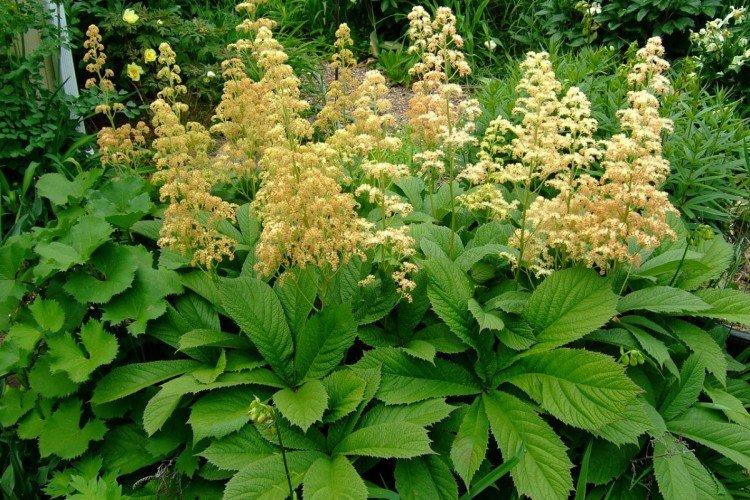

Rogers species
Basically, Rogers species differ in the shape and size of the leaves. Let's mark the most interesting and decorative ones!
Elderberry Rogers
As you can easily guess, the leaves of this rogers resemble an enlarged version of elderberry leaves. They are finger-like, but completely dissected into segments.
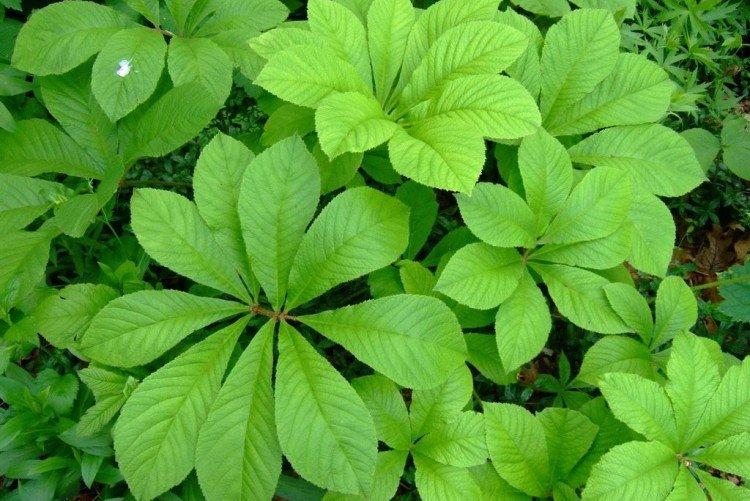

Nepalese Rogers
The leaves are collected on a long petiole at an impressive distance from each other. Because of this and due to their ovoid shape with pointed ends, they appear even more elongated.
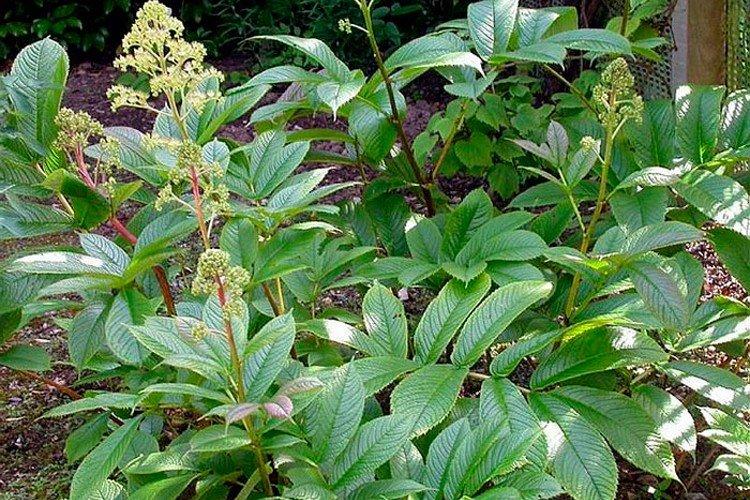

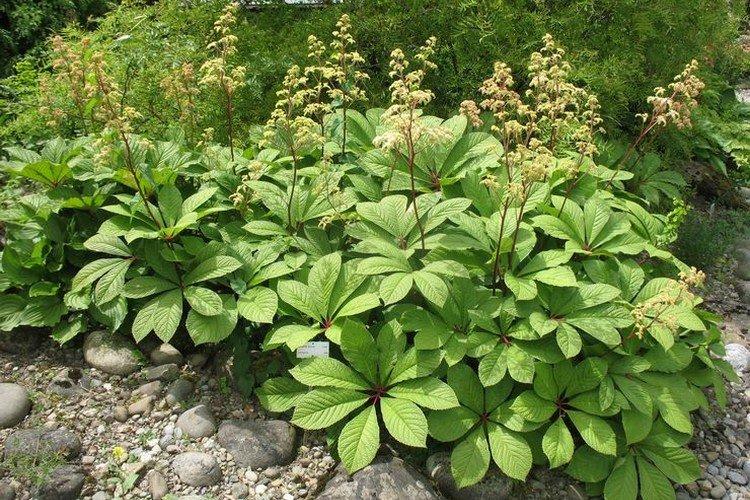
Horse chestnut rogers
The next species resembles the leaves of an ordinary urban chestnut. At first glance, they can even be confused, but if you put two samples side by side, the differences become obvious. The height of the bush is up to 1 m, and the height of the peduncles is up to 1.2 m.
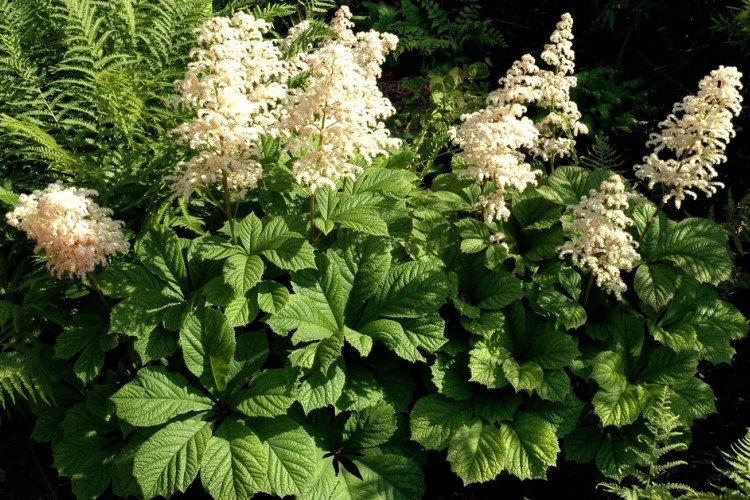

Rogersia Henrici
It is the brightest species with a very rich green foliage tint. And Rogersia Henrici is not afraid of the bright sun, and only changes the shade of the inflorescences, depending on the conditions.
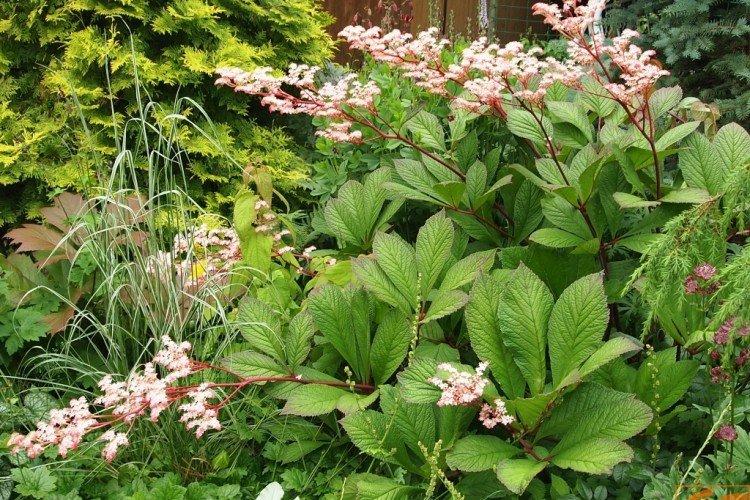

Feathery rogers
This species also has dissected leaves, but individual segments are narrower and elongated. The edge of the leaf plate is almost smooth, but the veins are embossed. This is a fairly compact species up to 60 cm tall.
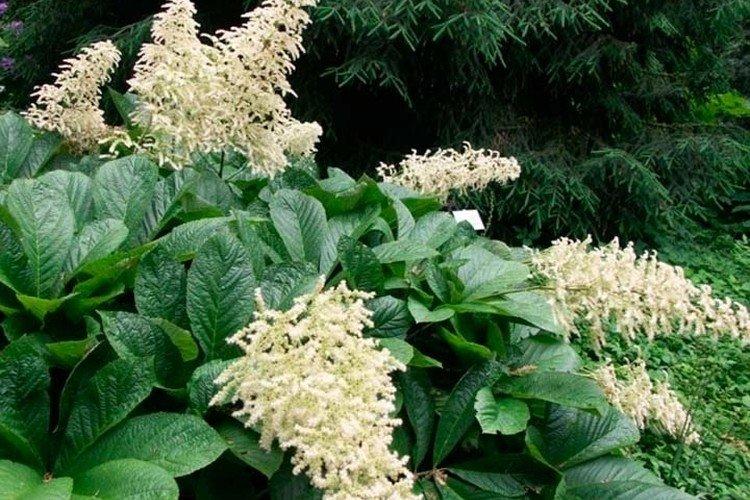

100-leaf Rogers
A very unusual decorative appearance with a complex chaotically serrated leaf edge. Due to their special shape, they resemble roughly cut inverted drops. Height - up to 1.5 m.

Rogers care
The spreading perennial has perfectly adapted to the conditions of our latitudes. The main thing is to choose the right site and provide the plant with all the nutrients!
Temperature and lighting
Rogers prefers shade or maximum - a few hours of sun in the morning or evening. This is a relatively winter-hardy plant with shelter. Be sure to avoid drafts and wind-blown areas.

Watering
The ground around the Rogers should not be allowed to dry out completely. Therefore, water it regularly, and spray it in the middle of summer. To preserve moisture, mulch the soil around the shrub.

The soil
For such an intensive growth of Rogers, a lot of strength is needed, so the soil should be primarily nutritious. Avoid areas with a close occurrence of groundwater, but an open body of water nearby is only a plus.

Fertilizers and feeding
Even before planting, humus, compost and peat are introduced into it to replenish the soil. If the soil is sufficiently nutritious, then additional fertilizing is not needed. Otherwise, add compost at the beginning of spring, and use mineral fertilizers 2 more times during the season.

Wintering
Rogersia winters right on the site, but it is important to protect the renewal buds from frost.In the fall, cut off the leaves and sprinkle the compost on the plant. In the spring, take off the shelter, but as it gets colder, use a non-woven blanket so that the buds of the inflorescences do not freeze.

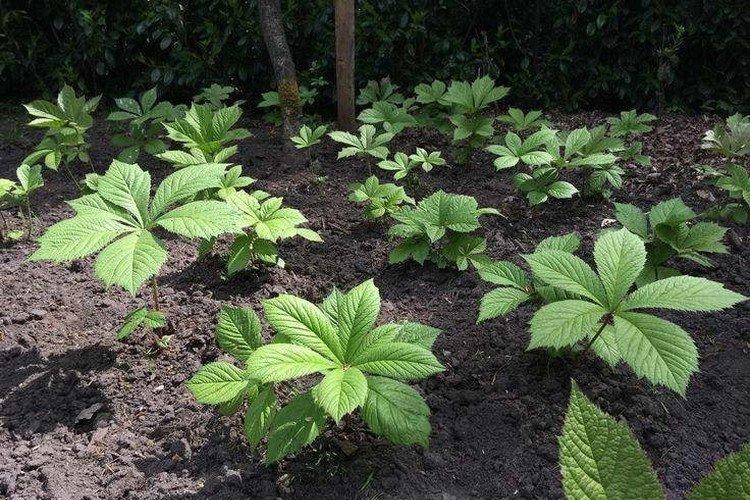
Planting and breeding
Reproduction of Rogers by seeds is a difficult and not the most rewarding process, because in a few months it is necessary to repeatedly change the temperature regime and the place for containers. And such a plant will bloom not earlier than in 3 years.
In summer, healthy, strong leaves with a petiole and a so-called heel are rooted. Treat it with a stimulant and root it directly in a light, moist soil mixture, and then transplant it into an open ground with an earthen clod. Young seedlings are planted at a depth of 6-8 cm and with a distance of 50-80 cm.
An adult bush can be divided very easily, and at the same time rejuvenated. It is better to do this in the spring and immediately plant the divisions on the site. During autumn propagation, the cuttings are planted in containers and left indoors until spring. It is impossible for the rhizome to dry out during the transplantation.

Rogers diseases and pests
Rogersia is resistant to almost all diseases except root rot due to moisture stagnation. Such a bush gradually darkens, withers and withers. It must be immediately dug up, the decayed parts of the rhizome must be removed and transplanted to a new place.
If red bumpy spots appear on the leaves, this is rust. Cut off diseased parts of the plant and treat it with fungicides. All this is best done in the morning or afternoon, so that the Rogers dries out until the evening.
Juicy large leaves are loved by snails and grape slugs. They will first have to be removed mechanically, and then the planting should be sprayed with special preparations.
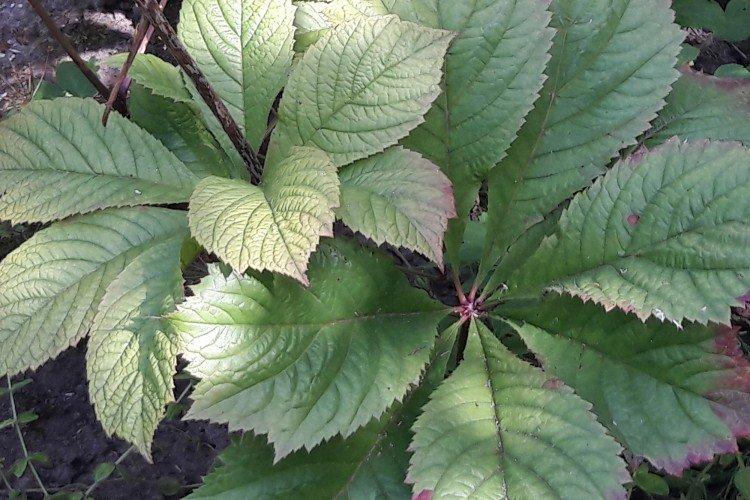

Rogersia - photo
Despite the fact that Rogersia is a flowering plant, it is appreciated for its spectacular leaves. Just look at how impressive they are in size!