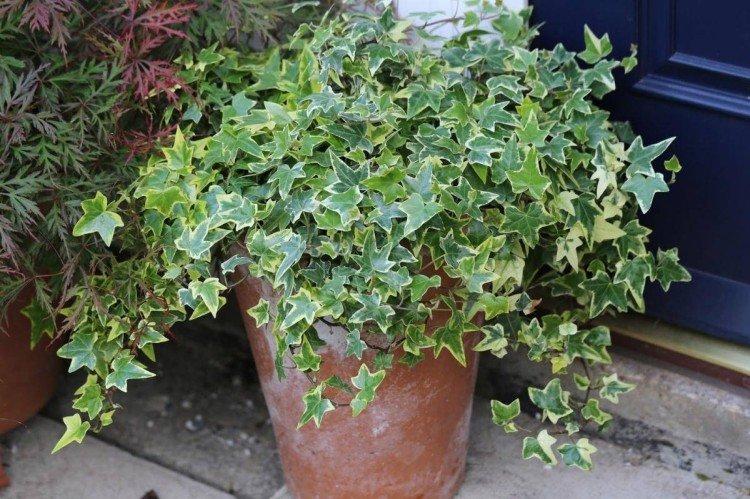
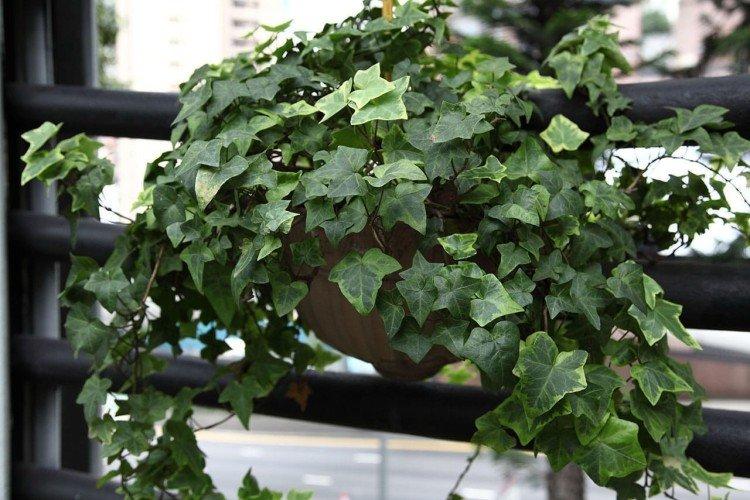
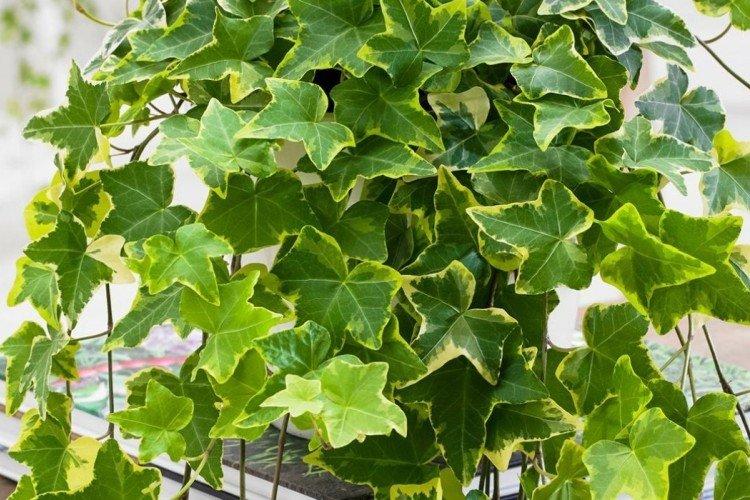
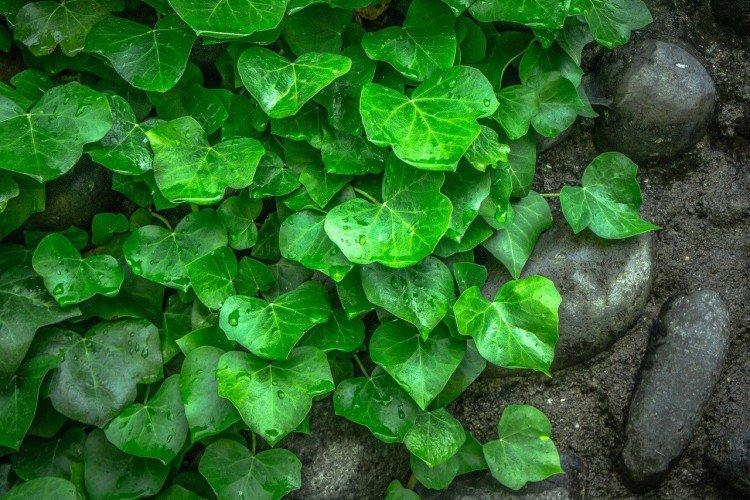
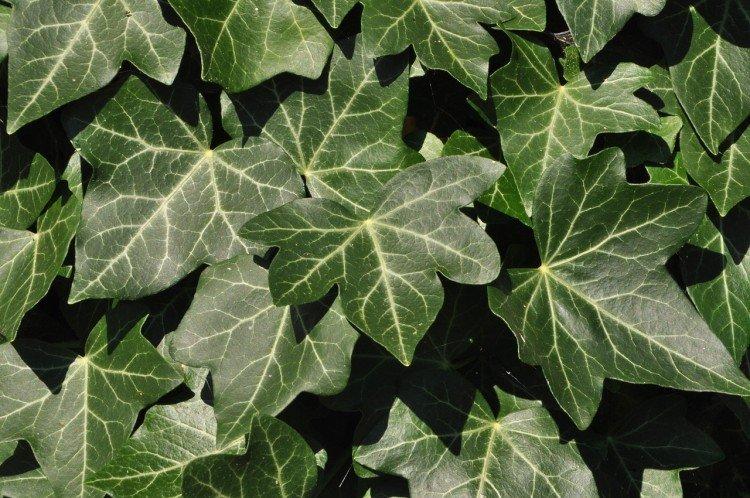
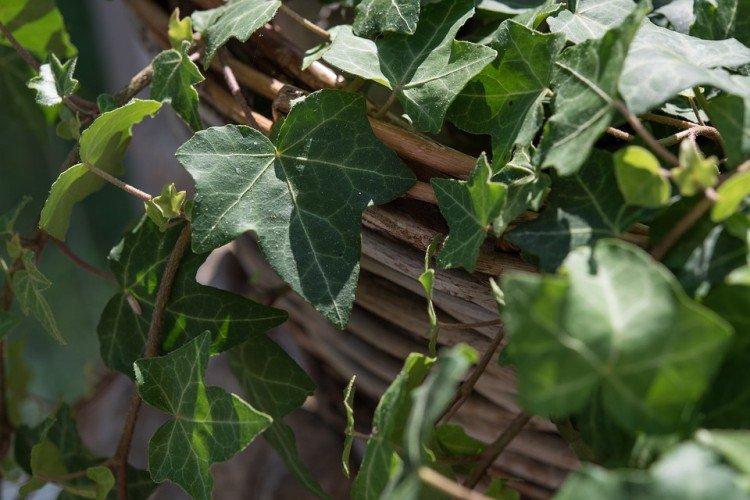
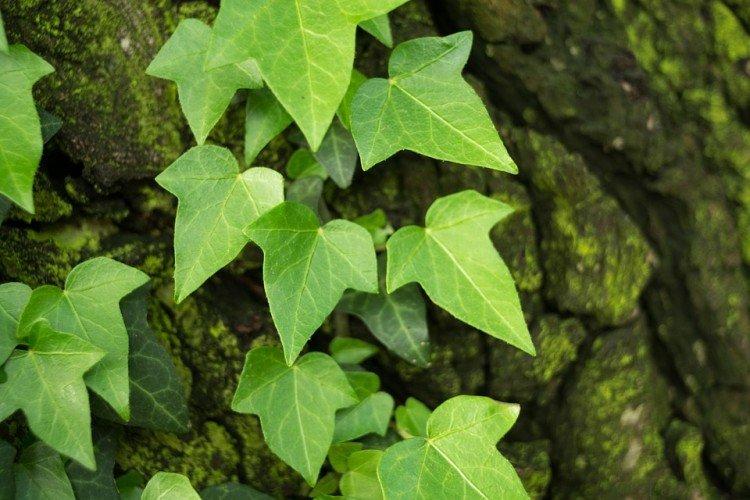
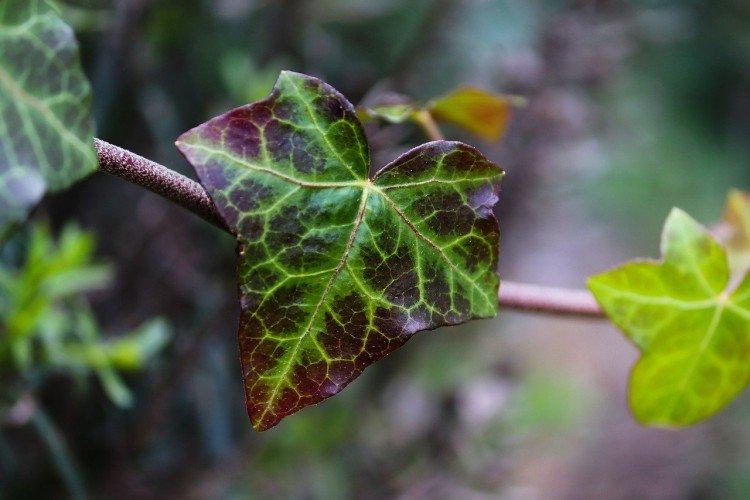
It is difficult to find a person who has never seen ivy in his life. They decorate gardens and facades, make decorative fences, create whole green walls in apartments and simply refresh the interior. But what do you know about this popular plant? Let's figure it out in more detail!
general information
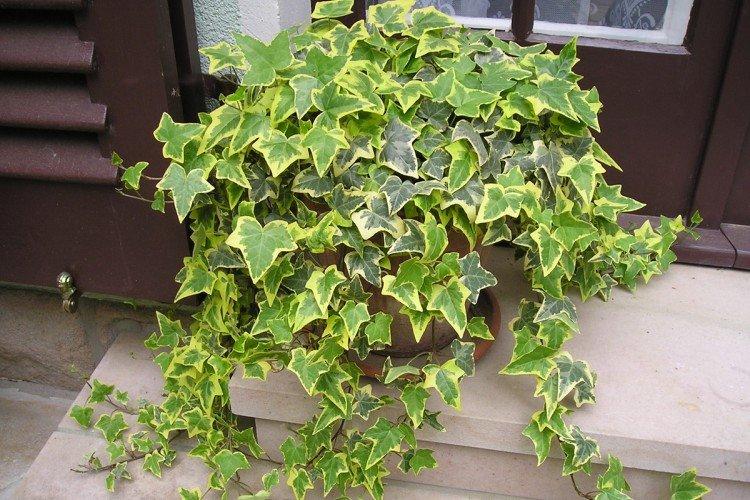
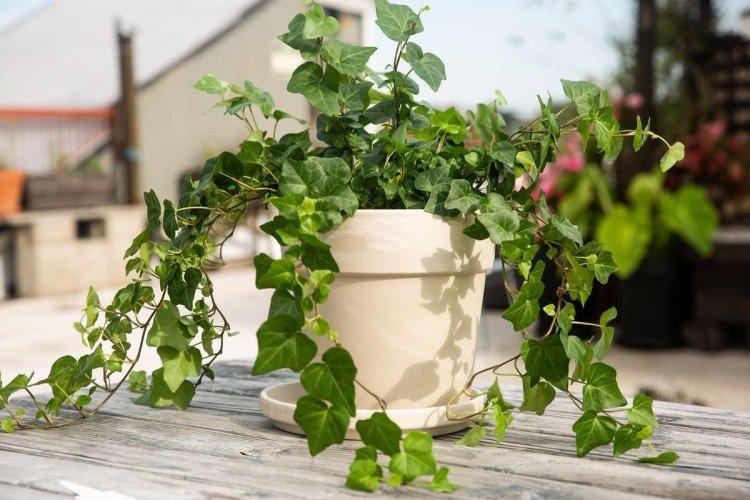
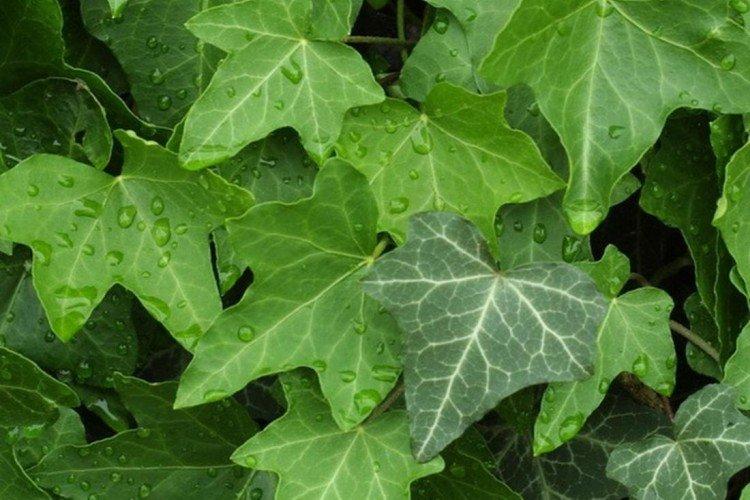
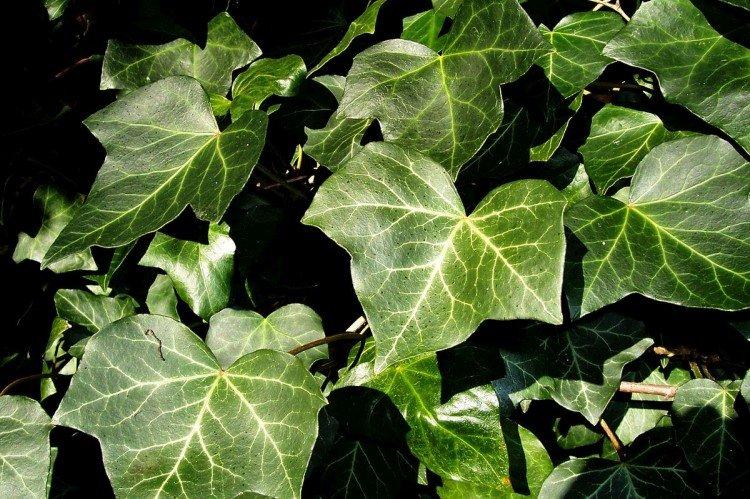
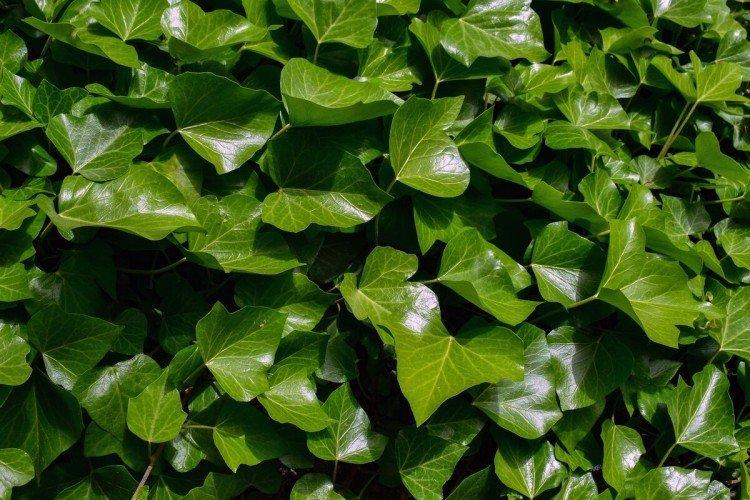
Ivy or heder has many names and names in different regions. Due to the special structure of the rhizome and shoots, it is able to cling to any surface. Large adult ivy in natural conditions can grow up to 30 m. Many varieties even bloom with small yellow-green flowers collected in a brush.
Ivy is common throughout Europe and in Russia. It is more common in warm and humid regions, but over the years the plant has learned to adapt. Ivy thickets in the Caucasus are especially impressive.
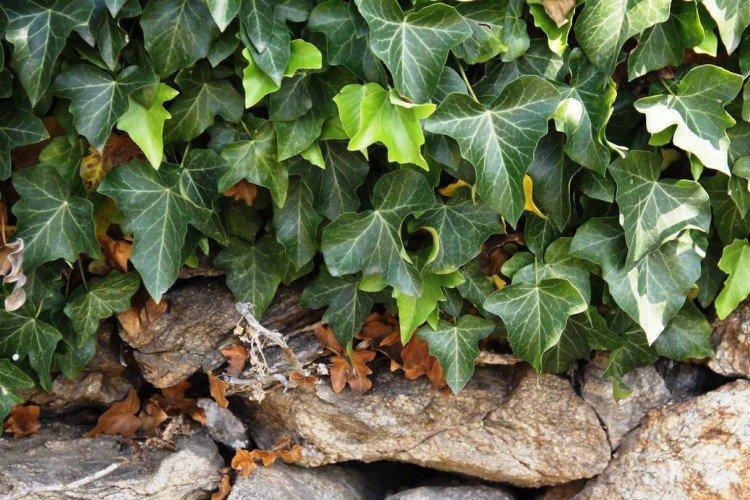

Ivy species
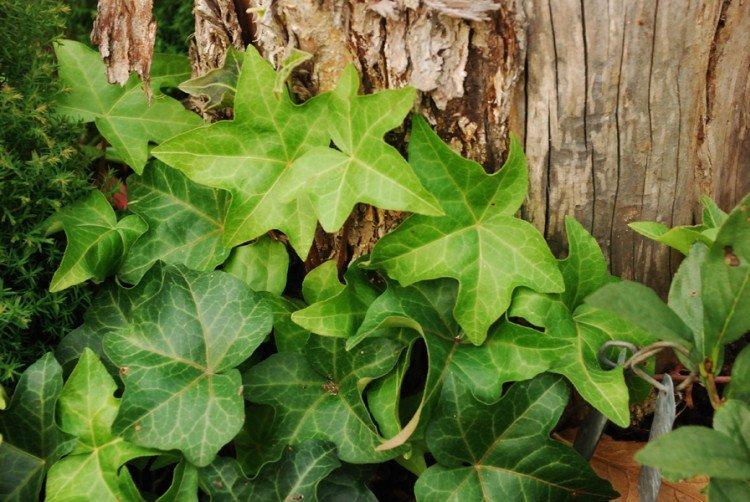
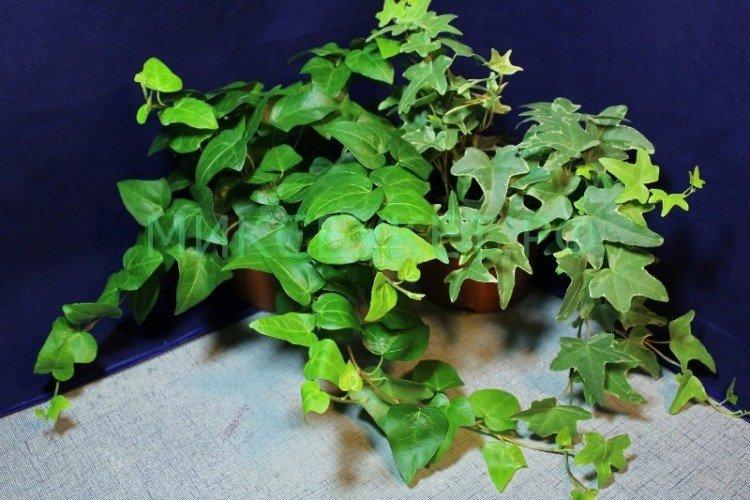
There are many varieties of ivy, which mainly differ in growing conditions and in the shape of the leaves. The essence remains the same - it is a tenacious and flexible liana, which captures entire territories at a fantastic speed. Only a few cold-resistant species are popular among gardeners in Russia!
Common ivy
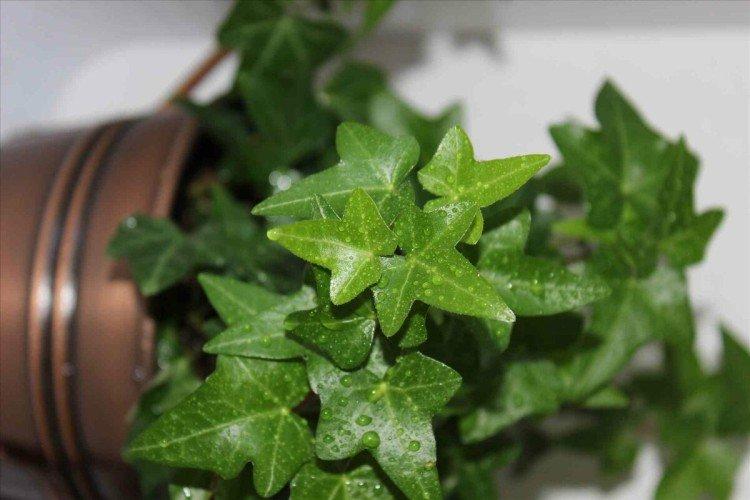
Grows well in an apartment or garden. It has beautiful small leaves and grows rather slowly. An excellent option for the design of reservoirs, paths and the site as a whole.
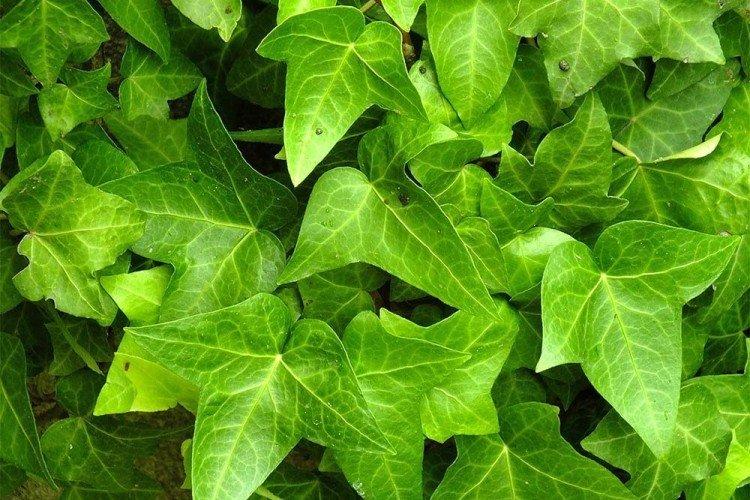

Algerian ivy
He is Canary. It is a thermophilic species, but it forms very beautiful green carpets on the ground. It can be guided and shaped, but bear in mind that it has no aerial roots.
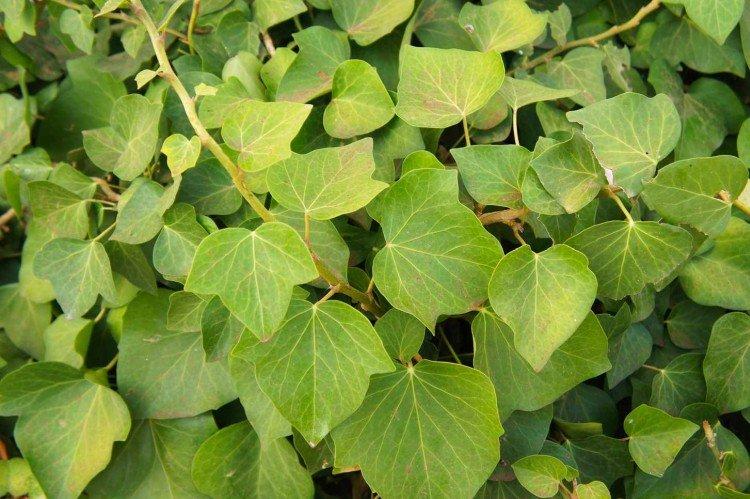

Crimean ivy
Suitable for the southern regions of the country and grows very quickly. It can be shaped, spliced with trees and other shrubs. Gradually, its shoots become lignified.
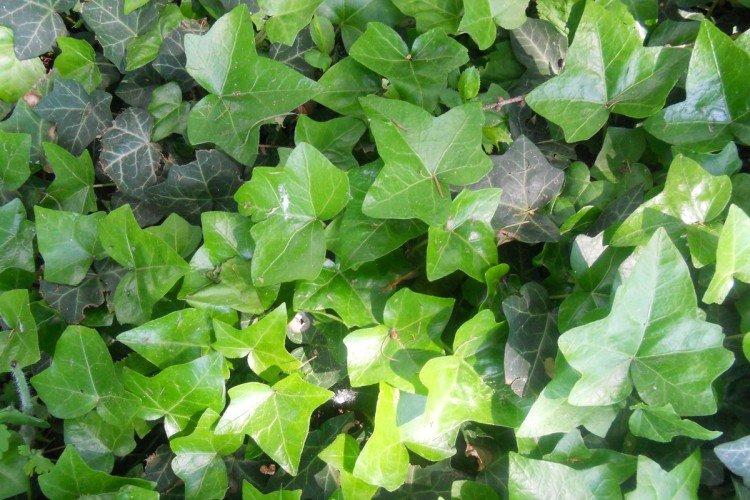

Caucasian ivy
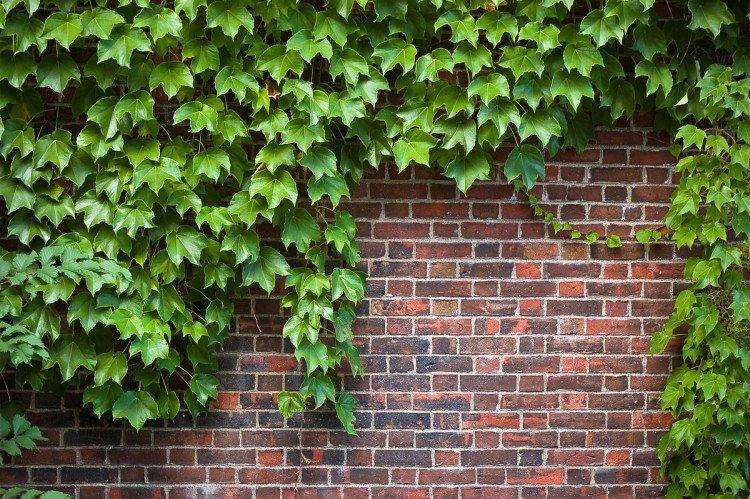
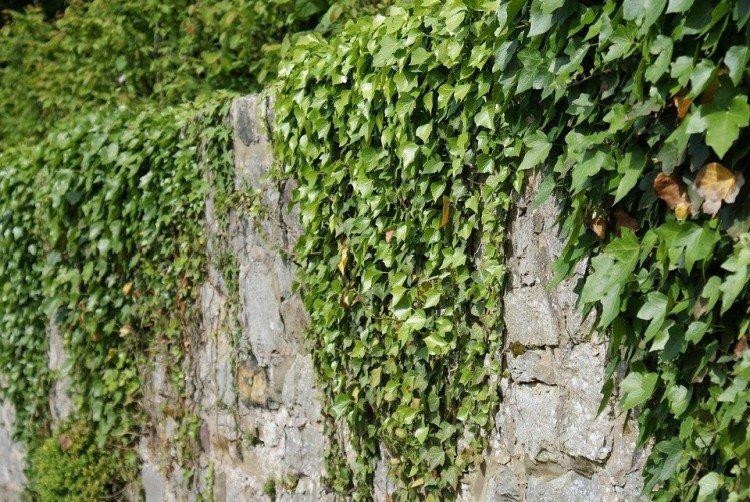
He is Colchis. It is planted to decorate facades and create green walls. This species grows beautifully upward and covers any base with a thick green carpet. With age, the leaves change shape and become larger and larger.

Plyushch Pastukhova
In nature, it is common in the mountains and valleys of Dagestan. It is a rare species with thin and small whole leaves. It is not fixed on steep walls and rocks, but it beautifully wraps around the supports with aerial roots.

Ivy care
Ivy is as unpretentious as possible in everyday life, and this is one of the main reasons for its popularity. It is enough just to find a good place, avoid transplants and rearrangements, and water on time.
Temperature and lighting
Lighting requirements differ for different ivy varieties. Most of them prefer diffused light and partial shade. You can grow different species in the apartment, but on the street - only frost-resistant ones. Temperature drops and drafts do not scare him.

Watering
Since spring, ivy constantly needs abundant watering with warm, settled water. The ground should be moist, but it is important not to overdo it here. The plant does not like drought, but it tolerates waterlogging even worse.

The soil
Ivy is completely undemanding to the soil, so any garden or all-purpose soil will do. We advise you to add a little peat and baking powder to it. In addition, you need good drainage and periodic loosening of the soil.

Fertilizers and feeding
Ivy grows very actively, so we advise you to fertilize it regularly during the warm season. Add mineral mixtures for deciduous plants every 1.5-2 weeks. Indoor plants can be fed even in winter, but less often - once a month.

Pruning
Ivy needs regular pruning, even if you don't plan on shaping it. At a minimum, old, painful, frozen and damaged branches should be removed. This is done in early spring before the start of active growth.

Wintering
This only applies to garden ivy, which will survive the frost in the garden. The most important thing is to provide protection for the roots.To do this, mulch them with a thick layer of organic matter even before the snow falls.

Transfer
It is better not to touch street ivy at all unless absolutely necessary. Homemade is transplanted as it grows out of the flowerpot. The new pot should be one third larger than the old one.

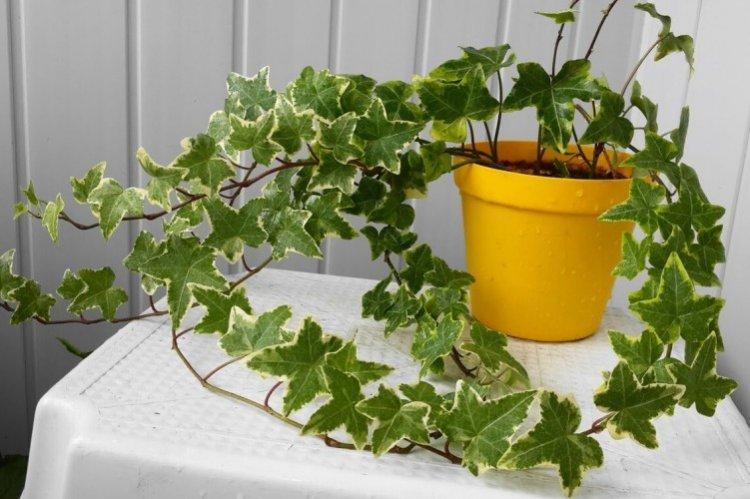
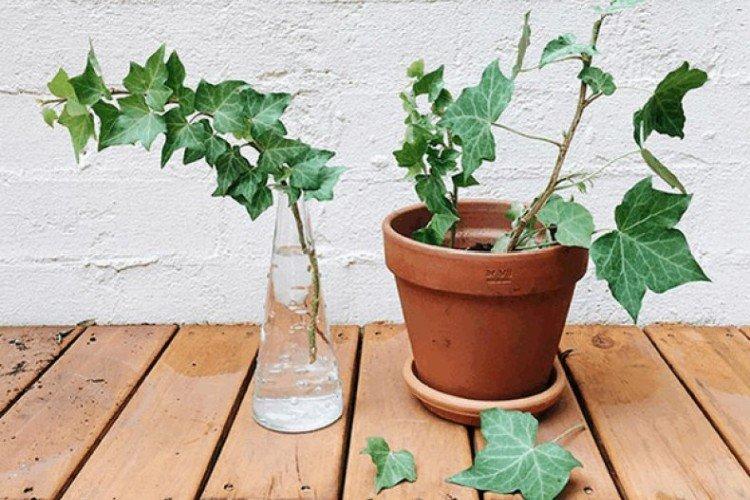
Reproduction and planting of ivy
The main method of propagation for ivy is cuttings. To do this, you need healthy shoots 10-20 cm in length, which root perfectly in ordinary water with sufficient humidity and warmth. You can root cuttings and immediately in a wet substrate.
Alternatively, layering can be used. Choose a long, healthy shoot, make a small cut in the middle and dig it into the ground. Fasten with a bracket so that it does not knock out, and after rooting, simply separate and transplant.
Another similar method is whole dropping. Choose a thin and healthy shoot and bury it completely in the sand, leaving leaves on the surface. After 2-3 weeks, it will grow overgrown with its roots.

Pest and disease control
The most dangerous enemy of ivy is the spider mite, which rapidly covers the entire vine. Less often, aphids, thrips, scale insects and whiteflies settle on the leaves. In all cases, it is important to identify the problem as early as possible and use insecticides.
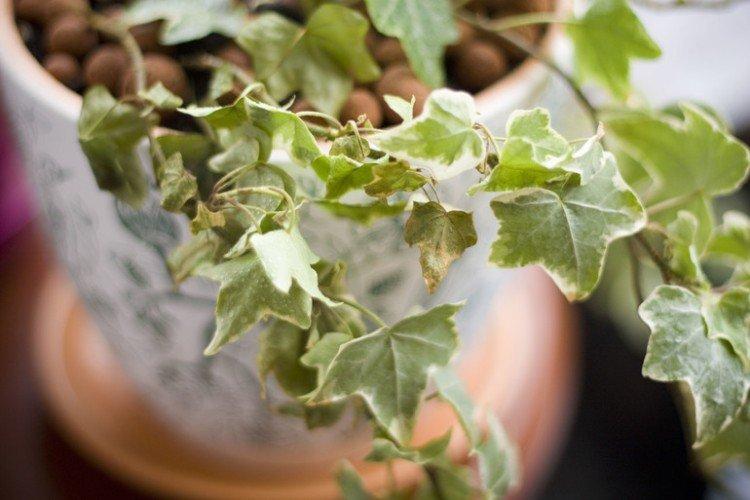
If the leaves of ivy fade, it lacks light, and if they turn yellow and dry, it lacks moisture. If the air is too dry in the heat, the shoots can be completely bare altogether. But with excess moisture, a fungus develops. In this case, you need to cut out all damaged areas and use fungicides.

Ivy - photo
The dense thickets of ivy inspired artists for a reason. They are an invariable decoration of ancient castles and fairy-tale forests in cartoons and movies. Just look how beautiful it is!