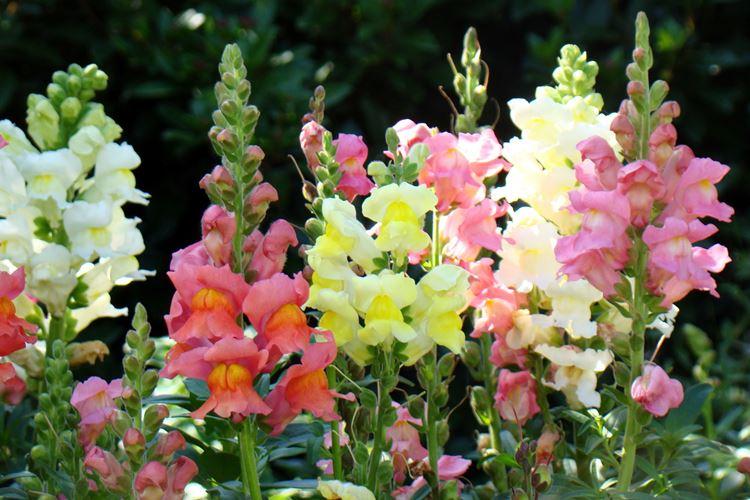
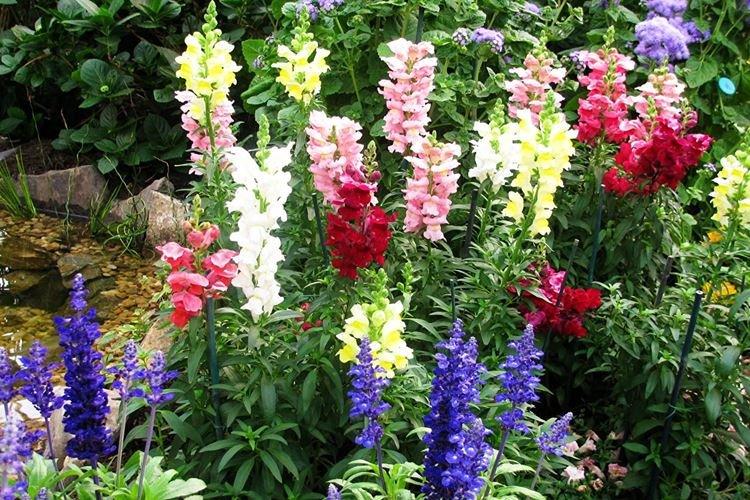
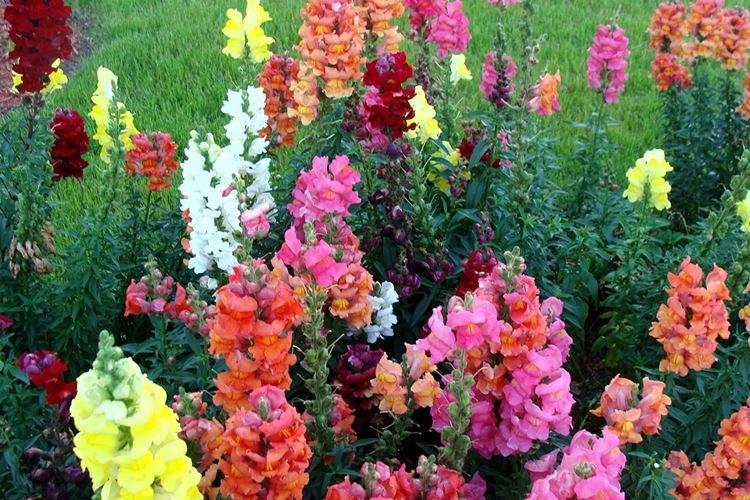
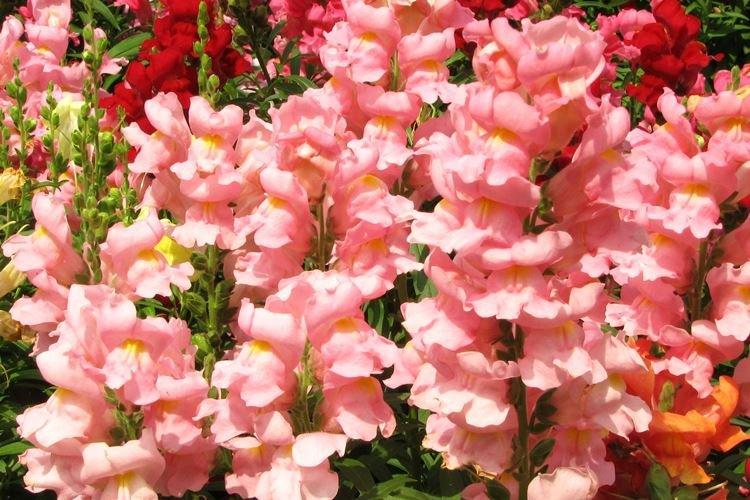
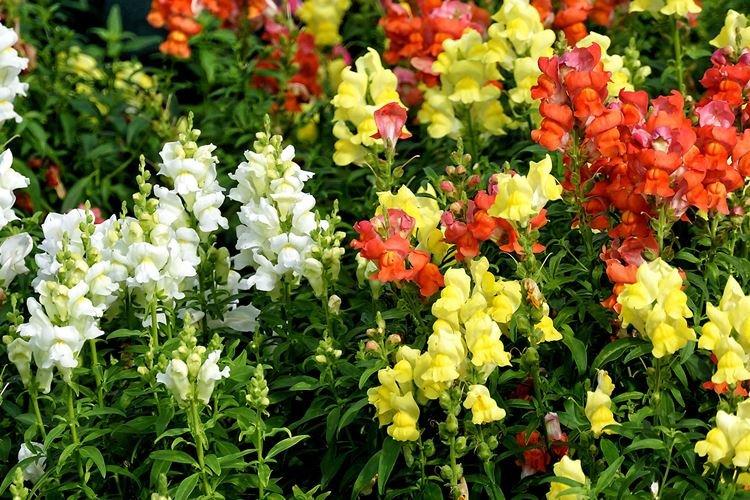
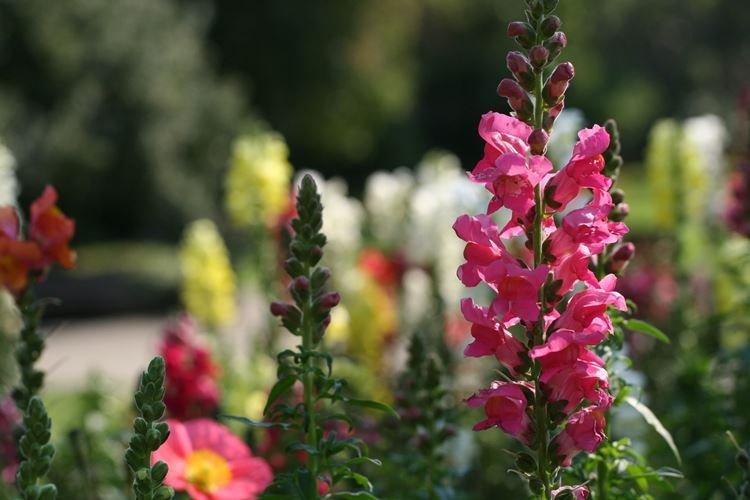
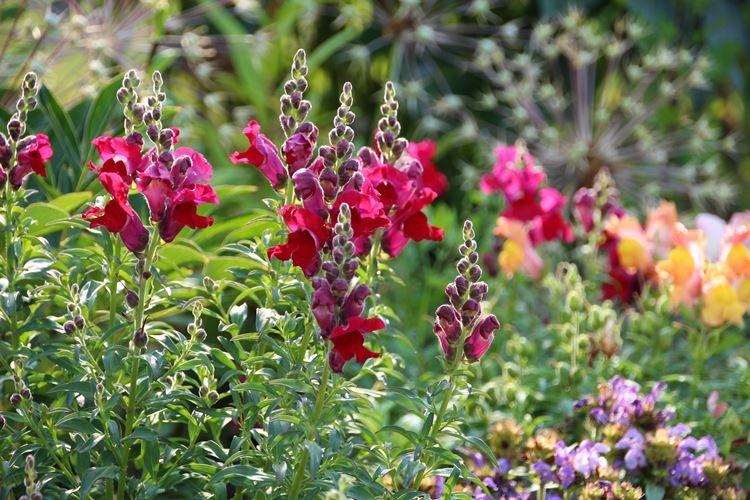
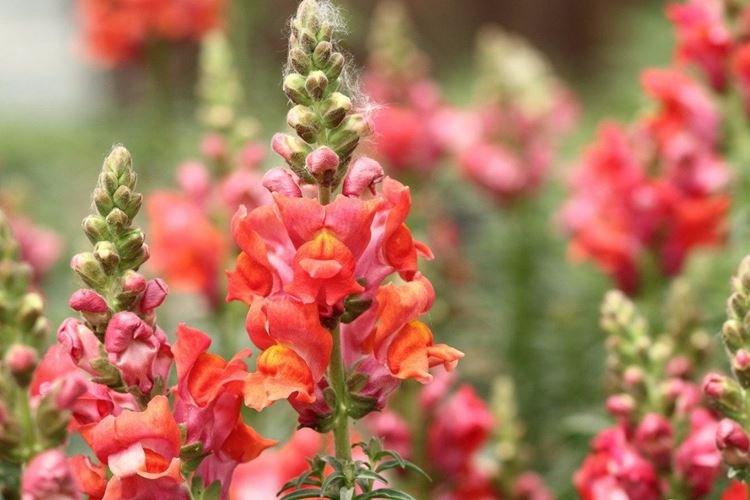
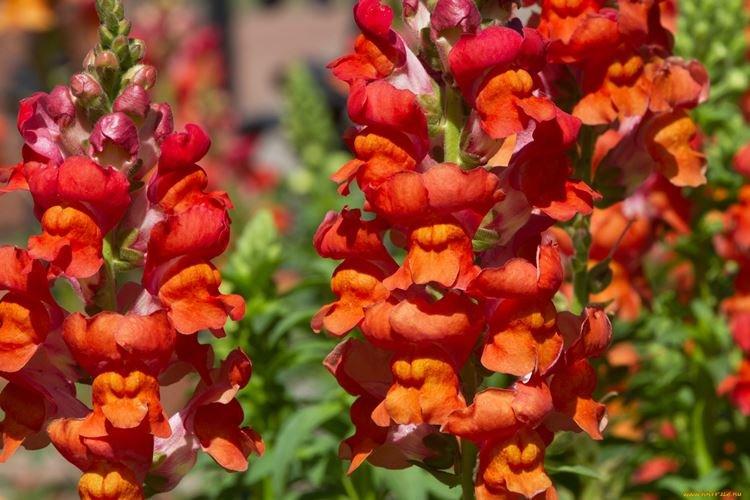
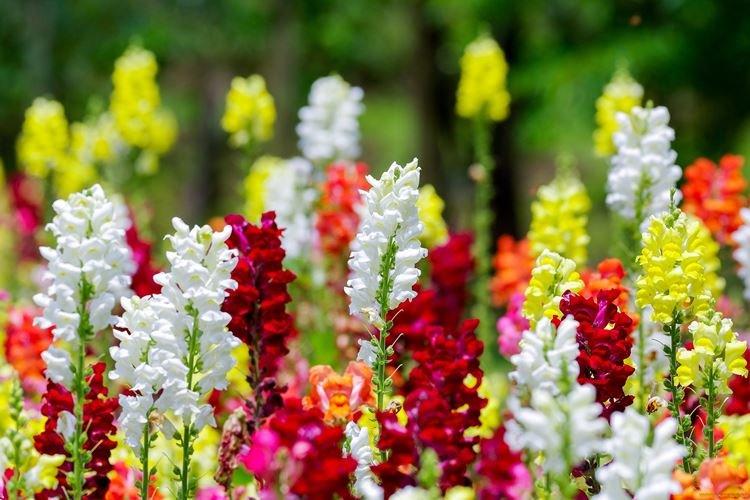
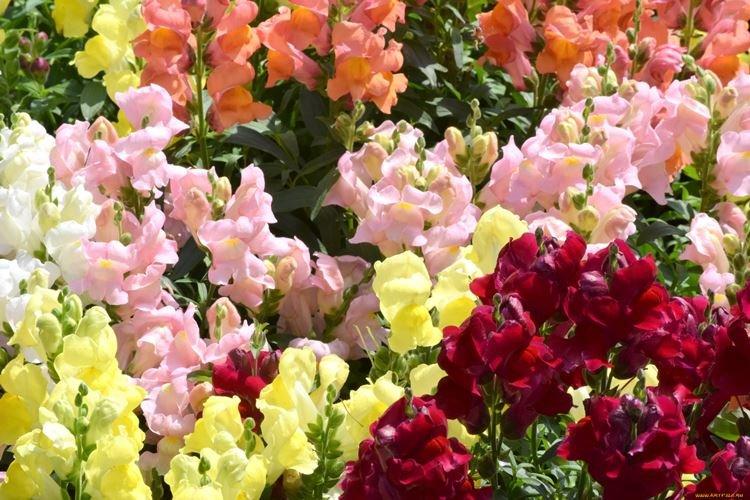
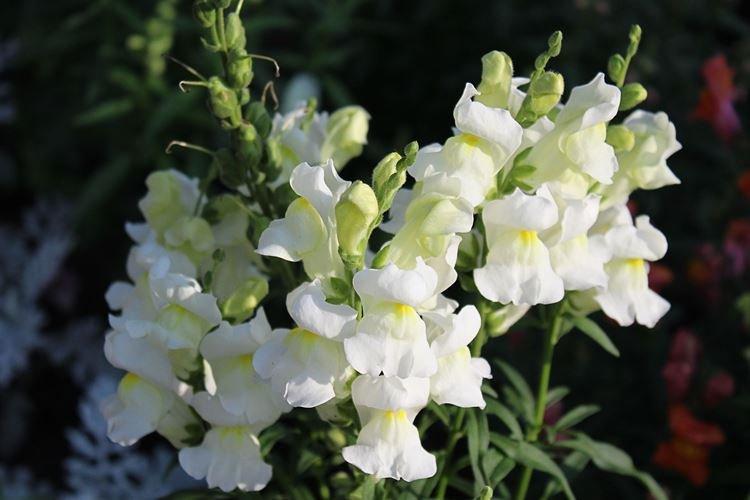
The history of this exotic flower is rooted in Greek myths. According to legend, it was his goddess Flora who gave Hercules for the victory over the Nemean lion. For their specific shape in different countries they are known as "dogs", "mouths", "nose" or "cleft palate." But it doesn't matter, what really matters is the unusual beauty of the snapdragon!
general information
It's hard to believe, but in nature, snapdragons belong to the herbaceous plantain family. This is a decorative perennial that came to us from warm latitudes, and especially from America. It has been cultivated in culture for more than five centuries, and professional selection began in the nineteenth century in Germany.
Now more than a thousand forms and varieties of snapdragons have been bred, but most often "in the face" they immediately recognize one - the Great antirrinum. Among them there are completely herbaceous species or branched dwarf shrubs. Large fragrant flowers in inflorescences-ears are notable for an irregular two-lipped shape.
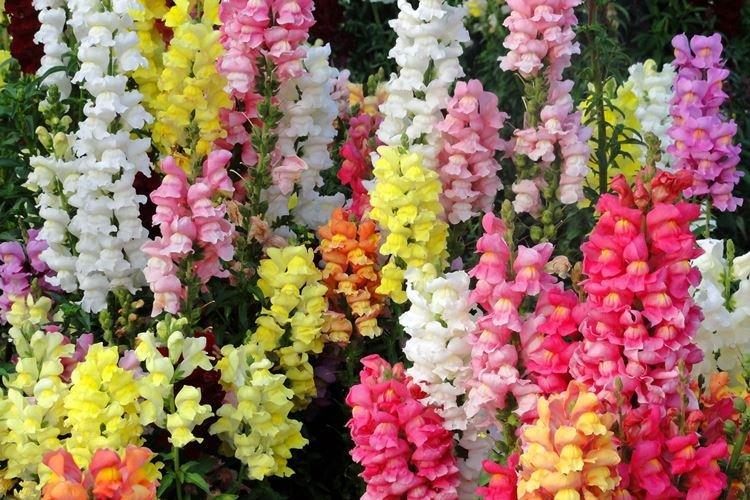

Snapdragon species
In modern gardening, snapdragons are very diverse, so connoisseurs use several common classifications. For example, by flower shape, size, color and other criteria. Snapdragon colors can be almost anything, and there are even two- or three-color varieties.
Snapdragon giant
These are large decorative varieties that are most often grown for cut flowers and decoration. The stems stretch up to 130 cm, but they are not too branchy. They are crowned with large smooth or double flowers in dense voluminous inflorescences.
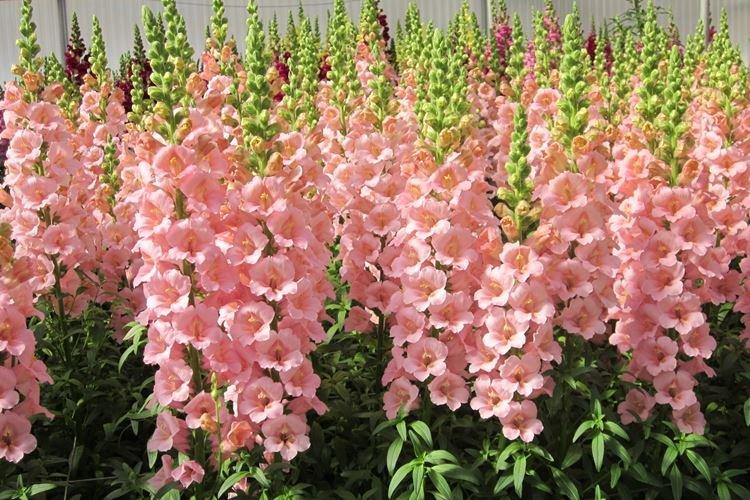

Snapdragon tall
The tall throats are not as long as the giant ones, but otherwise they practically do not differ from them. The height of the stems reaches 90 cm, and they are planted solo or in multi-tiered compositions. At the end of summer, the tall snapdragon is densely covered with large, lush inflorescences.
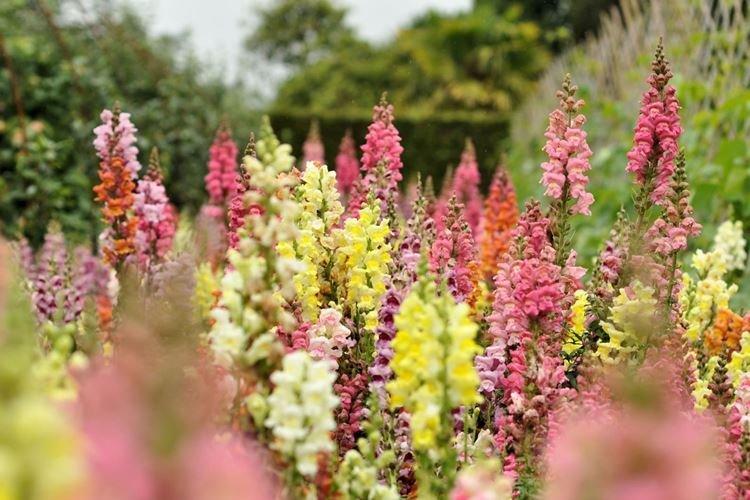

Snapdragon medium
This is a kind of intermediate option, which is considered the most versatile in horticulture. The stems grow up to 60 cm, and unlike their tall counterparts, they are much more branched. It is believed that this category contains the most varieties of snapdragons with different flowering periods.

Snapdragon undersized
Low varieties grow up to only 40 cm and are more like small voluminous bushes due to branching in several rows. They have lush foliage and the same lush multi-colored inflorescences. According to the flowering period, low varieties are divided into early and medium ones.

Snapdragon dwarf
Dwarf varieties of snapdragons up to 15-20 cm are very small and practically do not look like their giant ancestors. Bushes are dense and branched, with short and densely growing stems. The inflorescences are also small, compact, but very bright and graceful.

Snapdragon care
Snapdragon can be annual or perennial, but in mid-latitudes, even perennials are more often planted for one season. It is appreciated as a flower bed decoration and as a very effective border decor. Ample forms decorate terraces, balconies or large open-air galleries.
Temperature
The ideal conditions for lush flowering are warm summers with temperatures around 20-25 degrees. Snapdragon easily tolerates heat, but also copes with minor frosts. He is not afraid of night frosts down to -3 - -5 degrees.

Lighting
Snapdragon seedlings thrive in full sun and light shade. Therefore, the flower is so often used in flower beds, in mixboards and complex landscape compositions. The main thing is to choose an area without strong wind and drafts, or take care of shelter.
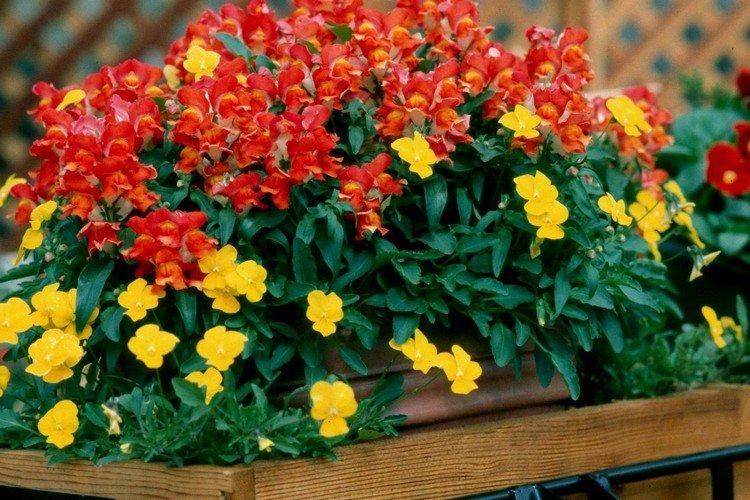

Watering
Snapdragon is very fond of water, but does not tolerate high humidity. Therefore, it is better to water it rarely, but abundantly, so that the earth does not remain constantly damp.Otherwise, it is fraught with a black leg and other putrefactive diseases, and it is almost impossible to save a flower rotting from the rhizome.
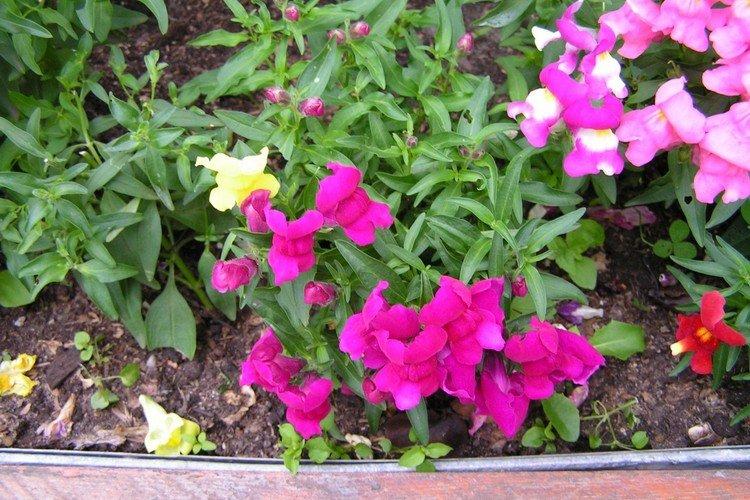

The soil
You definitely need nutritious soil, because snapdragons grow quickly and densely. To ensure healthy conditions, choose light soil or loosen it with sand and peat. You can add compost, but be sure to watch the acidity.
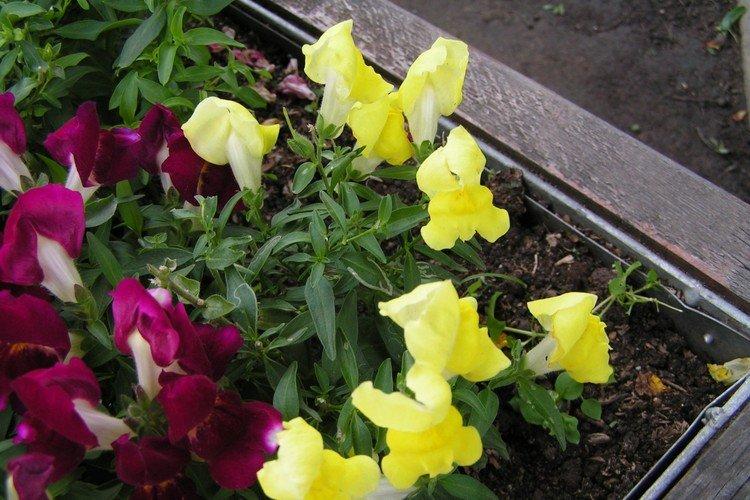

Fertilizers and feeding
Wait for the snapdragon to adapt after planting in the ground, and feed it with a mullein with nitrophosphate. And after the first buds have set, add urea and potassium. Be sure to monitor the calcium and magnesium levels in the formulations. For the rest, it is necessary to feed the seedlings only if it clearly demonstrates a deficiency of certain substances.
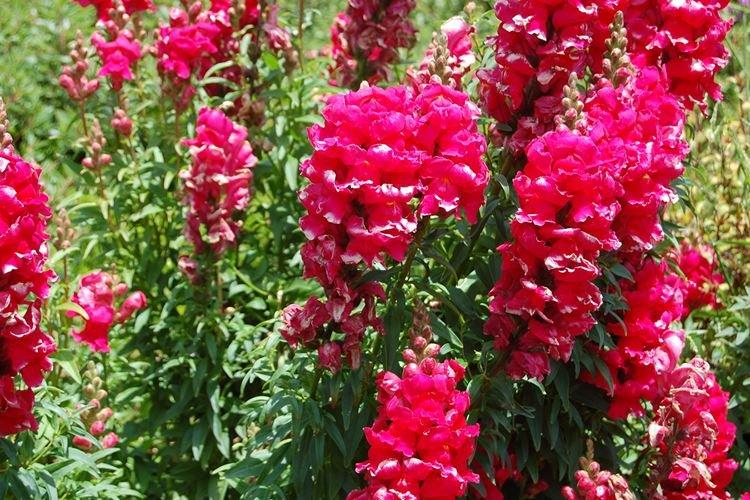

Transplant and reproduction
In warm regions, snapdragon seeds can be safely sown directly into the ground, and they rise in literally three weeks. If you are worried, first grow seedlings in containers or pots with a diameter of 10 cm or more. Sow seeds into compost soil in early March, spray with a spray bottle and germinate under glass.
At first, seedlings grow very slowly and require regular morning watering until the first leaves. After picking, you can teach them to outdoor conditions. By the end of spring, transplant the snapdragon into a plot and well of fields. Plant tall ones with an interval of about half a meter, medium - 30 cm, low - 20, and completely dwarf - 10-15 cm.
Snapdragon propagates well by cuttings, even dwarf varieties. Cut off young healthy twigs after winter and root them in dry sand. In the first year, it is better to leave perennial varieties to winter indoors, and only then - to plant them in the ground in a permanent place.

Pruning
Perennial varieties after flowering and closer to cold snaps should be cut as short as possible, leaving literally 5-7 cm of the stem. Then fill it with mulch - this way the root system will survive the winter better. Annual varieties should be pruned immediately to avoid self-seeding throughout the site.

Pest and disease control
The main pests of snapdragons are spider mites and aphids, which must be controlled with insecticides. Slugs will first have to be collected mechanically. The most difficult thing is to deal with nematodes, so the main thing is seasonal prevention and spring spraying.
Whitish areas on the leaves are a symptom of powdery mildew, and light reddish pads are rust. These are fungal diseases that need to be urgently dealt with with fungicides. To avoid brown or root rot, stick to a watering regime and try not to overmoisten the flower.

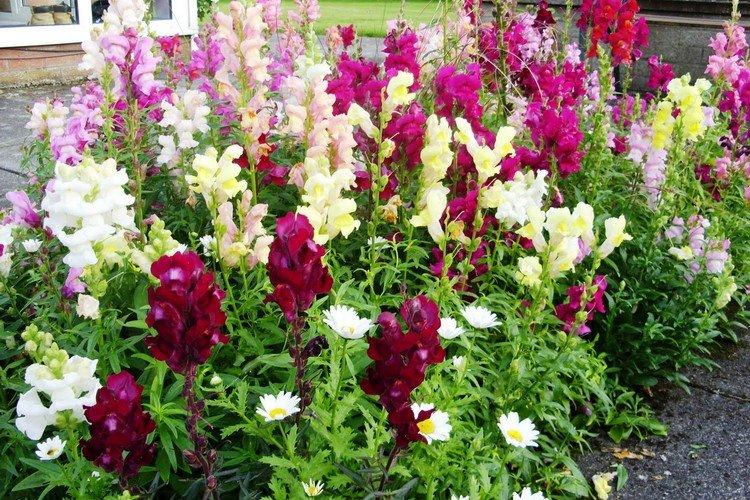
Snapdragon - photo
Snapdragon is equally good in flower beds, at curbs, along fences and in landscape compositions. We are ready to prove it in practice - that's why we have collected a large collection of photos!