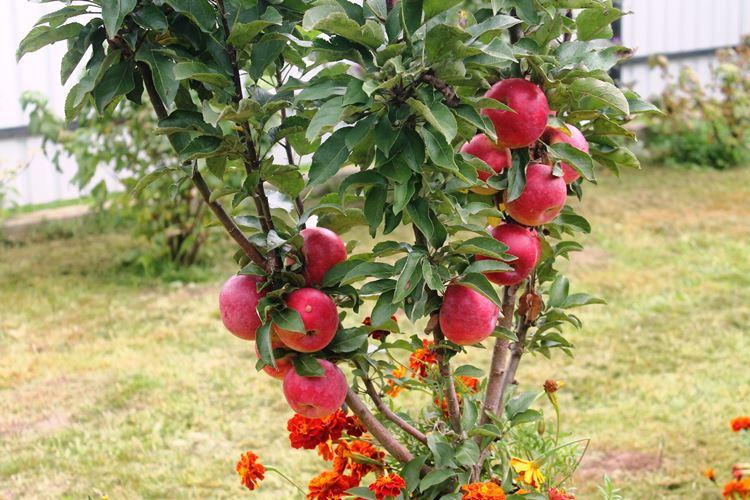
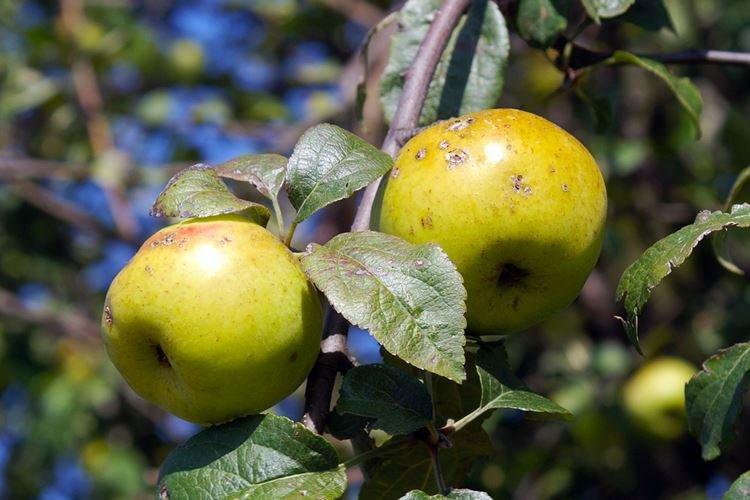
If there is not enough space in the garden, but you still dream of juicy and fragrant apples, there is a way out! Columnar apple trees are good because they have almost no side branches. Although they do not look very convincing and sometimes eccentric - as a result, you will get a good bountiful harvest. The main thing is to choose varieties and provide proper care!
general description
In the sixties, gardeners and breeders closely tackled the issue of optimizing areas and resources. I wanted the fruit trees to be smaller, and the harvest from them - more. During the experiments, it was possible to get an unusual mutated branch, which was then propagated into modern varieties. The first samples were received in the mid-seventies in the English county of Kent.
There is a gene that scientists have nicknamed the Co gene. He is responsible for the fact that the branches of plants grow at an acute angle almost along the trunk. Outwardly, such apple trees resemble a poplar a little, until they are densely covered with harvest. Dwarf varieties branch out half the size of the medium-sized ones and 4 times less than the tall ones.
Sometimes columnar apple trees are also called pyramidal, but this does not change the essence. The tree grows in the form of a rather narrow column up to 2.5 m - and this is completely without pruning! This is an ideal choice for owners of small areas, because the spreading crown will not take up space and shade other plants.
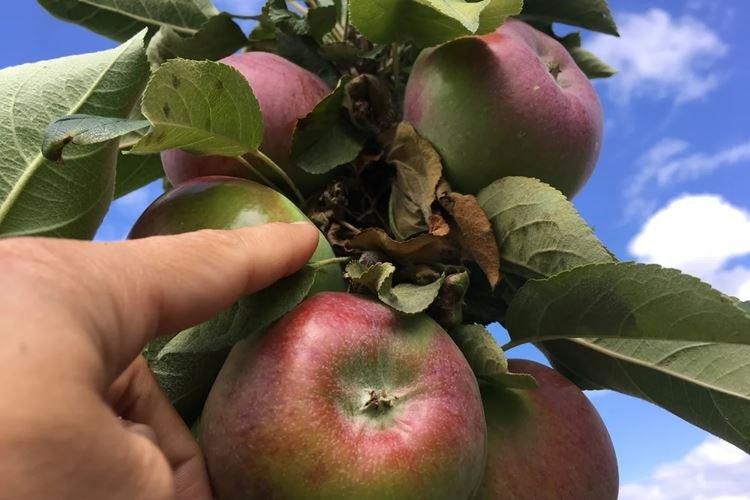

Columnar apple varieties
There are dozens of varieties with different characteristics, so there is no single recommendation for choosing. Pay attention to the size and properties of the fruit, ripening time, frost and disease resistance.
Nectar
A miniature early-growing variety with a crown diameter of up to 25 cm is notable for a rich harvest. Medoc is prized for its amazing resistance to frost down to -42 degrees.
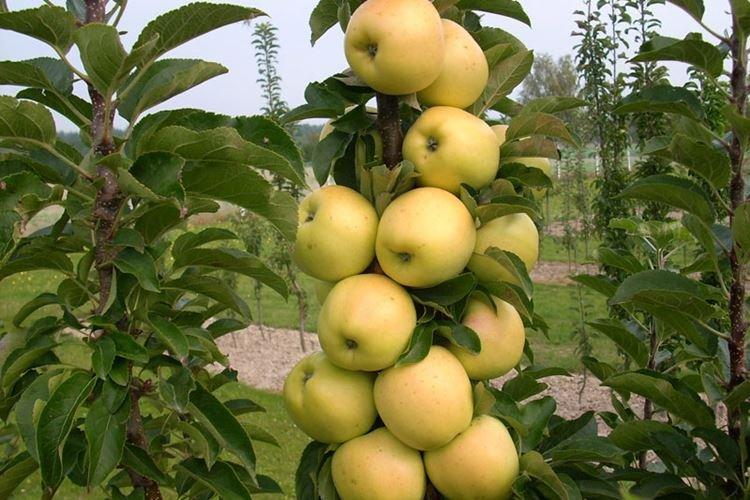

Senator
The main advantage of the variety is resistance to frost, drought, rain and other weather conditions. Fruits of an unusual speckled hue become almost black when fully ripe.

Baby
The dwarf dessert variety is one of the most compact, and produces the same small yellow-orange fruits. Well suited for the southern regions, because with an average frost resistance, it has a very high resistance to heat and sunburn.

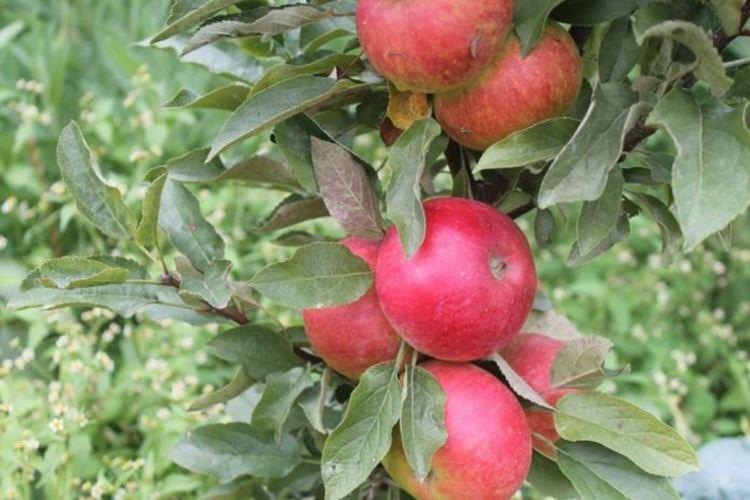
Gin
It is a dwarf autumn cultivar of a columnar apple with a maximum height of 2 m with medium-sized rounded sweet and sour fruits. Apples ripen by September, and yield rises to 15 kg with age.

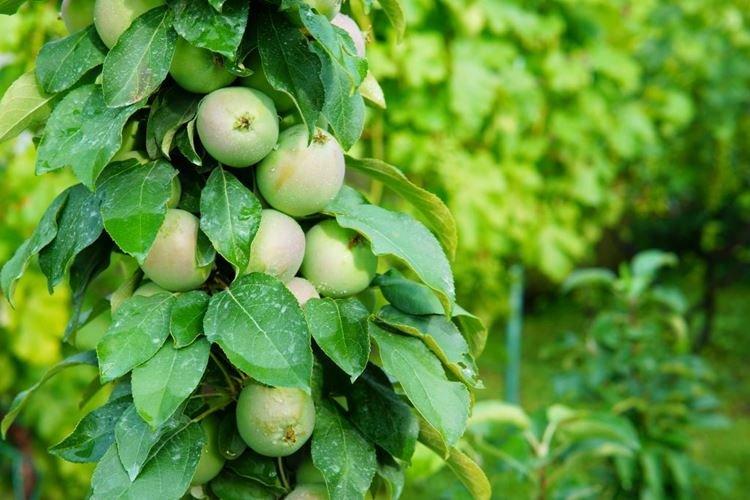
Iksha
A very tasty winter-hardy summer variety with small juicy fruits. But at the same time, it requires protection from scab and is quite capricious in content.

The president
An excellent summer variety for the middle lane, resistant to diseases and fungi. Sweet and sour fruits densely cover the entire crown almost from the very ground.

Currency
Winter variety for the middle band with sweet, slightly sour fruits in the aftertaste. The trees are resistant to frost and scab, and also very decorative, because the leaves remain green almost until the end of autumn.

Dialog
A fairly young variety with small yellow fruits with a rich sweet and sour taste. A pleasant feature is an extended ripening, which allows you to enjoy the harvest for a long time directly from the tree.

Ostankino
The compact high-yielding variety grows up to 2.5 m and produces up to 16 kg of fruit per season. Ripe fruits are kept in perfect condition until almost mid-winter.

Vasyugan
A medium-sized summer variety with sweet dessert fruits and a pronounced aroma. Frost-resistant apple trees winter at temperatures down to -40 degrees, so they are suitable for the Far East and the Urals.

Chervonets
Autumn dessert variety pleases with a rich harvest of large sweet apples with creamy pulp. Despite the low frost resistance, trees recover quickly.

Triumph
A very sweet, almost candy variety, ripens by autumn and gives a good harvest in the second year. Due to its mediocre winter hardiness, it needs shelter, but it is very resistant to scab and other diseases.

Moscow necklace
A compact, frost-resistant variety with very narrow medium-sized trees - up to 3 m. It needs pollinators and preventive spraying, but it yields a harvest already in the first year.

Caring for a columnar apple tree
In order for a tree to bear fruit safely for 15-20 years and not cause trouble, it must be properly looked after. Regardless of the variety, the general principles remain the same.
Seat selection
Columnar apple trees are very fond of the sun, so choose a bright sunny area for planting. But a thin tall tree is sensitive to strong gusts of wind, so we advise you to take care of protection in advance.

Watering
In summer, water young trees every 2-3 days, and adults every 3-4. But gradually reduce the frequency so that by August completely stop watering and the tree has time to finish growing in time before winter. To better retain moisture, mulch the trunk circle or plant siderates.

The soil
Apple trees need nutritious soil with groundwater at a depth of at least 2 meters. In too dense ground, make a drainage substrate of rubble and sand. In advance, the soil was degraded with dolomite flour, add several buckets of compost and 100 g of superphosphates with potassium each.

Top dressing and fertilizers
One small tree is densely covered with flowers, and then the harvest, so it needs a lot of fertilizers. Top dressing is applied throughout the season, supplementing organic matter with mineral nitrogen. Before the buds open, spraying is used, and at the beginning of summer, foliar top dressing with urea is used. From August, give up organic matter in favor of complex fertilizers and potassium.

Reproduction
It is most convenient to propagate columnar apple trees by grafting a varietal cuttings. Seeds are too long and ineffective, but air layering does an excellent job. To do this, at the beginning of spring, choose a suitable branch, make a 5 mm ring cut, treat with a stimulant and wrap it with wet peat, and then with a film. By the fall, you will receive the roots, and the layers can be separated.
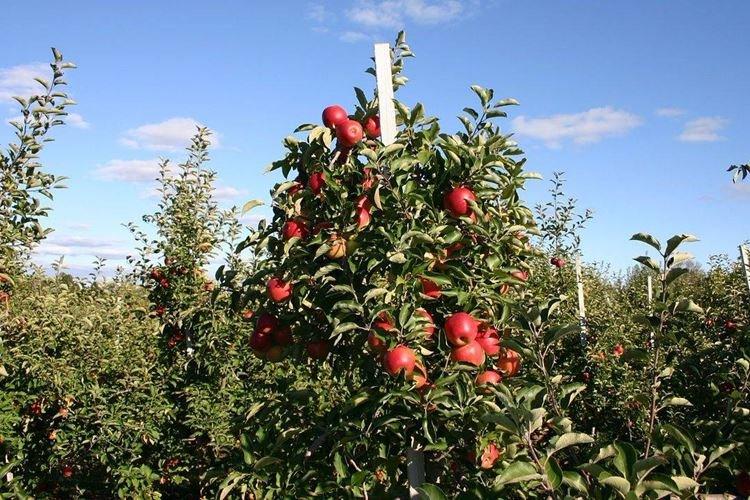

Wintering
To make the columnar apple tree survive the winter painlessly, choose varieties adapted to your region. Southern trees will not withstand severe spring and autumn frosts, therefore winter hardiness is a very important property.
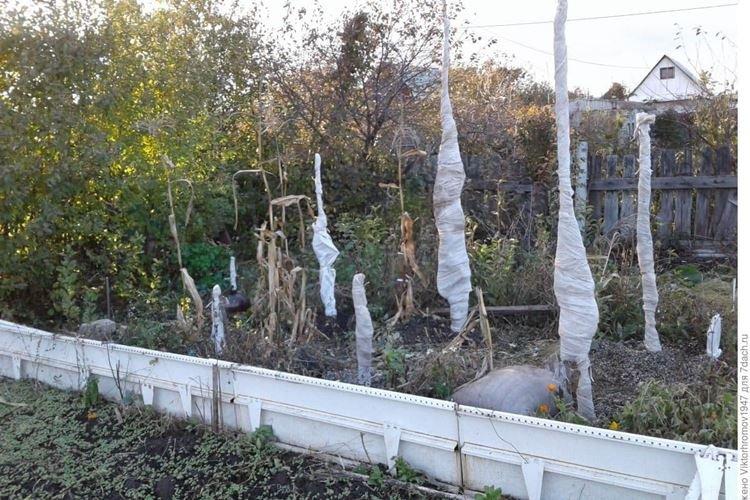
In addition, for the first 4 years, it is recommended to cover the top with a dense breathable material so that it does not freeze. Cover the stems with dry spruce branches or wood shavings, and as the snow falls, carry out hilling.

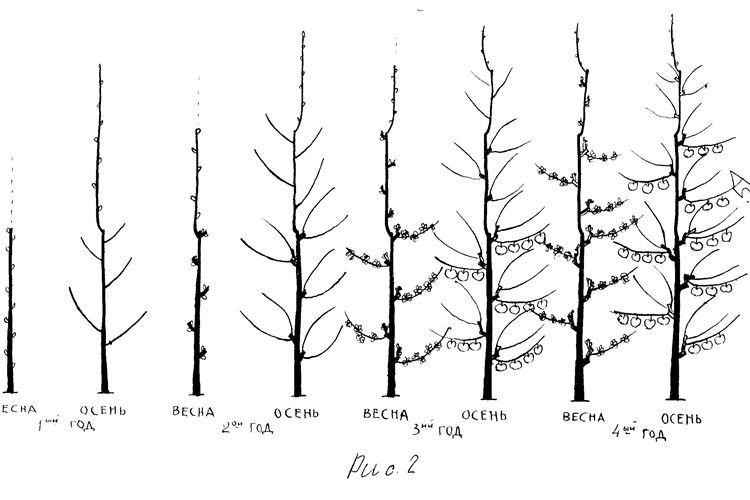
Pruning
After 2 years, we recommend regularly cutting off all protruding branches, controlling the growth of side shoots and thinning out dense thickets. The main thing is not to touch the base of the apple tree, because if you damage the growth point, the tree will try to compensate for this on its own and will begin to intensively grow branches.
Planting a columnar apple tree
Gardeners disagree on when it is best to plant columnar apple seedlings. This is either early spring, before the buds open, or warm autumn days at the end of September. One-year-old seedlings take root easier, but container apple trees can be planted even in summer.
Plant columnar apple trees in rows with a pitch of 50 cm and a row spacing of 100 cm. Pits approximately 1x1x1 m should be prepared a couple of weeks before planting. When planting, the root collar must be above the soil level.
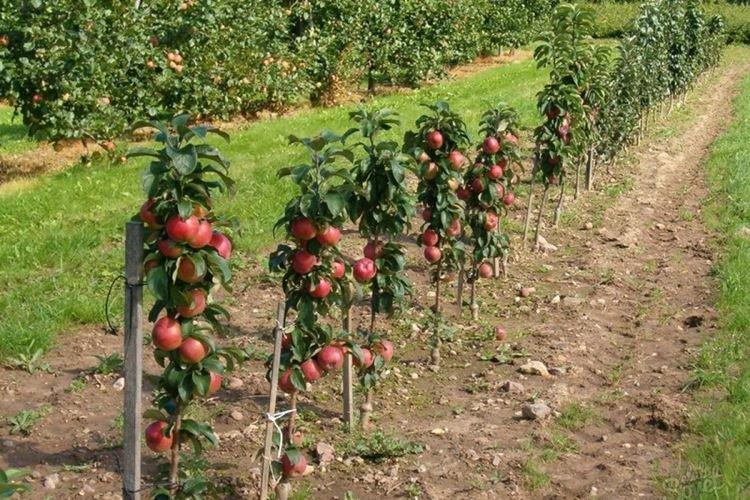

Mix the top layer of soil with humus, pour it into the hole in an even layer and let it tamp. After that, form an earthen slide on the surface and spread the rhizome of the apple tree over it. Sprinkle on top and compact the tree with the lower infertile soil and form a near-trunk circle at a distance of about 30 cm, and then - abundantly fields.
In the first season, it is better to pick off the flowers of the apple tree - it will still not bear fruit normally, but this prevents it from taking root.It is important to maintain the growth point for at least a couple of years so that the tree does not branch in the future. The first crop can be harvested for 2-3 years, and up to 6 years it will increase until it stabilizes.

Diseases and pests: how to fight
The main apple disease that can destroy crops is scab. After spring rains, its spores spread throughout the garden and in a matter of weeks infect trees. Dark spots with bloom appear on the leaves and fruits. To avoid scab, use fungicides and select varieties that are resistant to it.
Wedge-shaped apple trees are also susceptible to other typical garden diseases - rot, fungus, spots, cancer, powdery mildew. Fungal diseases are treated according to one principle - quickly remove all damaged areas and treat with fungicides. Viruses like mosaics are often incurable, so saving the rest of the trees is most important.
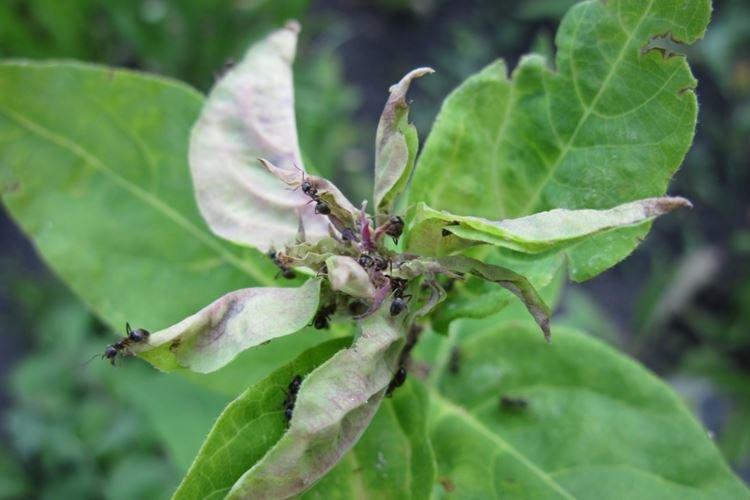

The most common problem with any apple harvest is the codling moth. Caterpillars eat up everything in their path and can destroy up to half of the crop. It is important to collect volunteers daily, dig up the soil prophylactically and carry out seasonal spraying.
The apple blossom beetle is a weevil that hides in the bark, and then its larvae eat the buds from the inside. Copperhead sucks juices from leaves and shoots, which is why the tree grows worse and loses its yield. Aphids hide on the back of deciduous plates and on the tops of the shoots. The most effective method in all these cases is specialized insecticides.