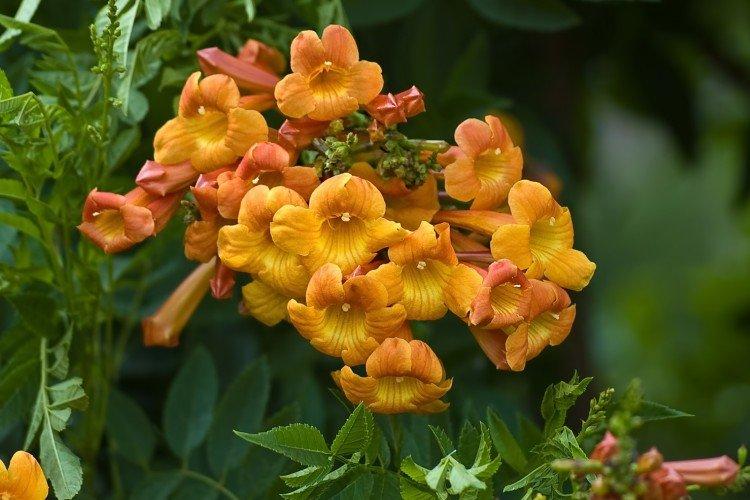
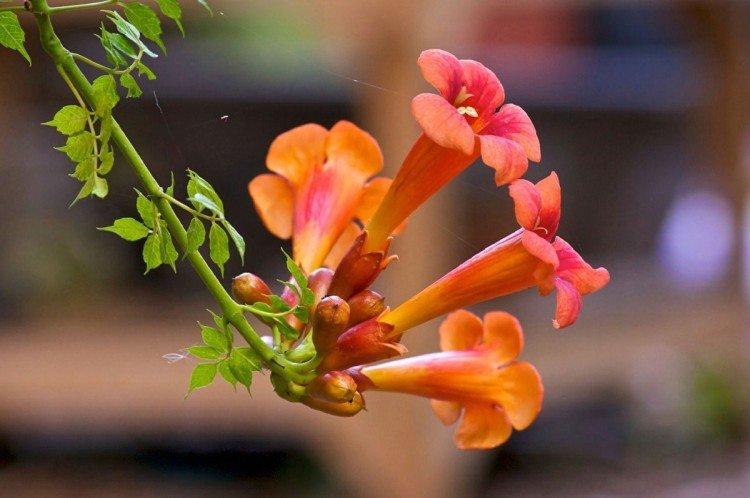
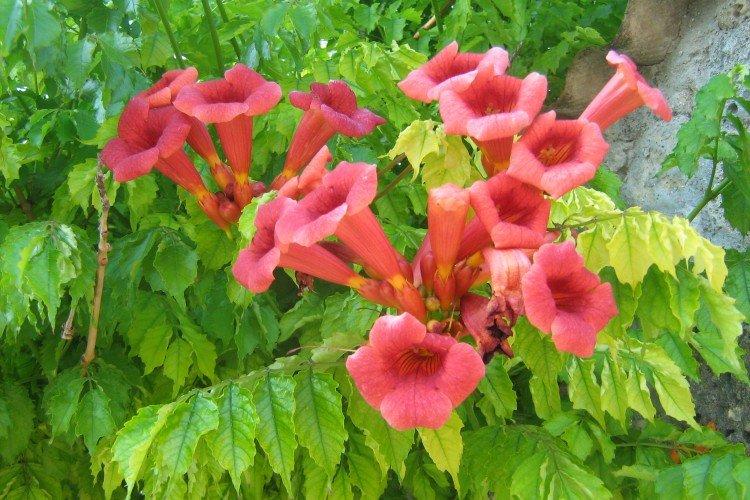
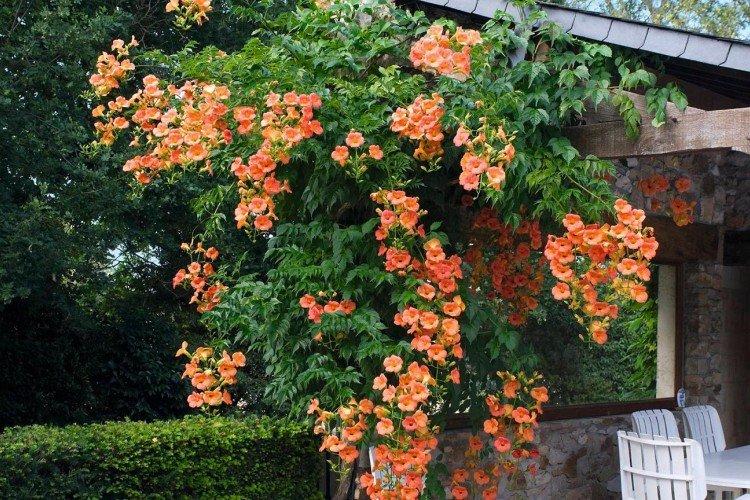
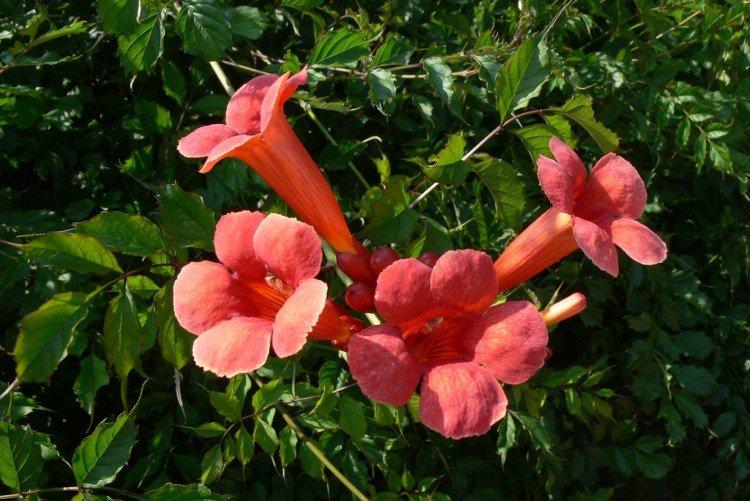
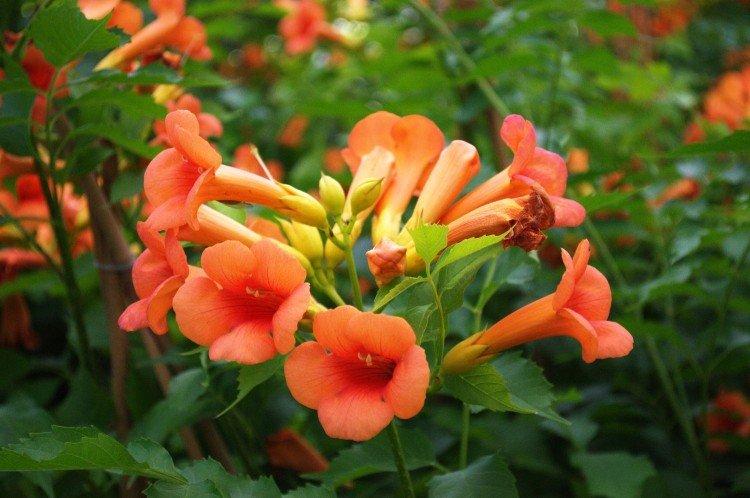
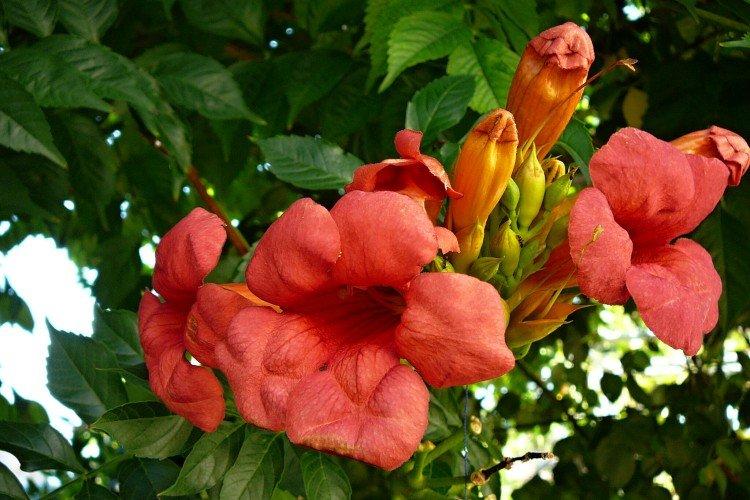
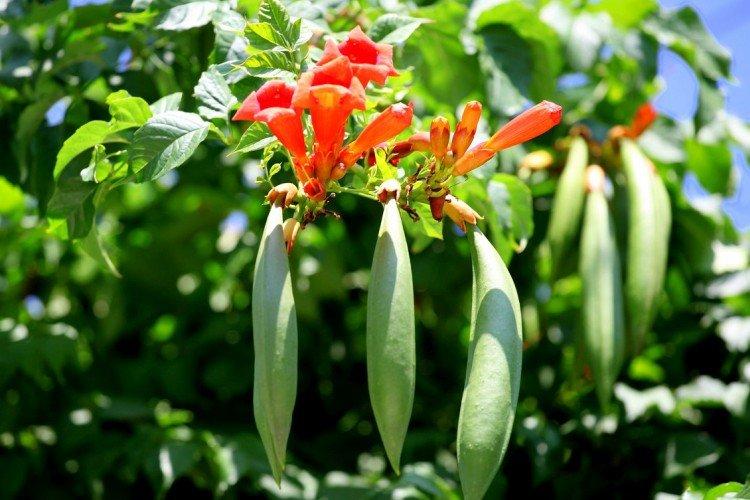
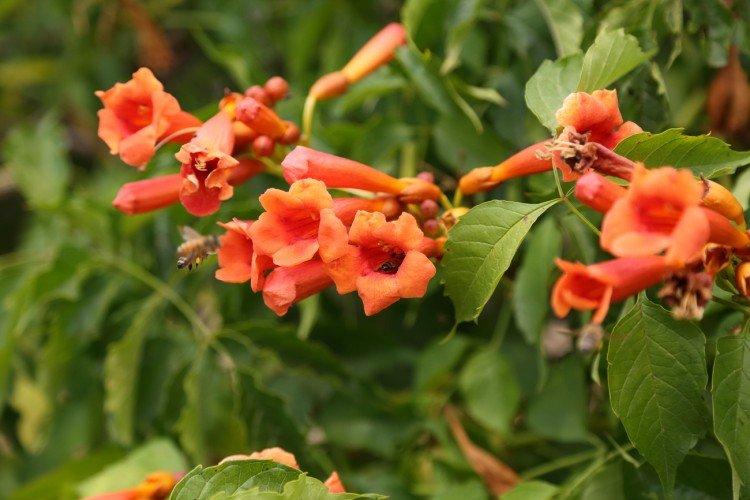
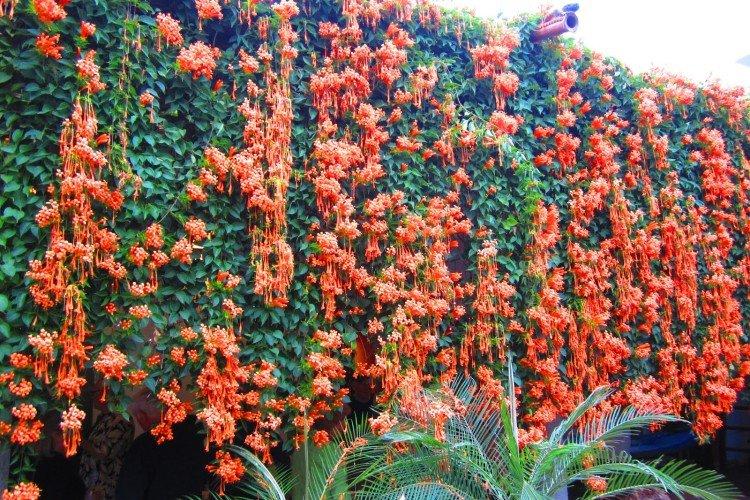
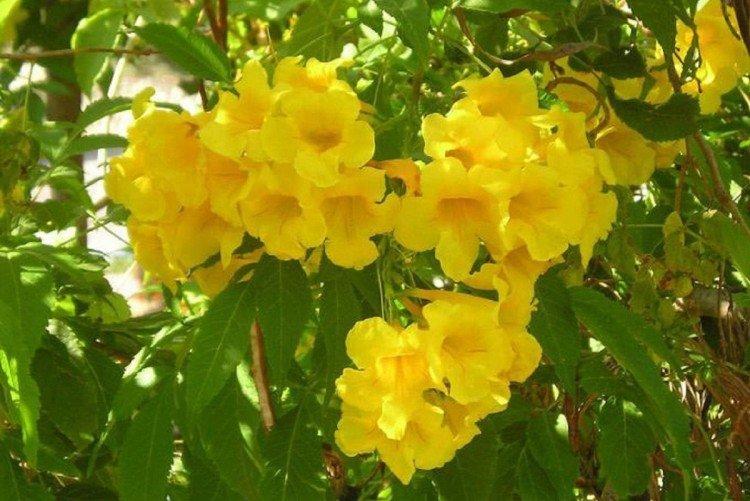
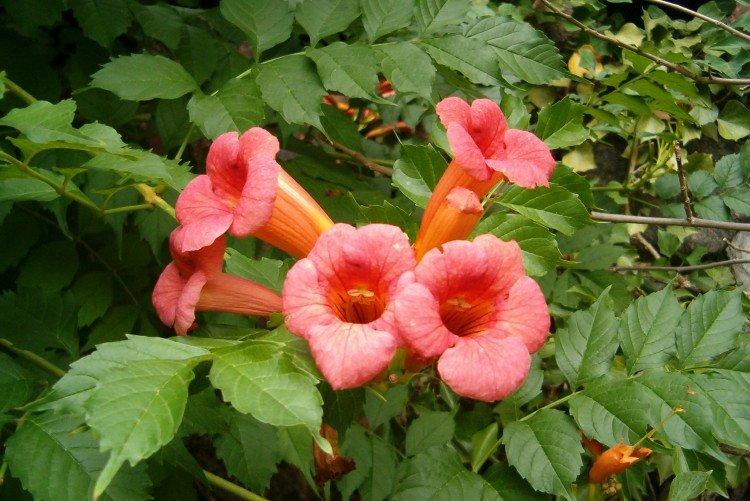
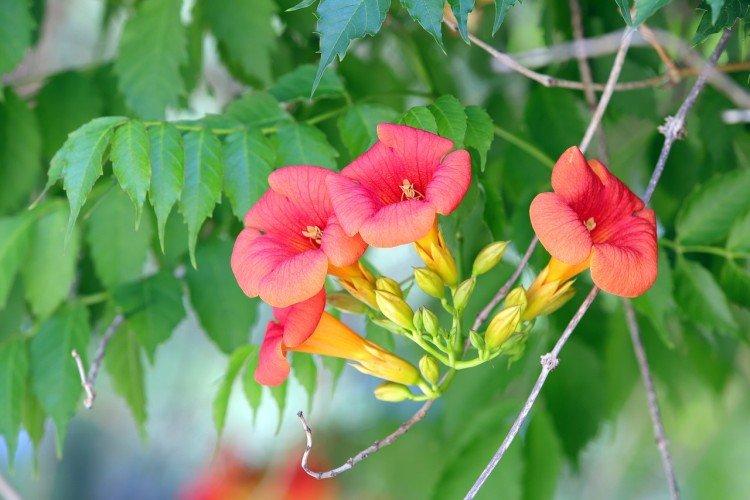
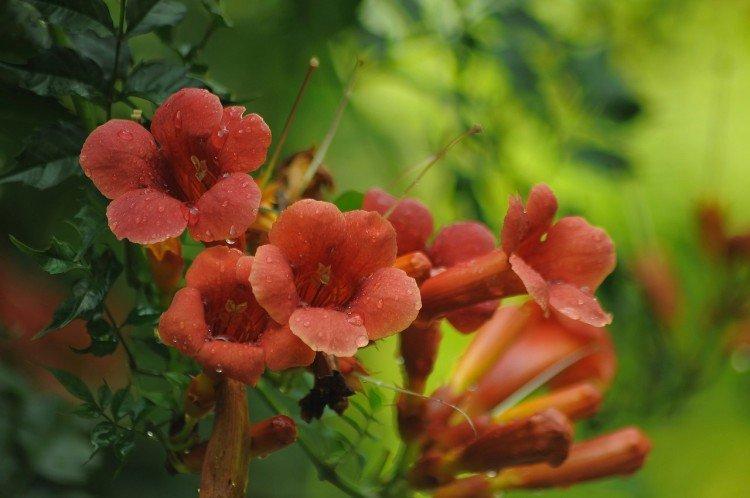
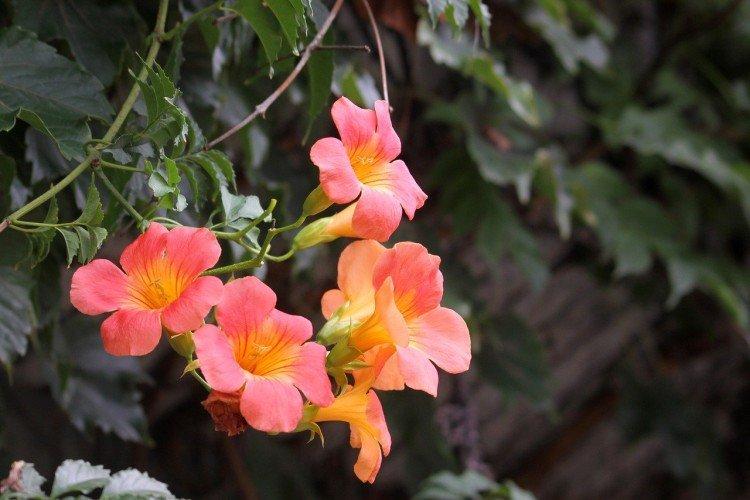
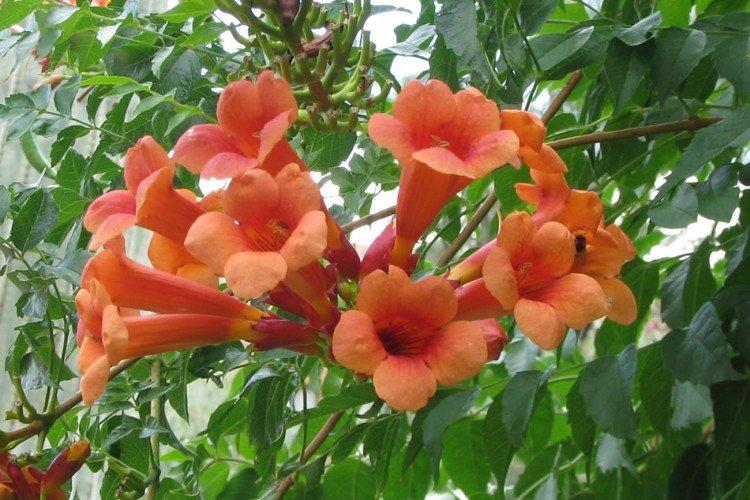
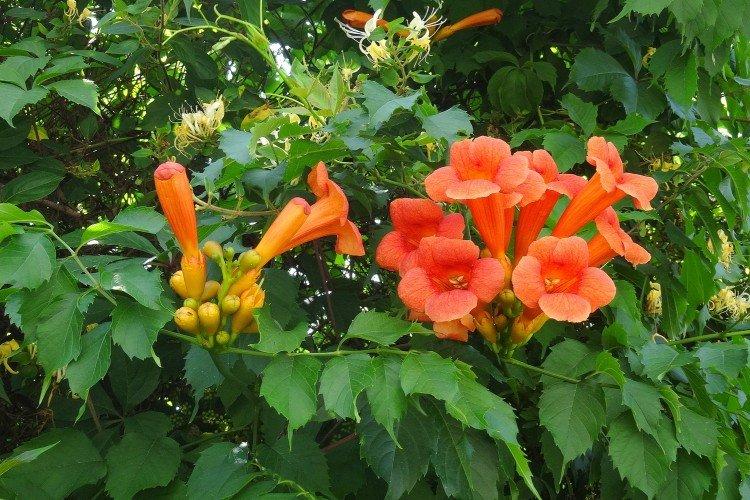
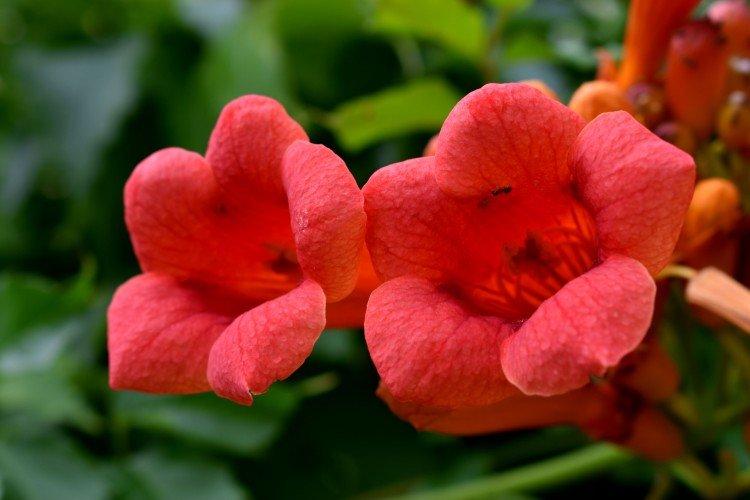
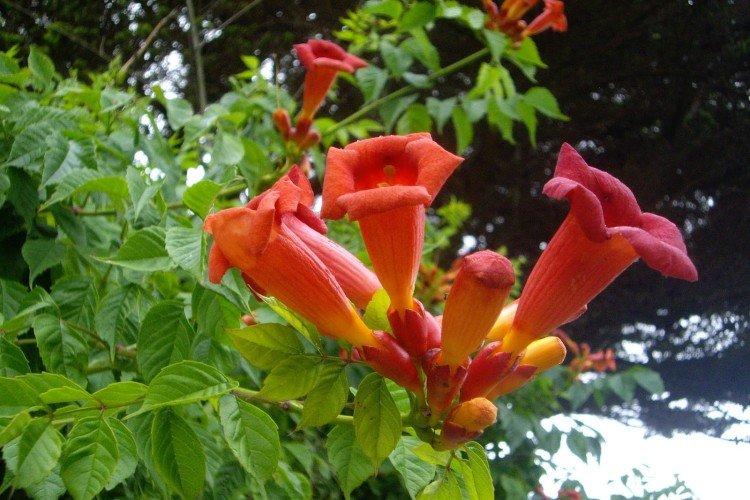
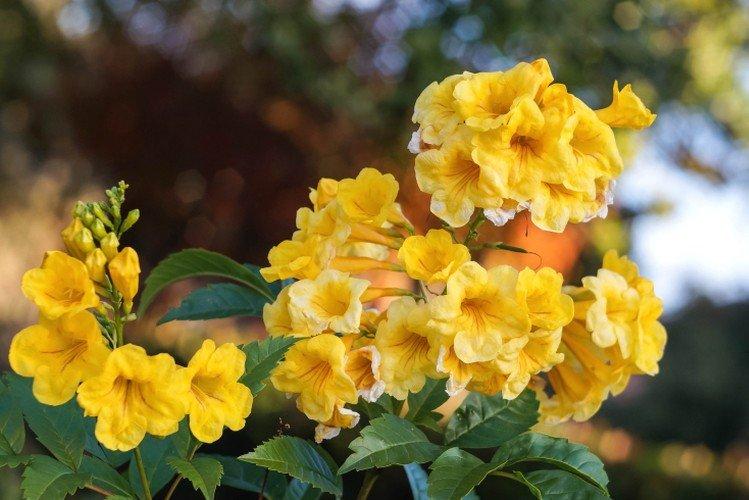
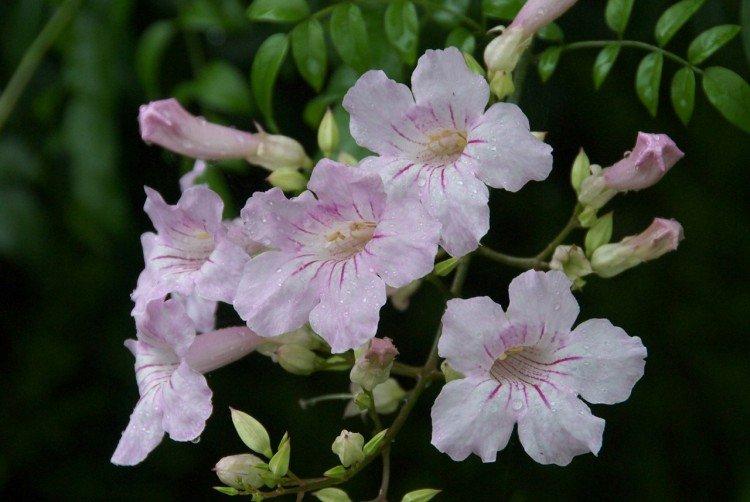
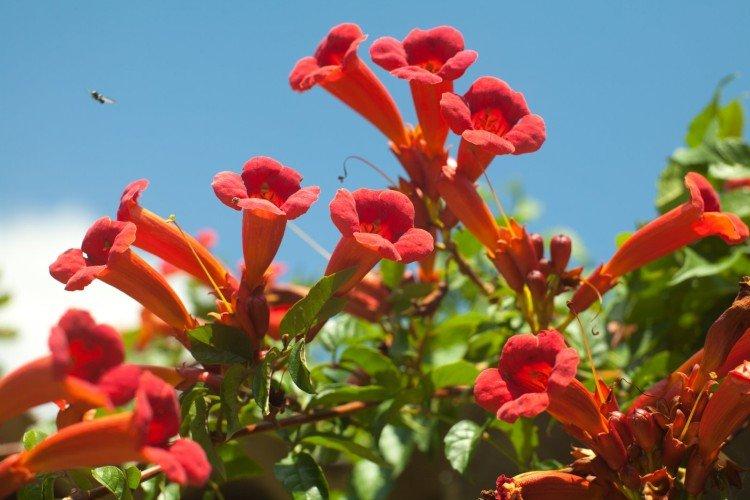
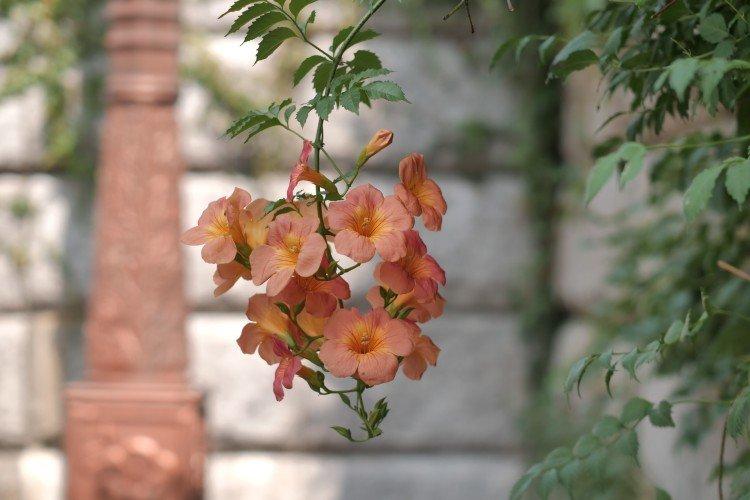
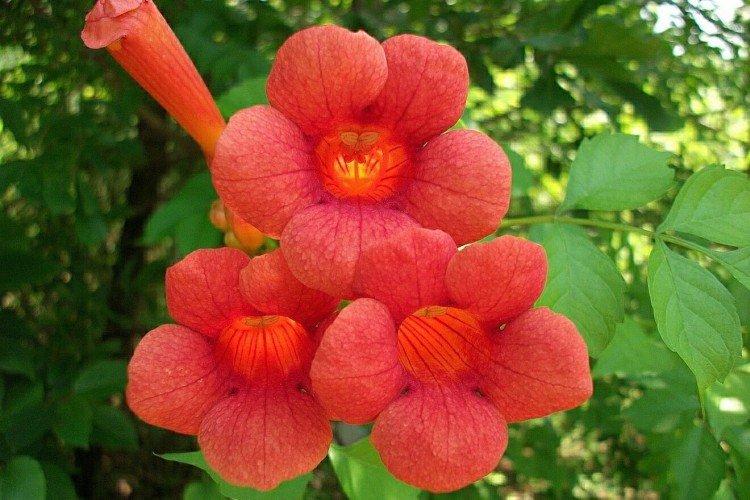
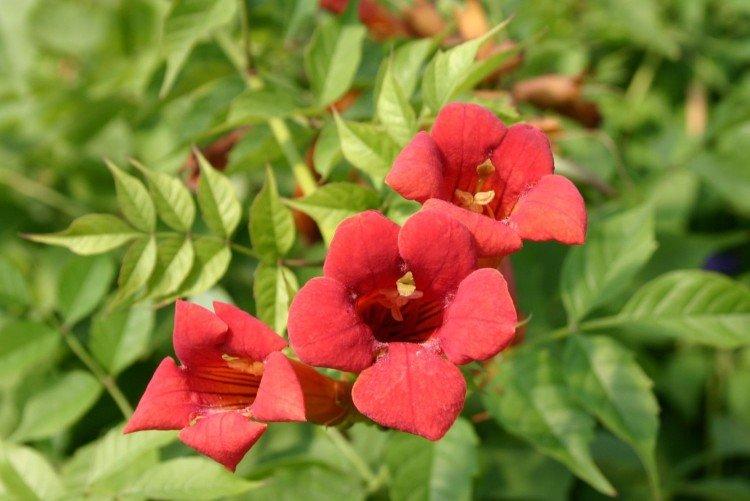
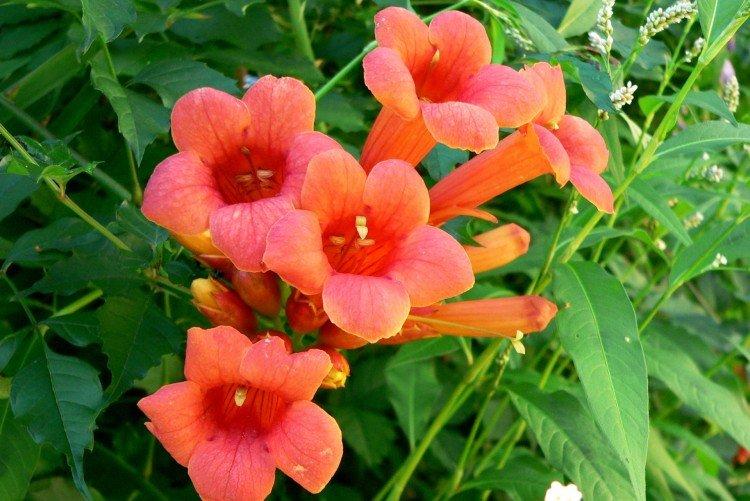
The fanciful Kampsis buds resemble elongated funnels or bells. They grow in lush clusters, and due to their special structure, they are very easy to distinguish from other garden flowers. And we will tell you about the other features of the plant further!
general information
In nature, Kampsis or Tekoma grows mainly in North America, and can stretch its shoots up to 15 m.In fact, it is an ornamental flowering vine, but individual varieties can be formed like standard trees.
Campsis is a large and vigorous plant with a powerful root system. Flexible shoots lignify with age and become covered with aerial roots. The leaves have a fancy serrated edge, and the flowers are red or orange. Kampsis blooms in June and continues to bloom until frost.
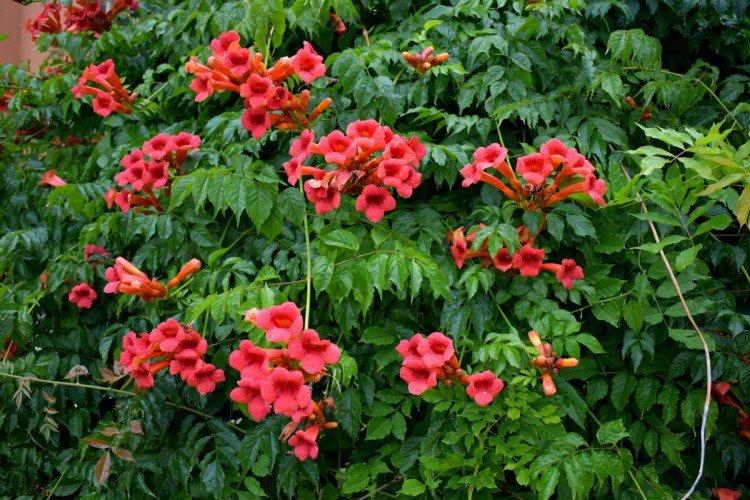

Kampsis types
Kampsis has only two main species, and another broad category bred by breeders. In gardens, the latter is most often found.
Rooting Kampsis
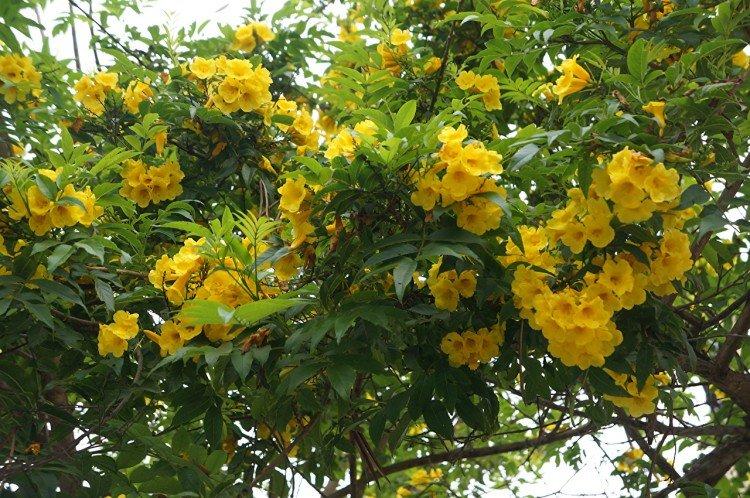
A strong and powerful rhizome, combined with strong shoots up to 9 m in length, allows it to grow on literally any surface. This species is distinguished by a variety of varieties, colors and even flowering periods. Tubular buds bloom up to 6 cm.
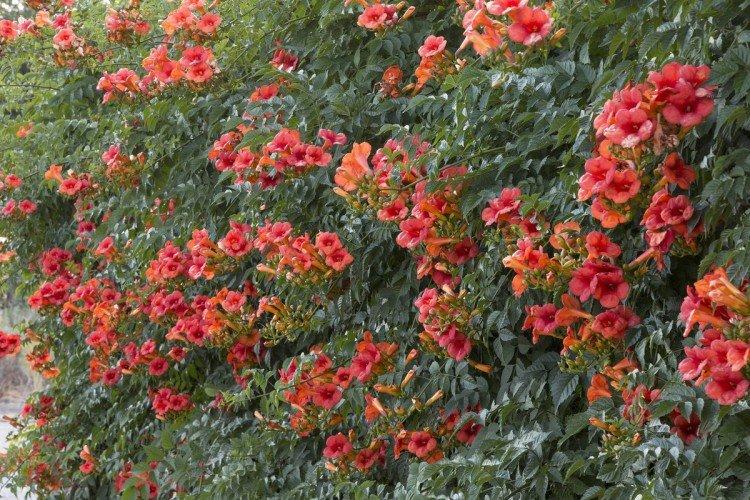

Large-flowered campsis
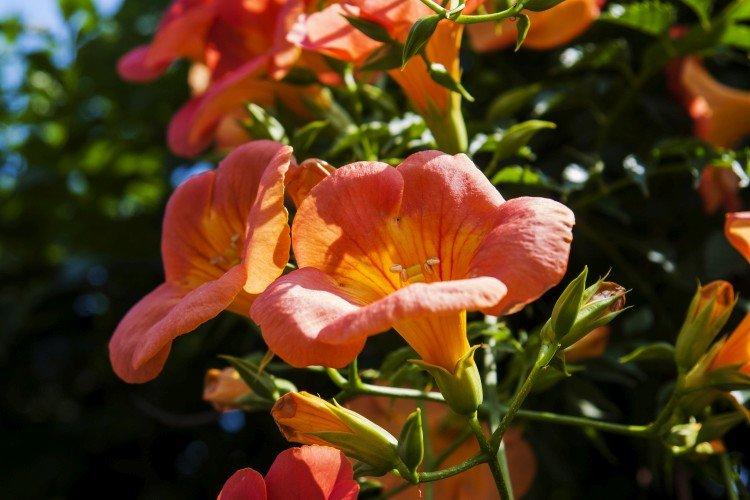
Its tall decorative flowers are collected in bright orange inflorescences. This is a flexible vine without aerial roots, so it only clings to the support with young shoots. The homeland of the large-flowered kampsis is China.

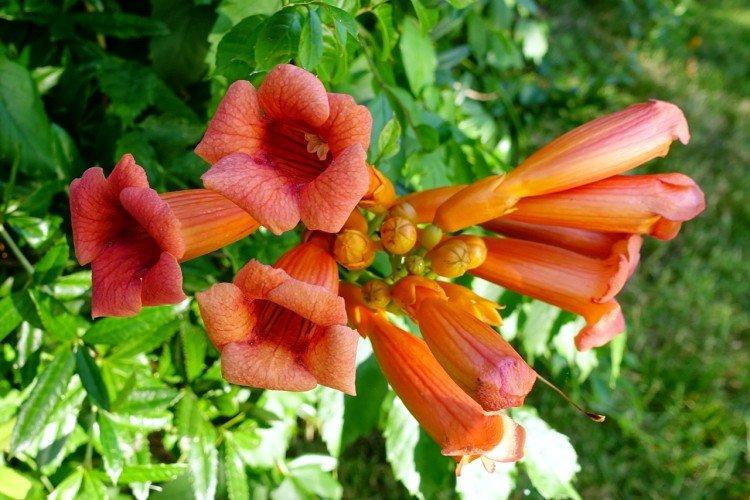
Hybrid campsis
The same diverse group of breeding hybrids that began to be artificially bred a century and a half ago. It combines the best properties of natural species - long flexible vines and large beautiful flowers.

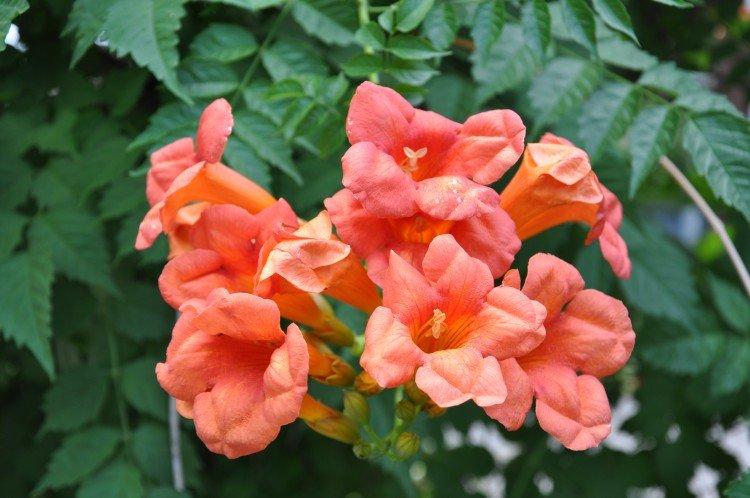
Kampsis care
The main problem of Kampsis is not how to grow it, but how to prevent it from taking over the entire garden. This is an aggressive vine, so pay special attention to pruning and shaping!
Temperature
Campsis feels great in the middle lane in the summer. In addition, it tolerates short-term frosts even down to -20 degrees. He is also not afraid of direct sunlight and heat. When wintering indoors, the liana needs a rest period at 5-10 degrees.

Lighting
Campsis definitely needs good lighting for both growth and flowering. Moreover, it should be uniform, so watch out not only for the amount of light, but also for the density of the vines. And thin it out in time.
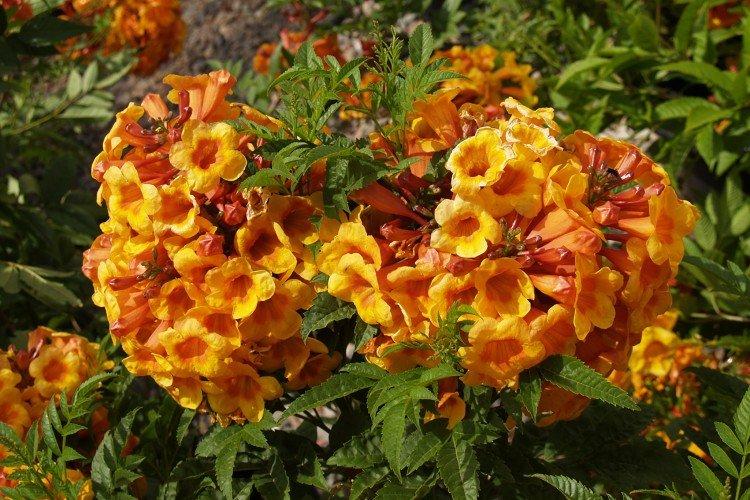

Watering
Campsis does not tolerate overdrying and waterlogging poorly, therefore, the regime is especially important in irrigation. It is better to water the plant often, but a little, and do not forget to gently loosen the ground after that. Mulching the soil or planting around small shrubs with similar requirements will be helpful.
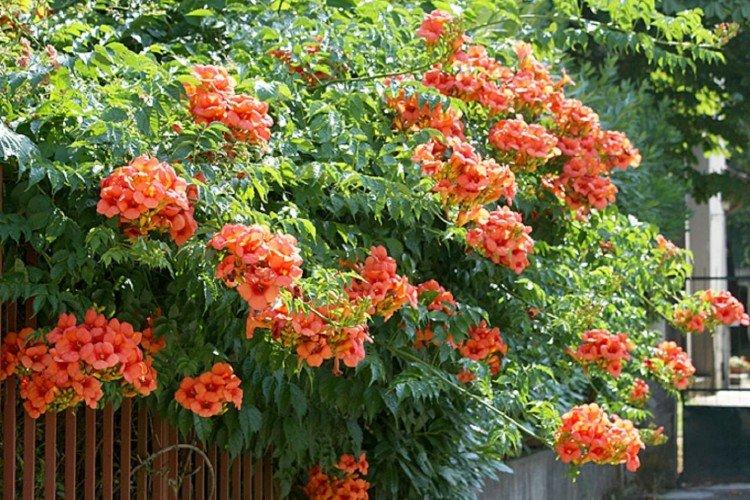

The soil
Campsis is able to grow in almost any soil from all possible. But still, for uniform growth and lush flowering, loose fertile soil is needed, preferably neutral or slightly acidic.
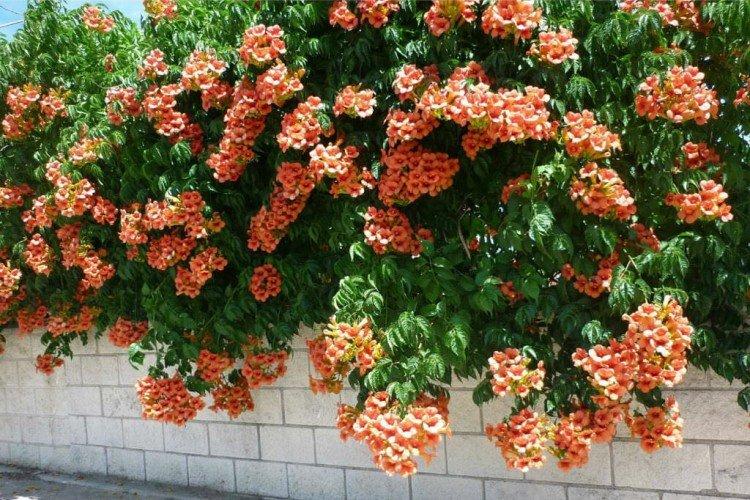

Fertilizers and feeding
For all the splendor and growth rate of Kampsis, it does not need constant feeding. Unless in poor soil, you can periodically add nitrogen for the deciduous mass and phosphorus to prolong flowering. We recommend using liquid fertilizers for watering and spraying.
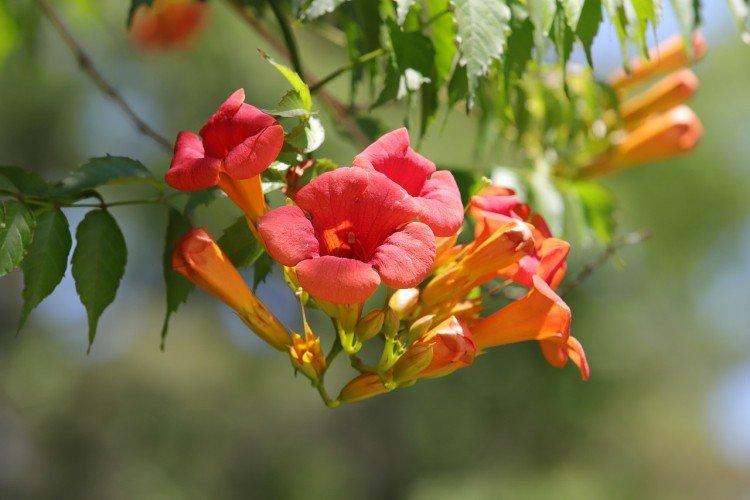

Pruning
Like all vines, Kampsis needs formative and sanitary pruning. Moreover, any time is suitable for a haircut - it is perfectly restored. But it is better to postpone radical pruning until the beginning of spring, before the buds open, and until autumn after flowering.
It is recommended to leave only the strongest lignified shoots annually, because Kampsis is rapidly growing young branches from scratch. The longest branches are shortened to 3-4 buds. It is also worth cutting out the oldest, most painful and growing shoots in the wrong direction.

Wintering
Campsis is a relatively winter-hardy perennial, but it needs shelter. Young plants are completely removed from the support, bent to the ground and covered with spruce branches and non-woven material. With adult specimens it is more difficult, because it is almost impossible to remove lignified branches from the trellis. In this case, you need to wrap them with special agrofibre, cover the bush with foil and insulate the roots.
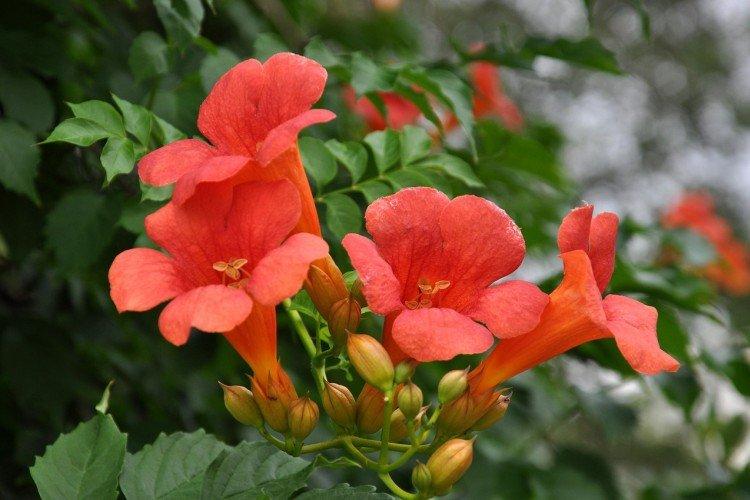

Planting and breeding
Campsis germinates quite easily from seeds, but this is too long, and it will begin to bloom in at least 6 years. Therefore, cuttings are more often used. At the beginning of summer, green shoots are cut into about 30 cm each, and at the beginning of spring - last year's lignified ones.
Cut off all the leaves from the cuttings, except 2-3, and cut the remaining ones in half. Root the vine in loose, fertile soil in the shade at a 45-degree angle. Most often, the plant takes root rather quickly and easily.
An adult powerful liana actively forms root shoots under favorable conditions. In this case, you can separate such a process with a part of the root and immediately transplant to a permanent place. Kampsis is divided in early spring or late autumn.
Also, in the warm season, layering is used for reproduction. A healthy stem that grows closer to the ground is completely bent to the ground and fixed. Dig it a little and moisten and loosen the soil around it throughout the summer, and by the spring it will take root completely.
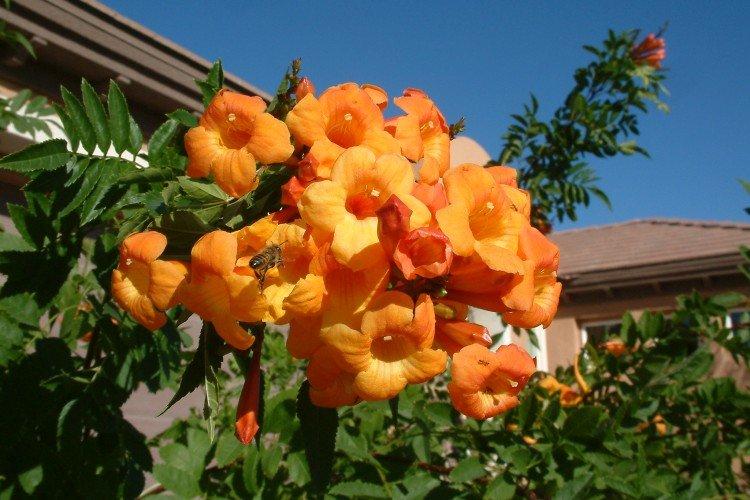

Diseases and pests of kampsis
Kampsis does not have many illnesses and problems. Watering too often can cause roots to rot. In the early stages, it is enough to dig up the plant, cut off the damaged areas, disinfect, dry and transplant, and then adjust the regime. But if the root system is damaged too much, it is better to destroy the plant.
In dry hot weather, aphids settle on the leaves of Kampsis. This can be avoided by prophylactic spraying with infusions of aromatic herbs or tobacco. If there are already a lot of pests, treat the planting with insecticides.
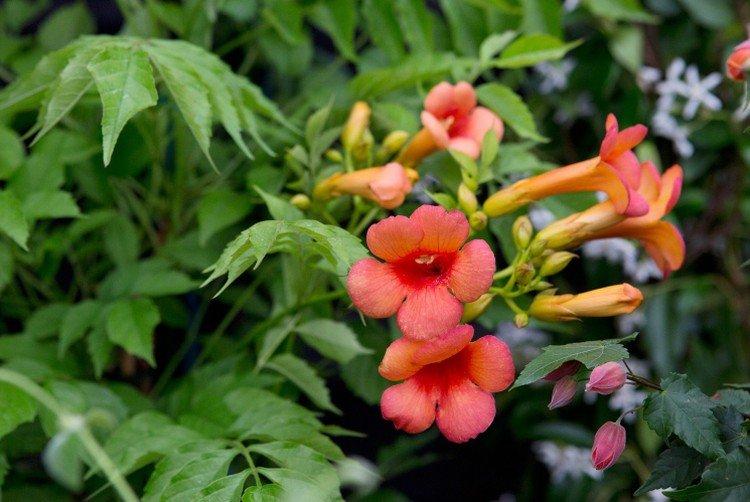

Campsis - photo
Campsis is the star of vertical landscaping and whimsical decorative compositions. And this photo gallery is the best proof of that!