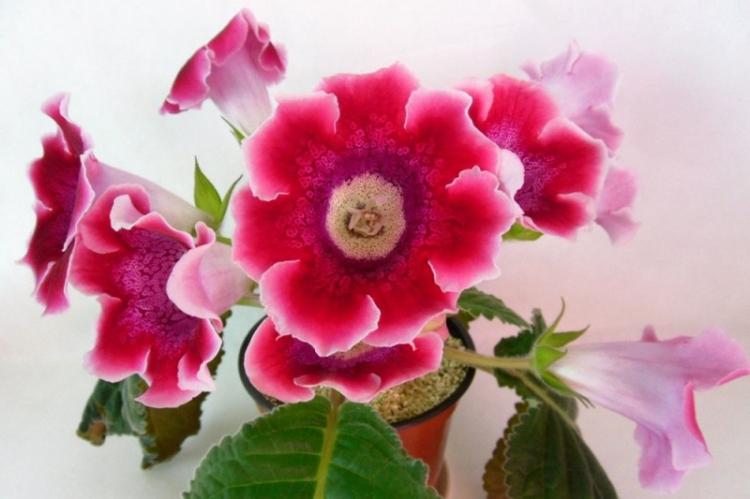
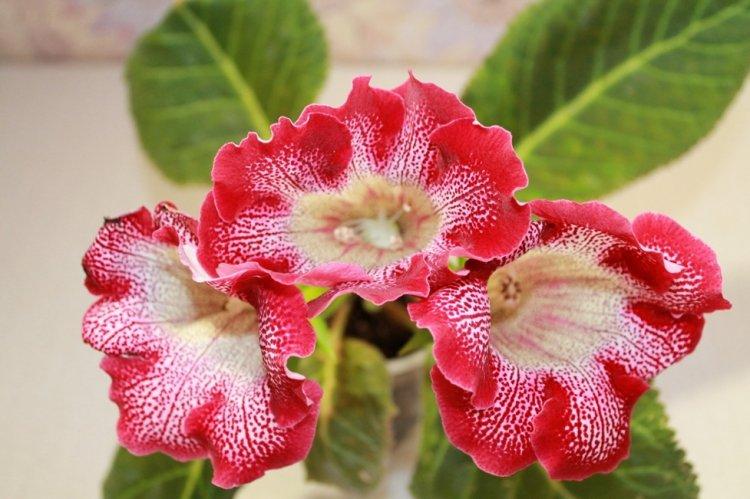
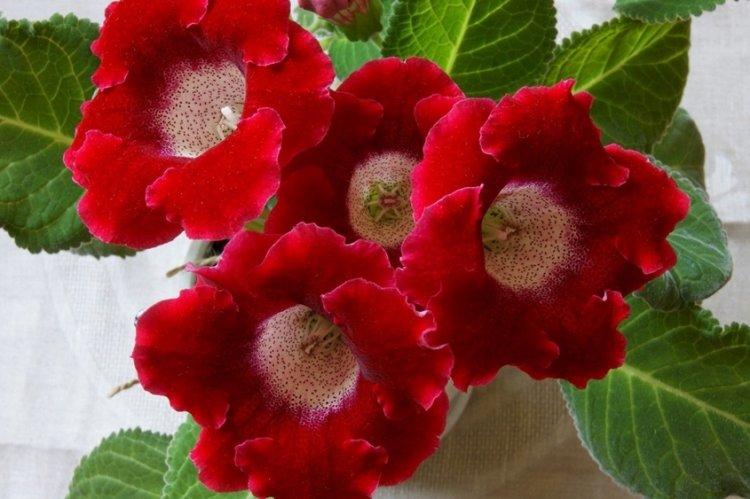
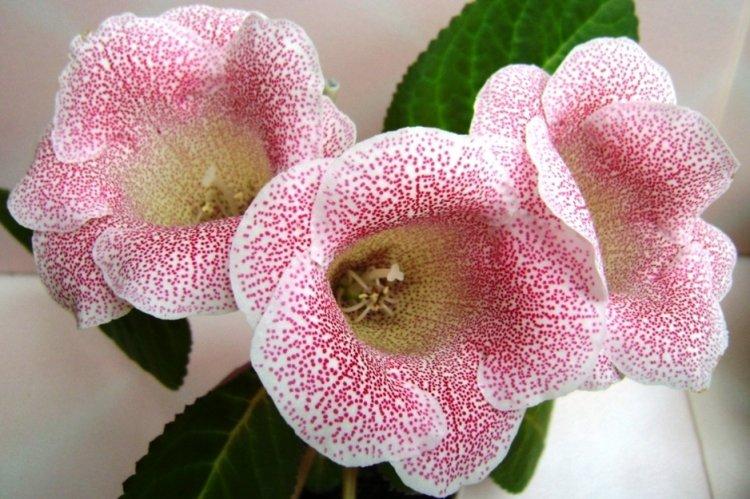
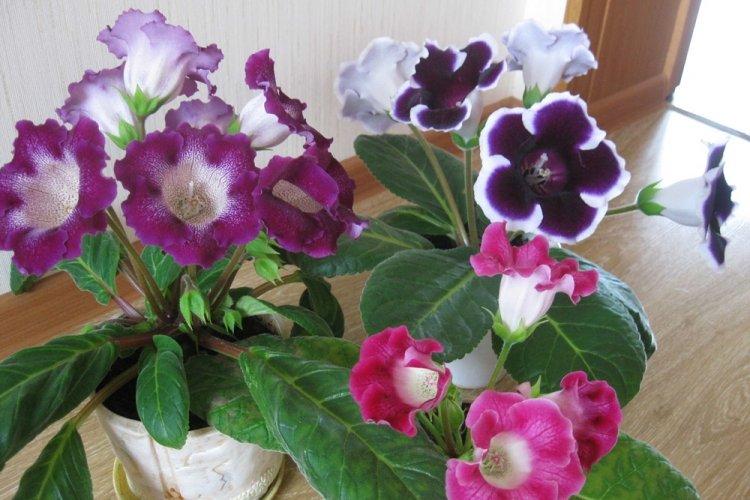
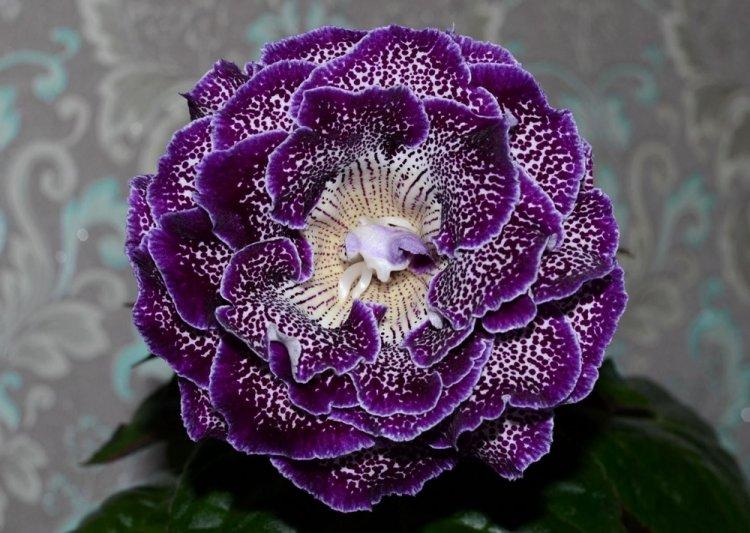
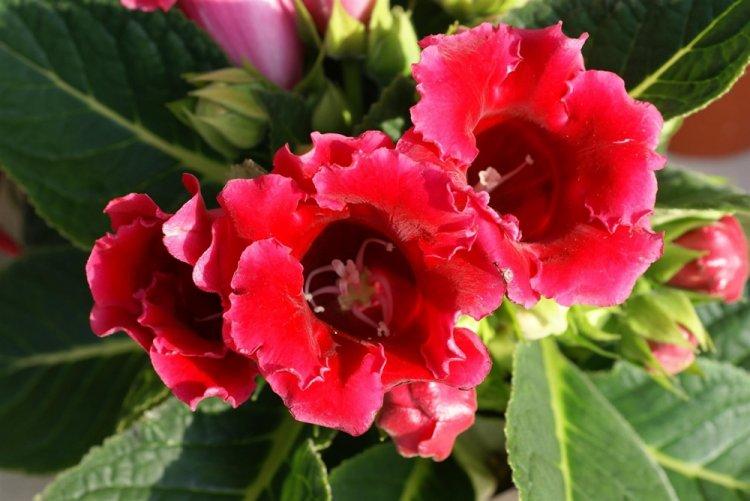
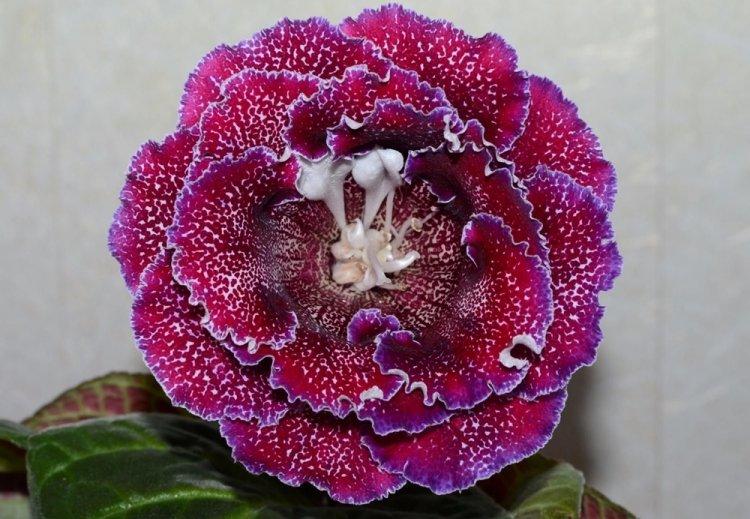
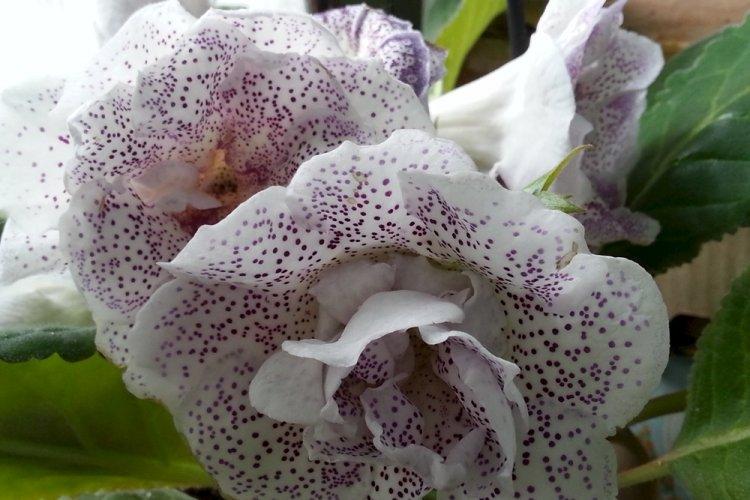
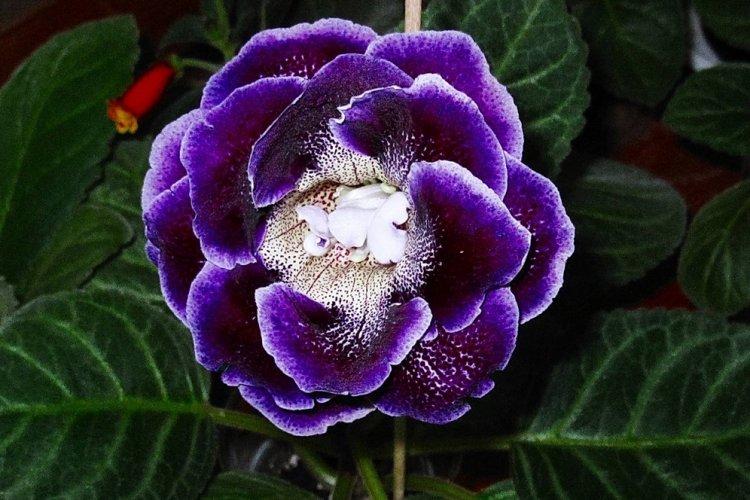
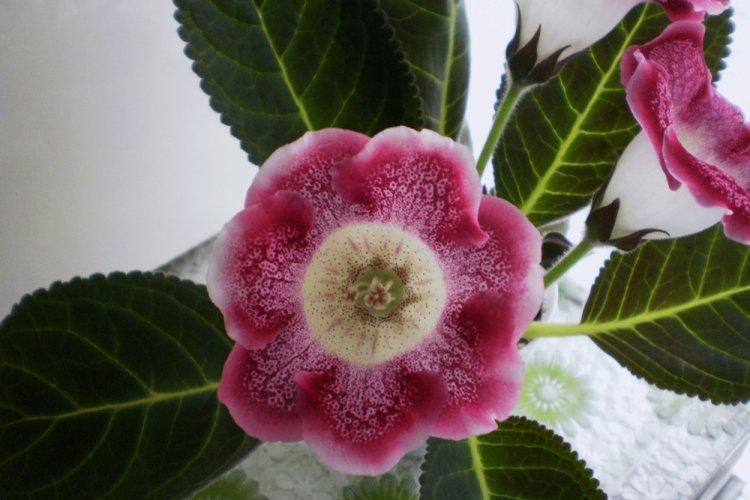
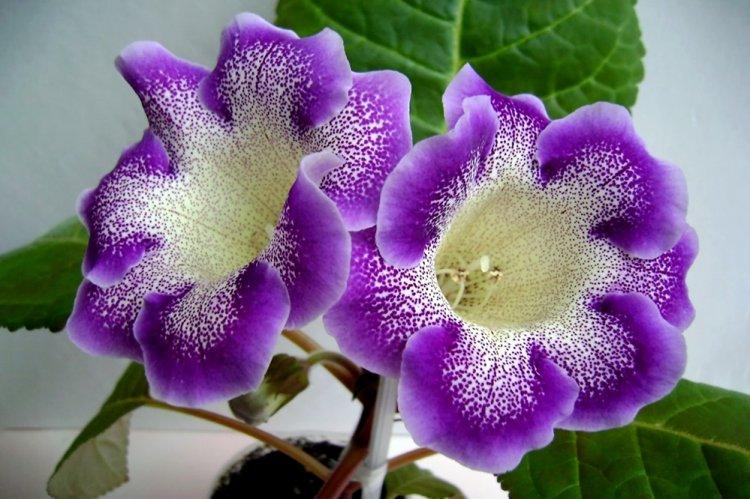
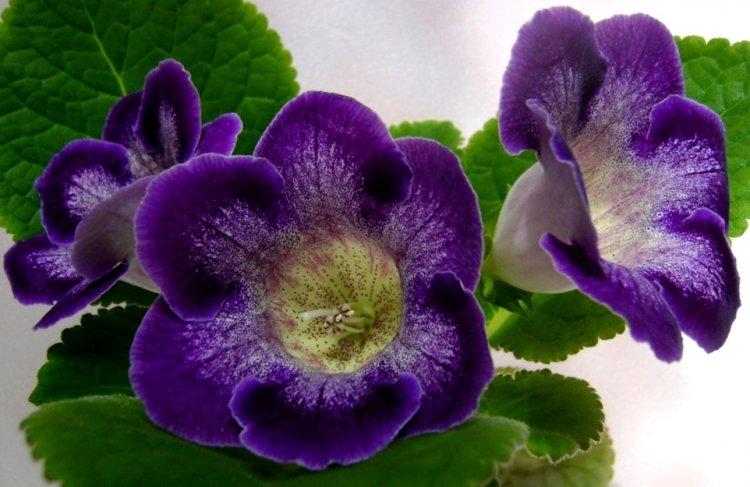
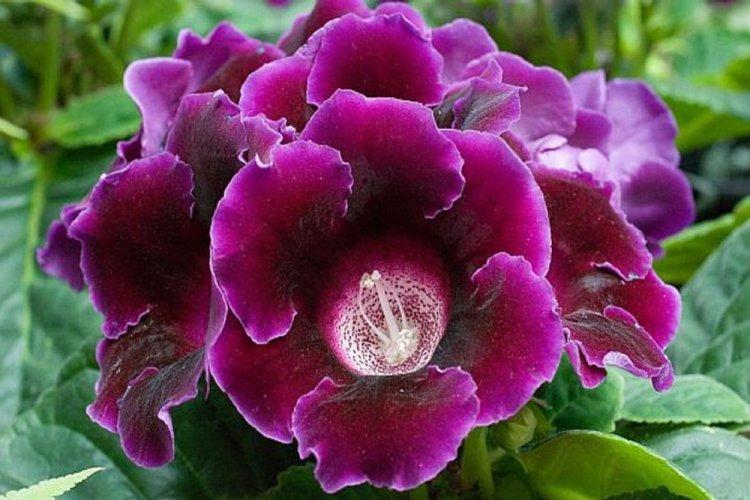
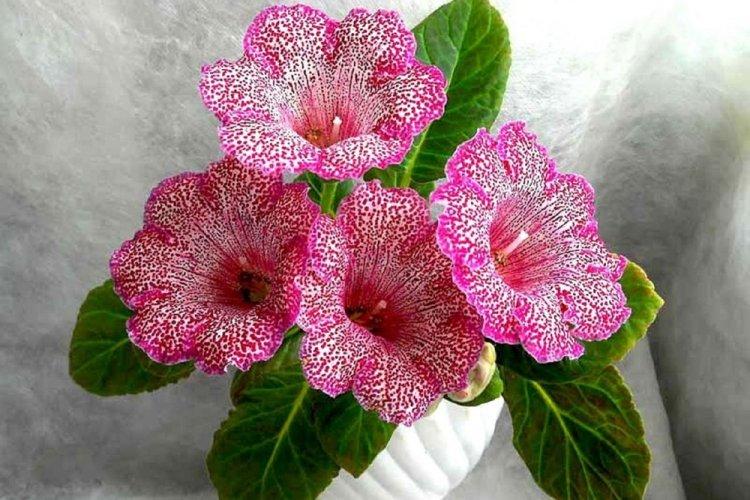
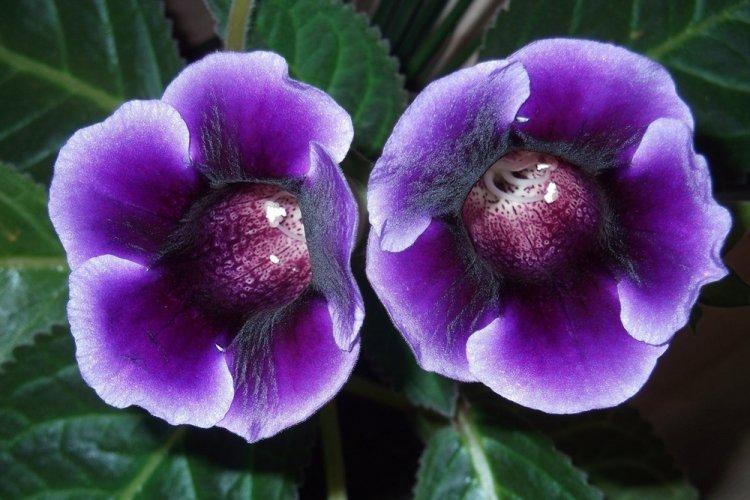
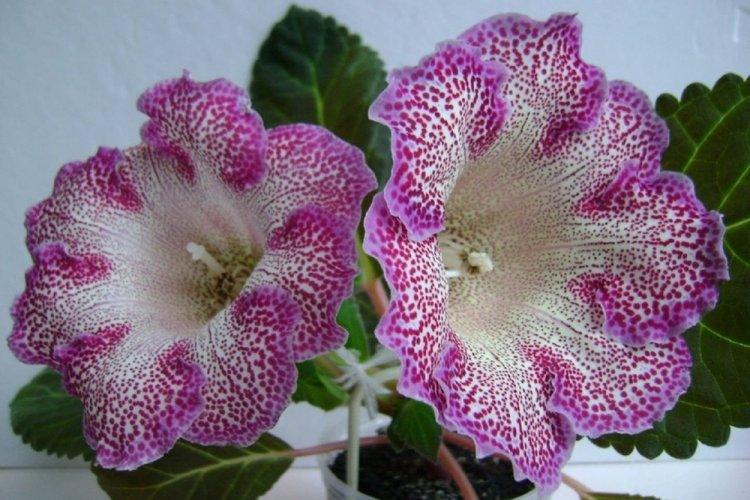
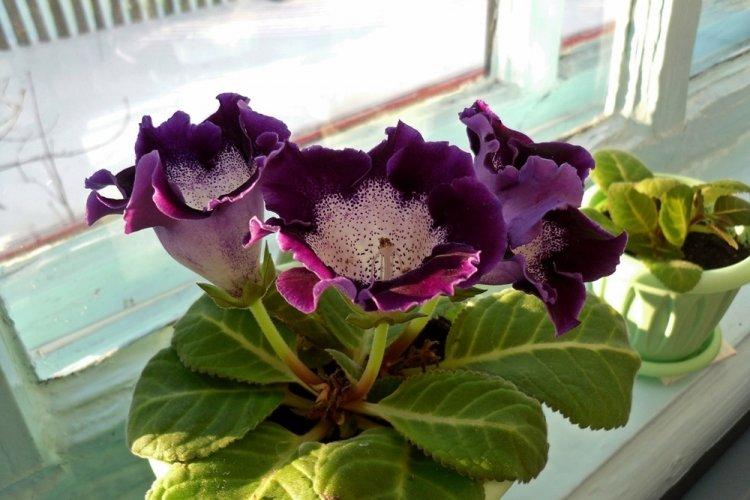
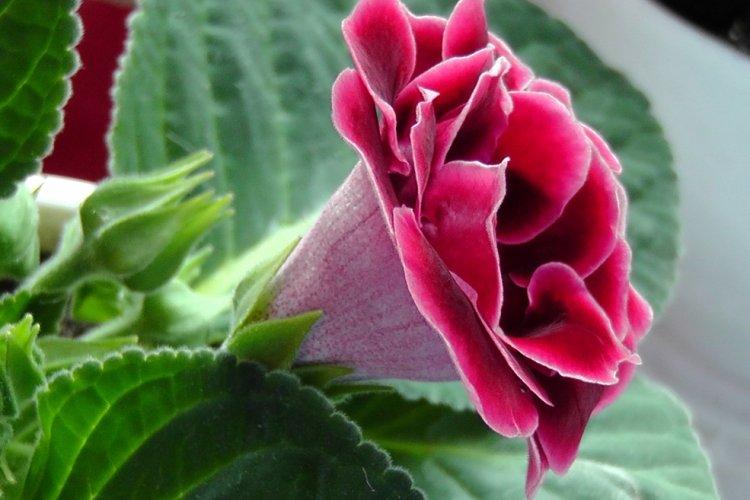
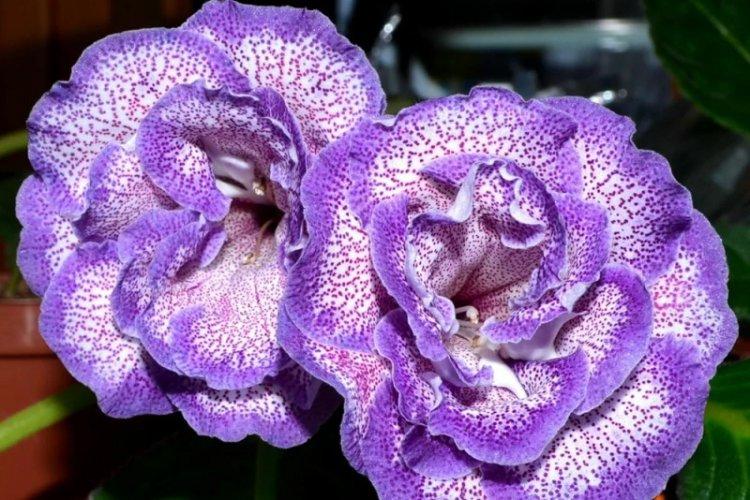
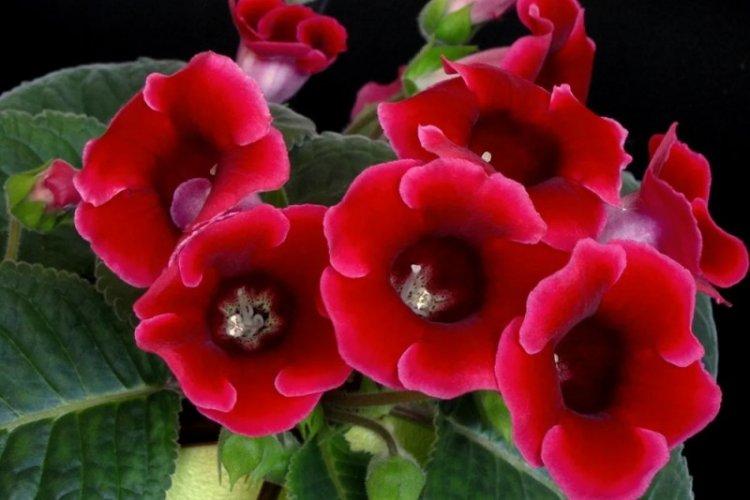
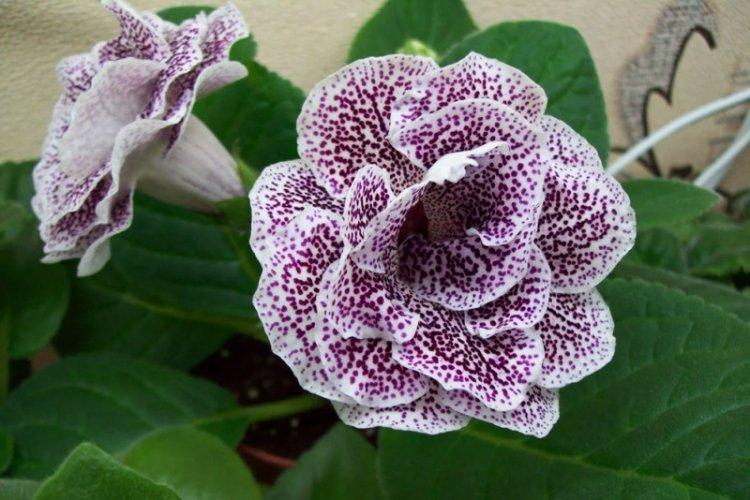
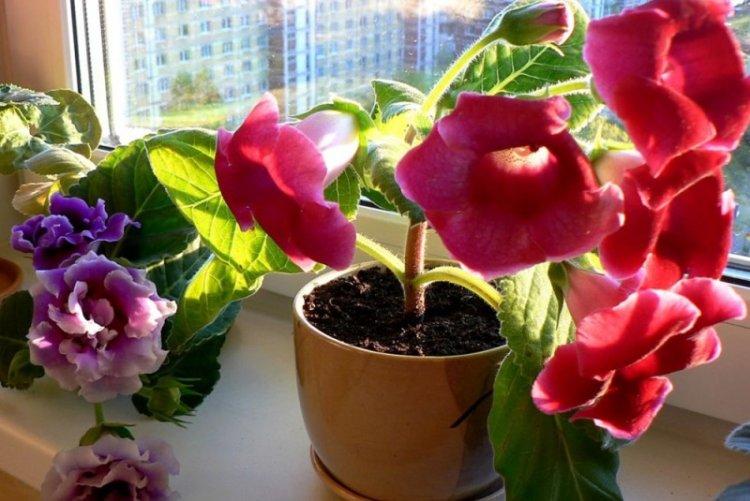
Indoor gloxinia resembles a mixture of violets and bells. This is a very beautiful flower that will become a real decoration of your windowsill. The varieties with velvety and double flowers are especially good! Now we will tell you how they differ and how to take care of them!
general information
Gloxinia belongs to the large family of Gesneriaceae, which includes chrysotemis, coleria, gesneria and streptocarpus. This is a spectacular tropical perennial that came to us from Central and South America. Most often in their natural environment, it is found in Brazilian and Peruvian forests, in the mountains of Mexico and in the Andes.
Gloxinia received its unusual name in honor of a medic and botanist from Alsace - Benjamin Gloxin. The second name is sinningia, and this is another most important name in the history of floriculture. Wilhelm Sinning is a Boston University gardener who has developed many new varieties and species of flowering plants, including the domestic hybrid gloxinia.

Types of gloxinia
Gloxinia species are relatively few - about 25 in natural conditions. But this flower is a longtime guest of apartments and houses, so the breeders have bred different and bright and colorful subspecies. But they work mainly with two main varieties.
Lovely gloxinia
The variety is notable for its large, bright bell flowers of violet, pink and purple flowers. Less common are white and blue petals, as well as subspecies with double petals. On the wide oval leaf plates, an expressive embossed pattern of veins and a short dense edge are visible.

Tiny gloxinia
The name of the species reflects its whole essence - a tiny shrub reaches only 2-3 cm in height. It has very small velvety leaves up to 1 cm, and one miniature flower blooms on each peduncle. Below the petals are white, but towards the top they gradually change color to deep purple.
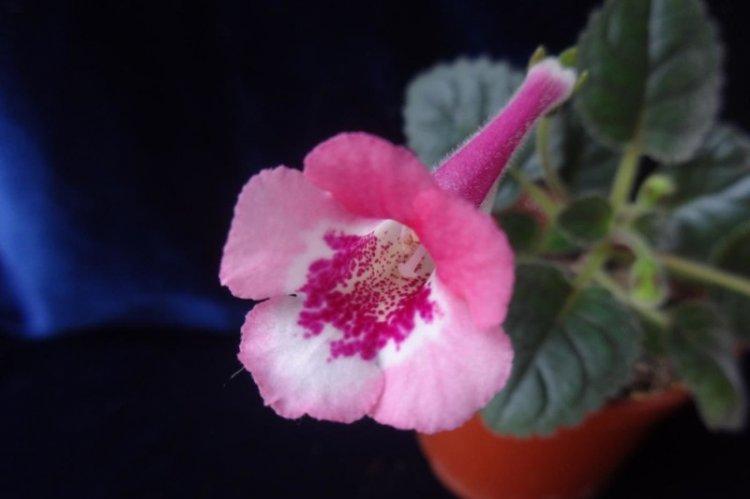

Royal Gloxinia
Its peculiarity is erect stems and shoots, due to which the flower forms a neat little bush up to 10 cm in height. Flowers reach 7 cm in diameter, and the flower stalks of royal gloxinia are longer than most other varieties. The dark pubescent leaves show a silvery pattern of veins.
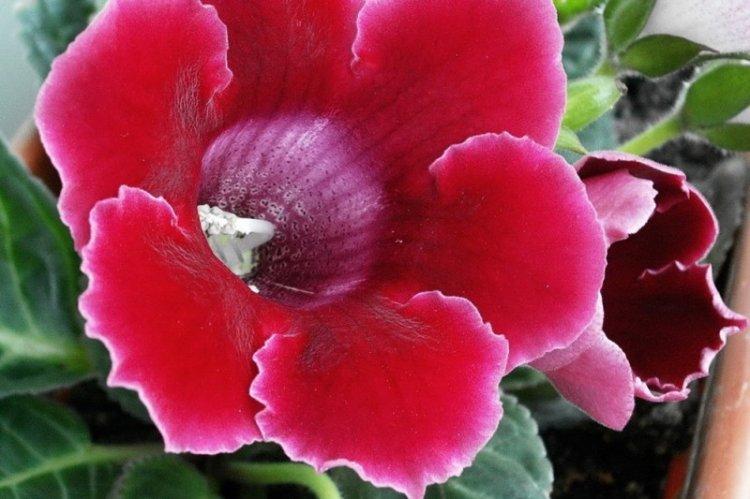

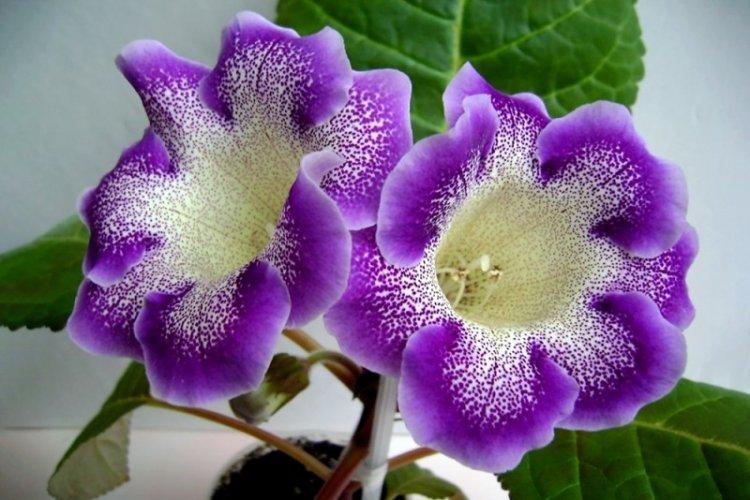
Beautiful gloxinia
This variety is very similar to royal gloxinia, but more varied. It has more variations in colors and shapes of petals, and the leaves are slightly lighter, with a pronounced relief.

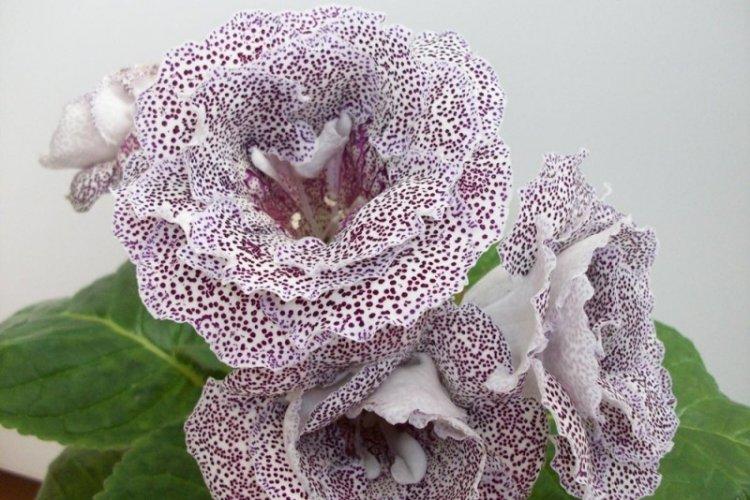
Speckled gloxinia
The exact name of speckled gloxinia is Gloxinia perennis or perennial gloxinia. Particularly interesting are its leaves, which acquire a reddish tint on the reverse side. Large, fleshy shoots reach 70 cm, and several flowers are collected on them.

Gloxinia care
For all its decorativeness, it is not too difficult to care for gloxinia. A little more attention will be needed during flowering, but at rest it will not cause much trouble.
Temperature
During the flowering season, Gloxinia thrives at normal room temperature. But in winter, she definitely needs a coolness of about 10 degrees, so that the flower leaves at rest and gains strength before a new phase of growth. If the leaves fall down, the gloxinia is too cold, and if they stretch too much, it is hot.
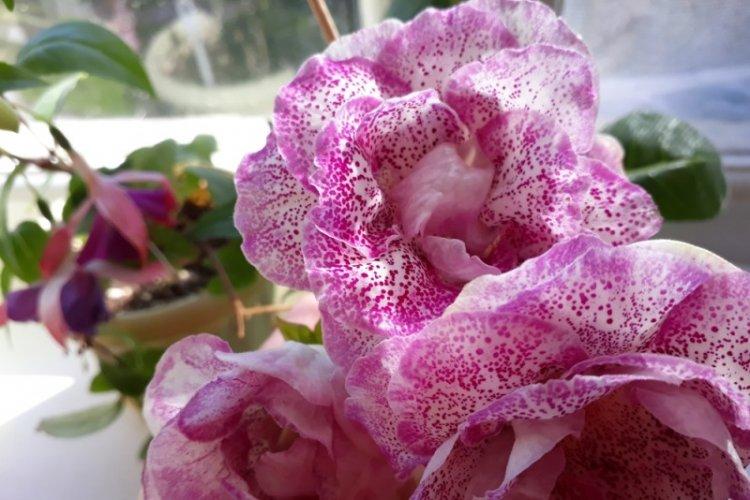

Lighting
Gloxinia needs bright light and a lot of free space around, and the minimum day length for its growth is 12 hours. So if you live on the north side, take care of the phytolamp in advance. Be sure to avoid drafts and aggressive direct sunlight.
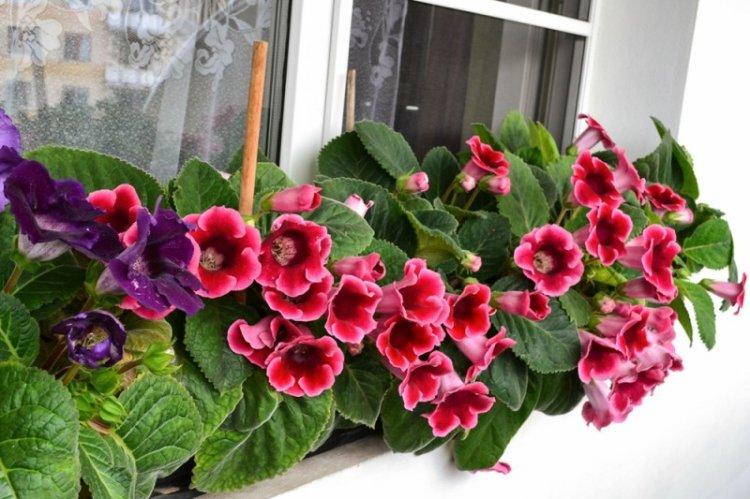

Watering
To water gloxinia, you need well-separated and ideally filtered water at room temperature. Water the flowerpot when the top layer dries up so the roots don't start to rot.Reduce the frequency towards the end of the flowering period to smoothly bring the plant into dormancy.
Although gloxinia loves moisture, you cannot spray and wash it, otherwise the leaves and flowers will begin to deteriorate. So just use a humidifier or put a bowl of water on the windowsill by the flowerpots. For the same reason, experienced gardeners recommend using bottom watering during flowering.

The soil
The similarities with violets and begonias are also evident in the choice of soil. Feel free to use specialized mixtures for gloxinia just for them. Or add half as much humus and sand to the deciduous soil.

Fertilizers and feeding
After the gloxinia has bloomed, add some admixtures to the soil for growth. After the buds appear, you need the usual fertilizers for flowering, like violets. If Gloxinia has enough nutrients, it can even bloom twice, just a second time - more poorly.
In the active phase, feed the flower every 10-14 days until mid-August. Mixtures with boron are definitely needed, otherwise the buds become smaller, and the leaves seem to be frayed, with a cut edge.

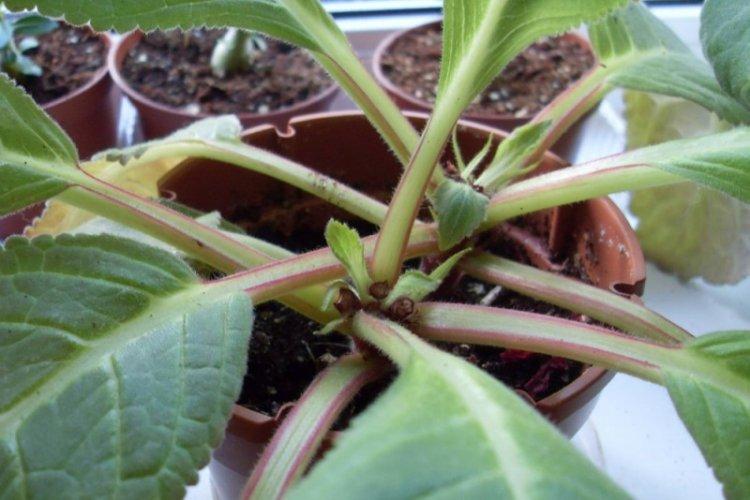
Post-flowering care
When the gloxinia has faded, cut off the stem and top leaves, leaving only the bottom layer. Reduce watering and feeding until the plates turn yellow and dry on their own. New rudiments will appear in their sinuses, of which only a couple of the strongest need to be left, and everything else should be cut to hemp 1-1.5 cm high.

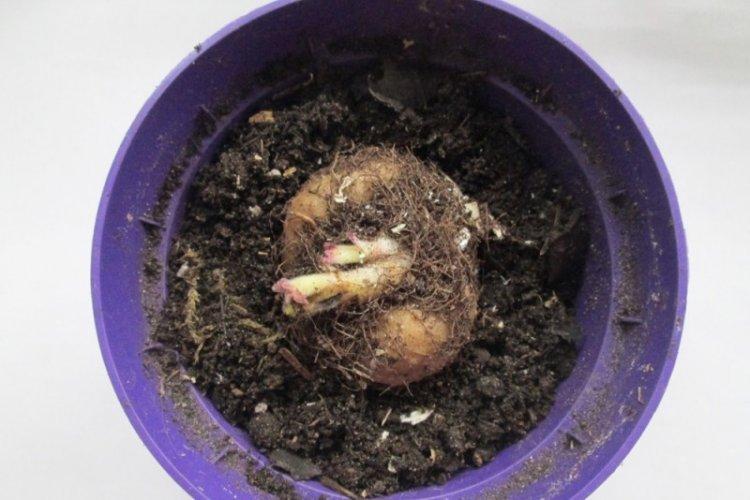
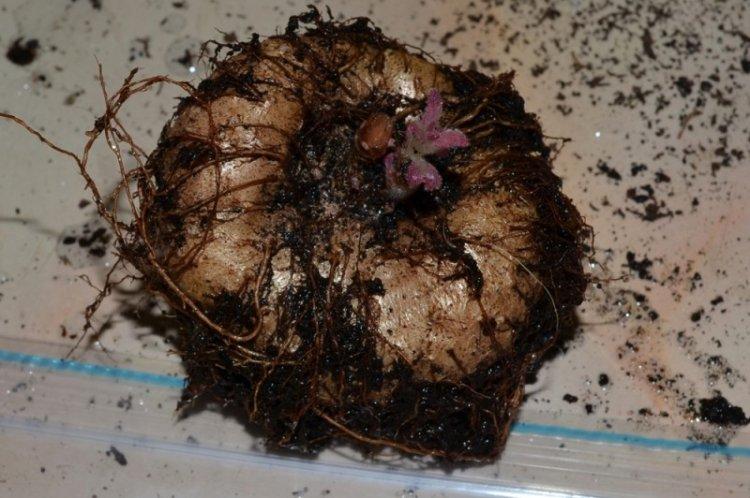
Transplant and reproduction
The easiest and most effective way to propagate gloxinia is from leaf cuttings. Moreover, you will not need the largest and most beautiful sheet, but on the contrary - a small and inconspicuous one. A large plate will have to be divided into parts parallel to the transverse veins and cut off the petiole to 1.5-2 cm.
Leaves do not need to be placed in water - immediately root them in a damp substrate in separate flowerpots. Build a small greenhouse on top or cover the flowers with a plastic bag. Without touching anything for at least 4 weeks - the seedlings do not need to be watered or ventilated separately. After that, gradually transfer them to normal mode and remove the shelter.
Gloxinia is transplanted annually when the bush is removed from dormancy at the end of winter. This is done by the transshipment method together with an earthen clod so as not to damage the root system. The new pot should be slightly larger than the old one in order to renew the drainage and the top layer of the substrate.

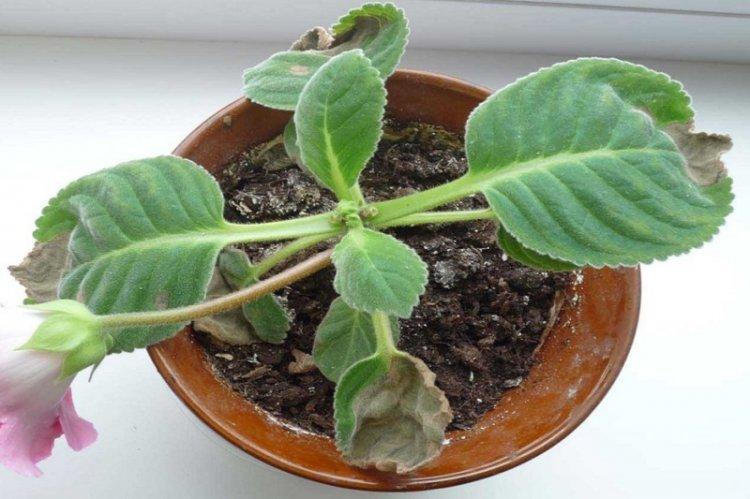
Pest and disease control
Gloxinia most often suffers from cyclamen and spider mites. These are small pests that are difficult to see - in large numbers they resemble plaque or a layer of dust. The leaves begin to deform and curl, and the buds wither. Use a flowering plant insecticide solution to control parasites.
Another problem is thrips, which can be detected by the appearance of light dots on the leaves. In this case, in addition to processing, it is necessary to replace the entire topsoil, because it is there that the pest lays the larvae.
If brown rot appears on the leaves, the damaged areas must be removed immediately and treated with fungicides. It is more difficult with root rot - most often it can be detected when the stem begins to deteriorate. In this case, it is almost impossible to save the flower. Therefore, be sure to keep an eye on watering, do not overfill with gloxinia and do not use too cold water.

Gloxinia - photo
Gloxinia is a very colorful flower that can transform and revitalize any room. Just take a look at this collection of photos!