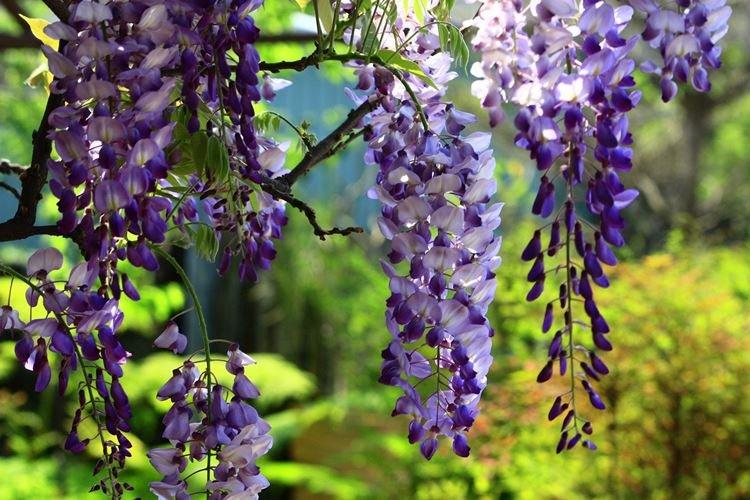
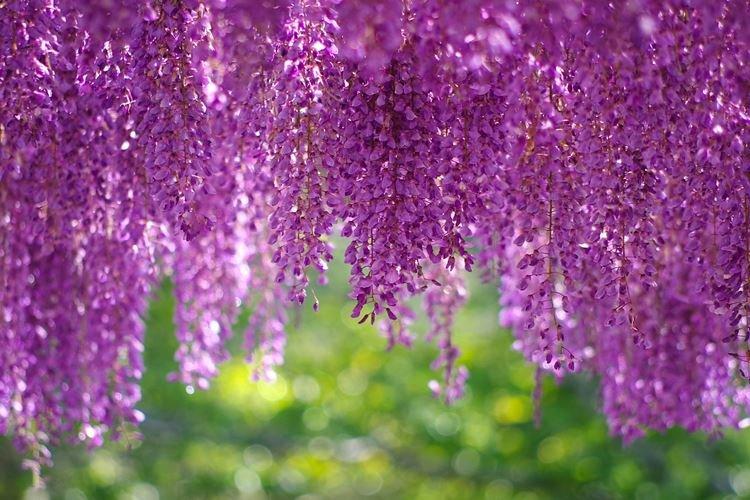
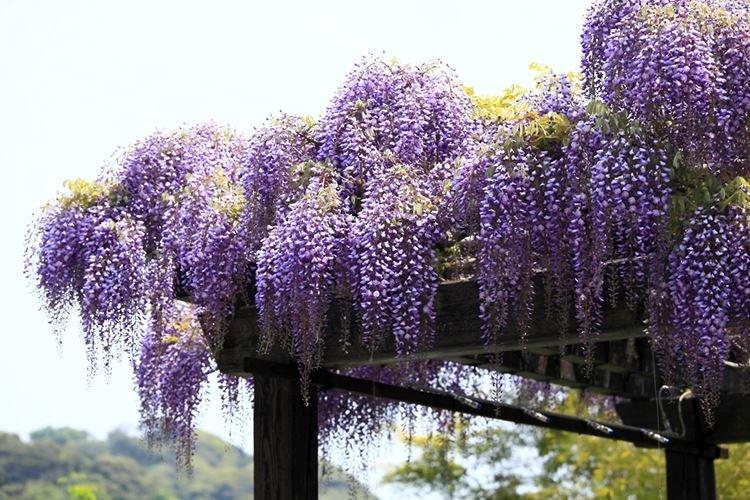
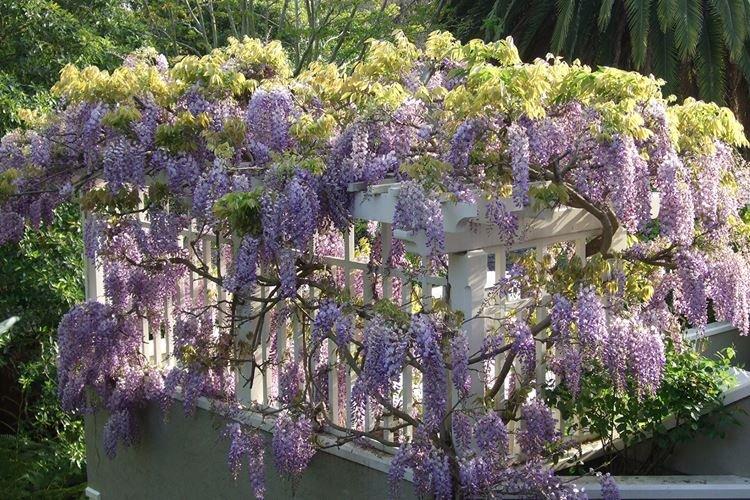
Previously, it was believed that seeing a blooming wisteria is a colossal luck and a prediction of good luck. And according to an ancient Japanese legend, with a branch of wisteria, the goddess ward off evil from the sacred Mount Fujiyama. Now a mystical vine with huge flowering brushes can be grown independently. And it's not even too difficult!
general information
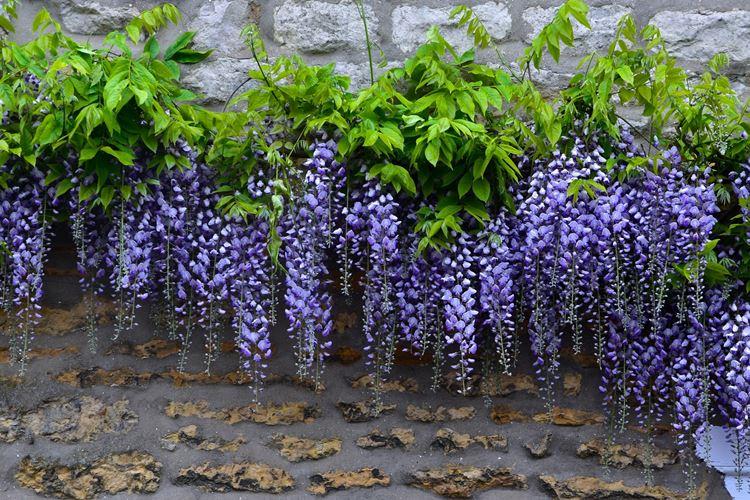
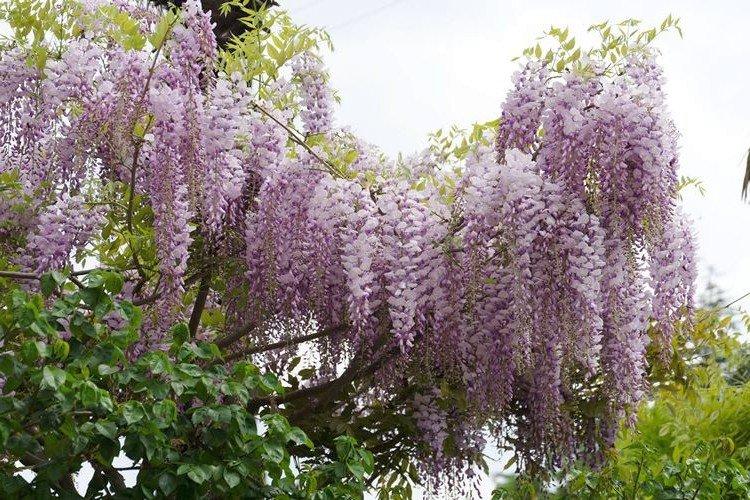
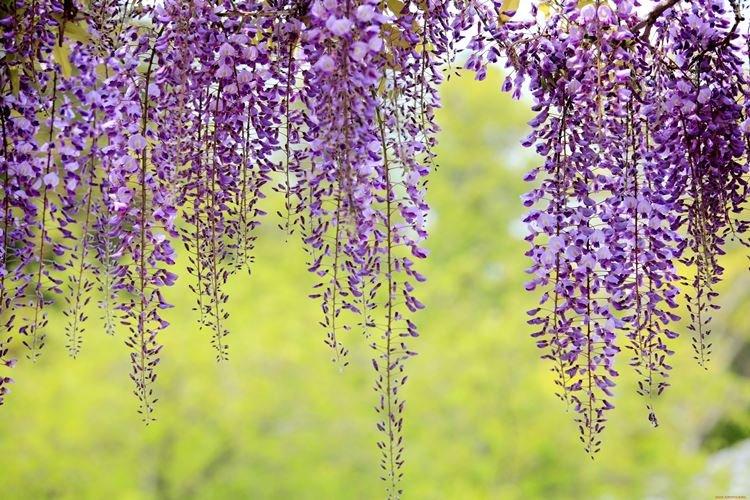
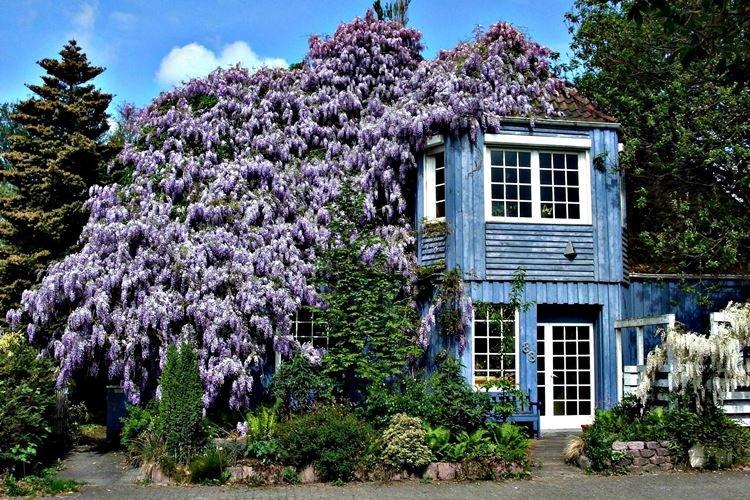
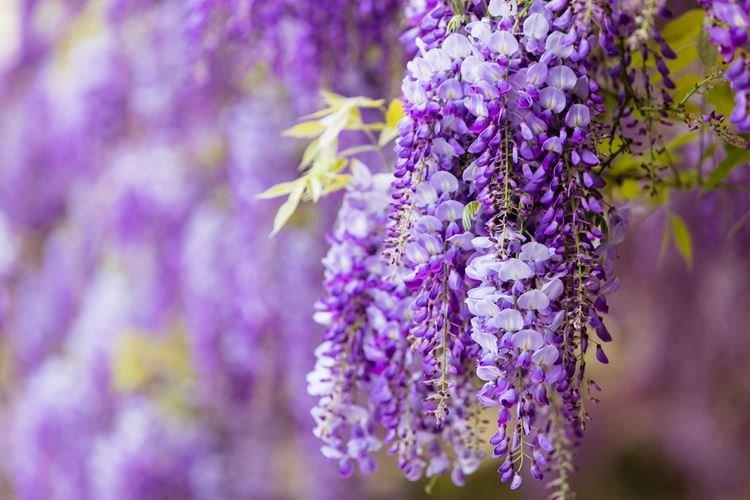
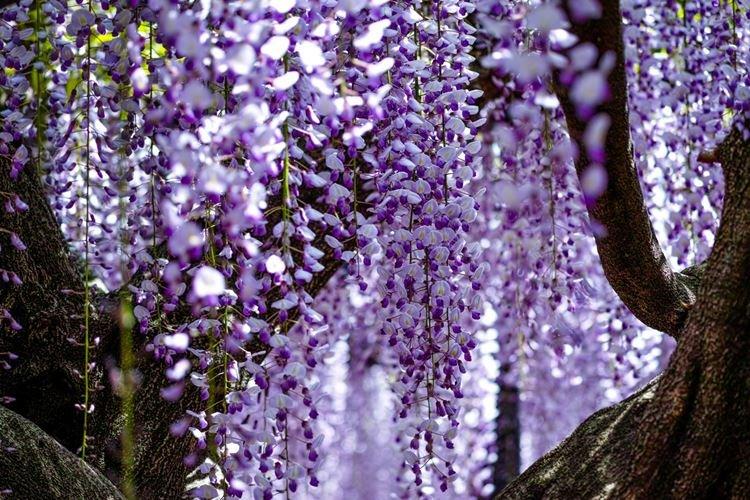
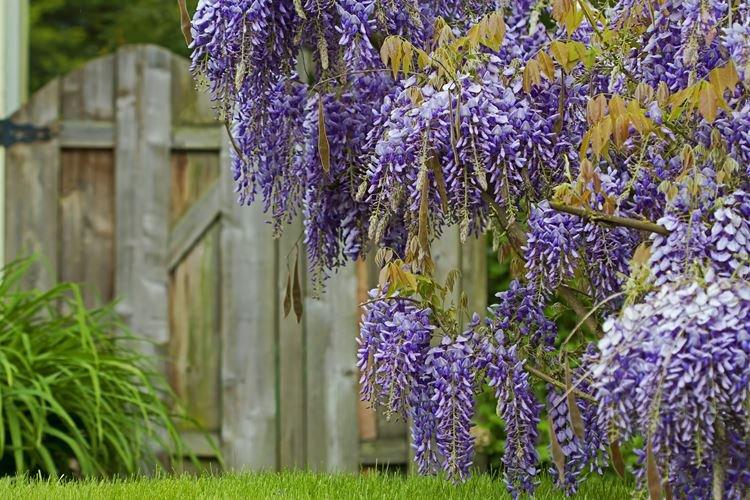
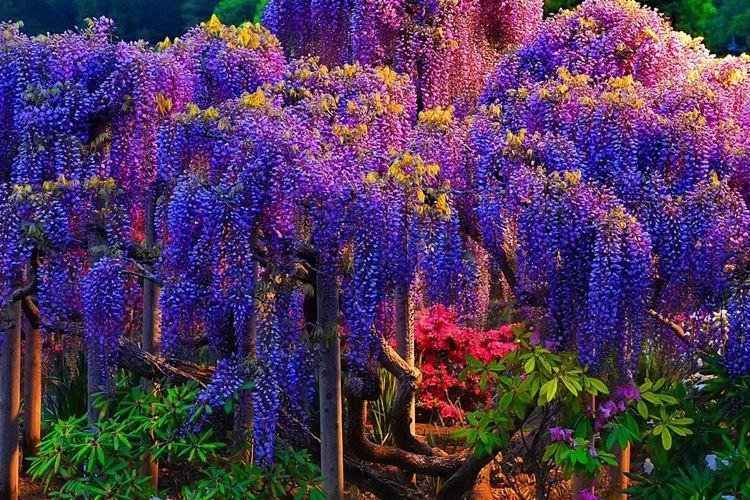
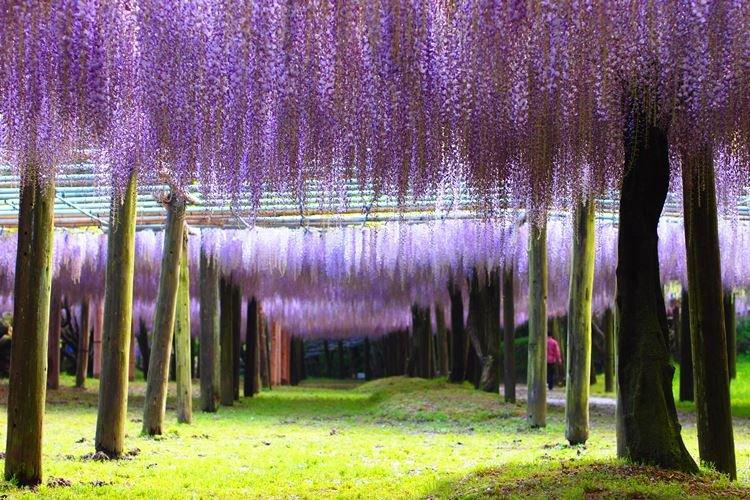
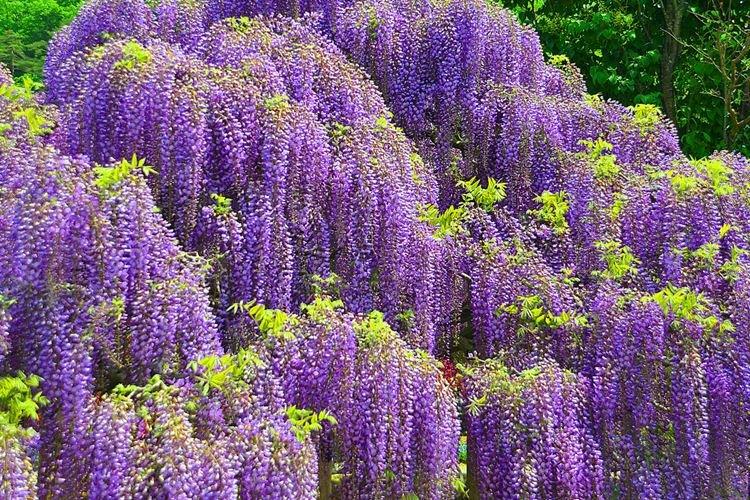
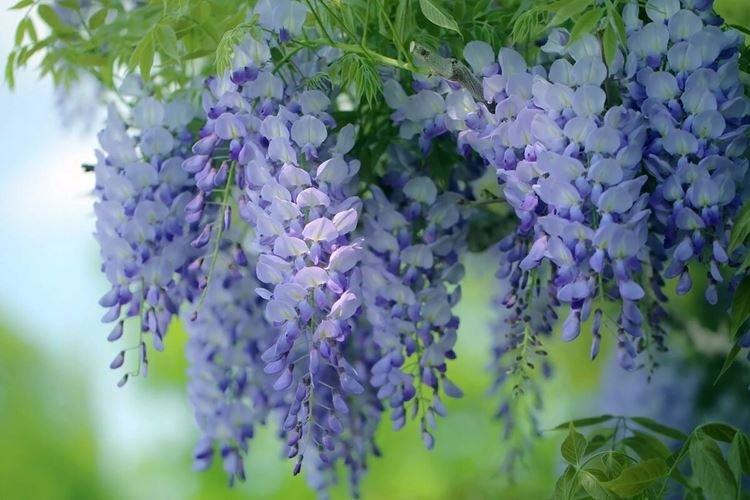
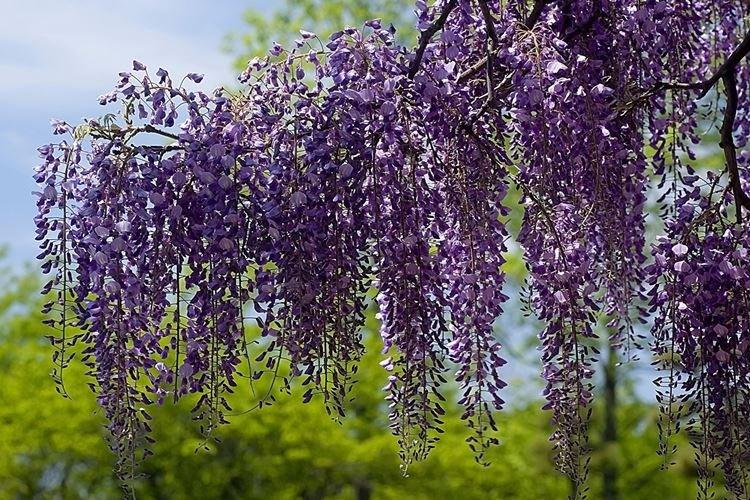
Wisteria or wisteria is a beautiful climbing vine that grows in East Asia and North America. It received the second name in honor of Professor Kaspar Wistar. Scourges can stretch up to 20 m, and individual bushes live up to 150 years. Long feathery leaves are arranged alternately, and large decorative brushes up to 50 cm hang between them.
Wisteria leaves are quite poisonous, so it is not recommended to grow it where pets can feast on it. For the same reason, the vine is not planted near water bodies so that the leaves do not fall into the water and poison the fish. Flowering begins at the end of March and the inflorescences are very fragrant.
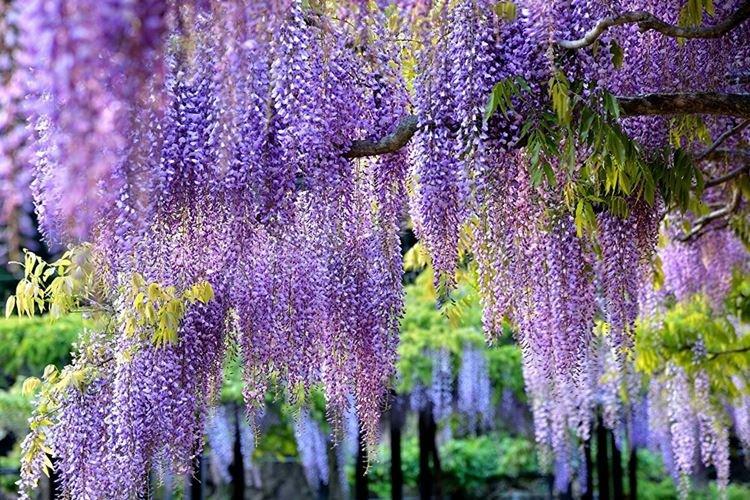

Types of wisteria
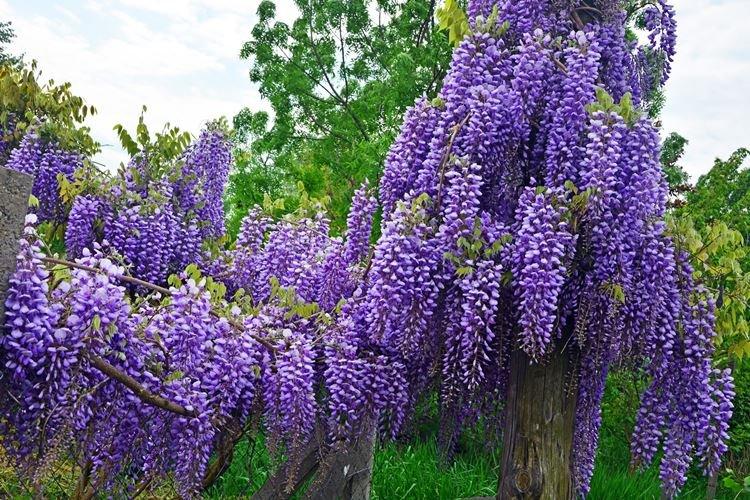
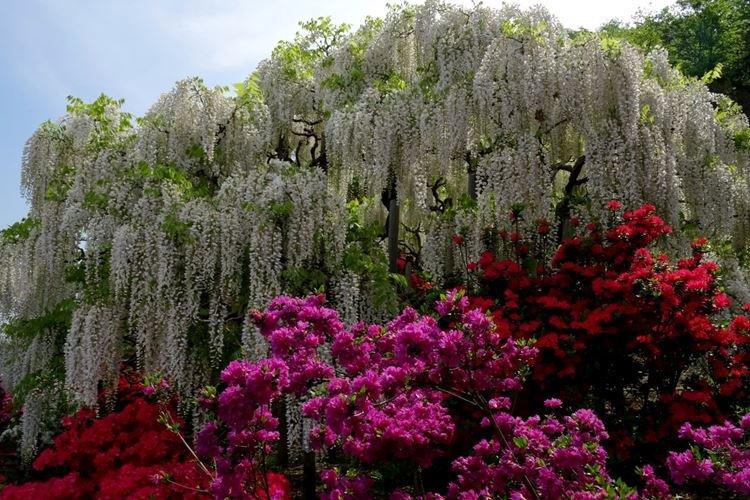
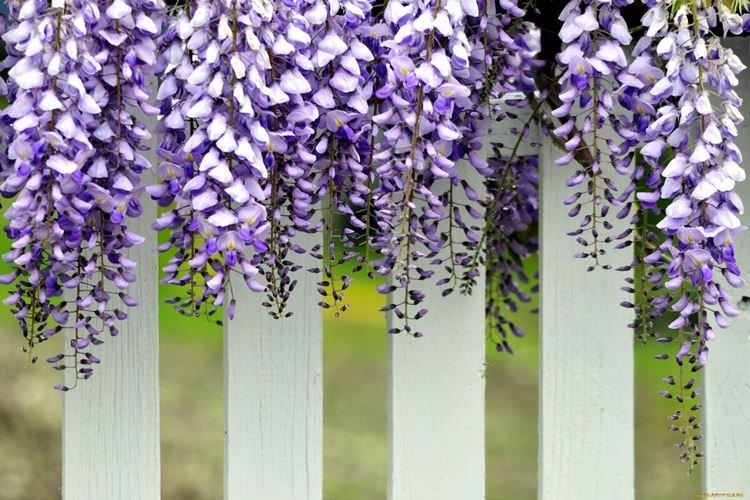
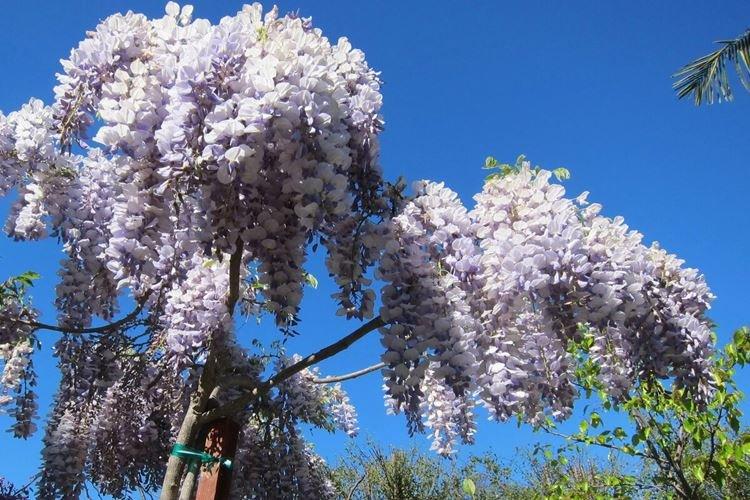
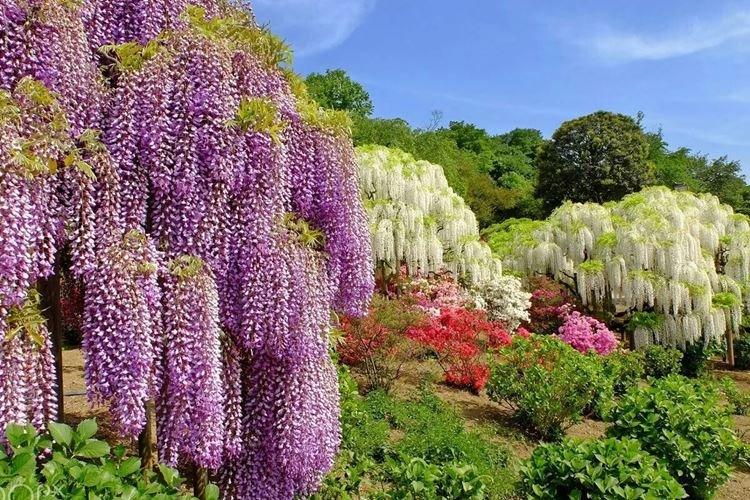
There are nine main types of wisteria, but only three are used for decorative purposes in landscape design. Purple and lilac shades are more common, although there are whites, blues and pinks.
Lush wisteria
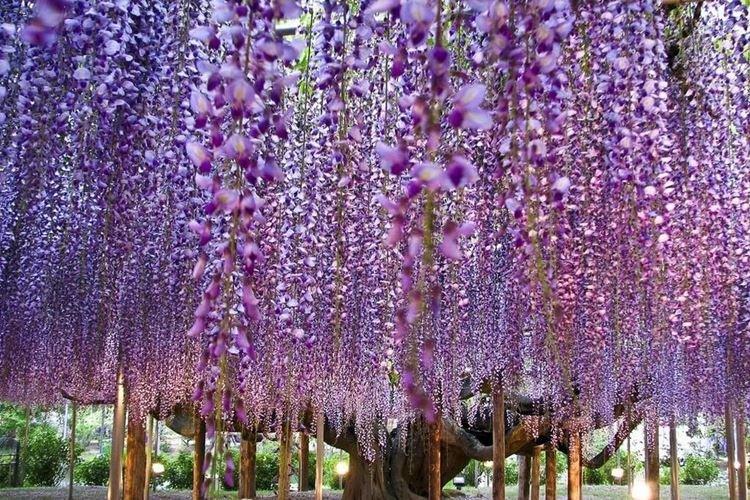
A large liana stretches up to 15 m and is dotted with large snow-white or blue-purple brushes. Its main advantage is its amazing frost resistance up to -40 degrees.
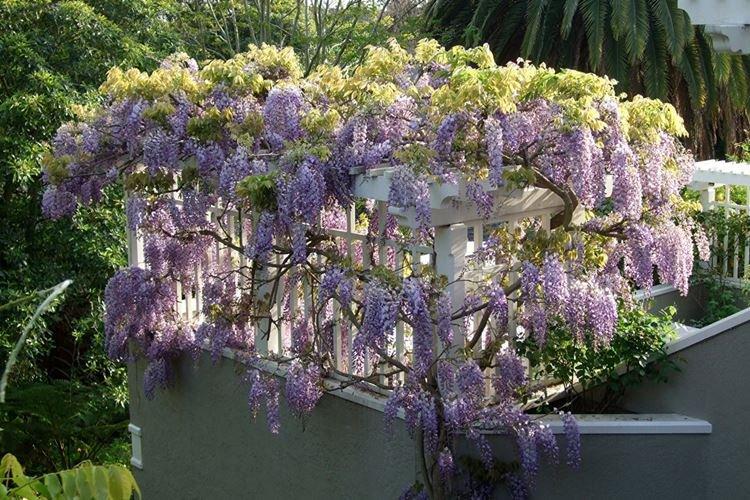

Wisteria multiflorous
Such wisteria is more compact and more like a tree with its lignified shoots. Her brushes are even larger - up to 60 cm, but the leaves are large. Mostly multiflorous varieties are colored blue or pale purple.
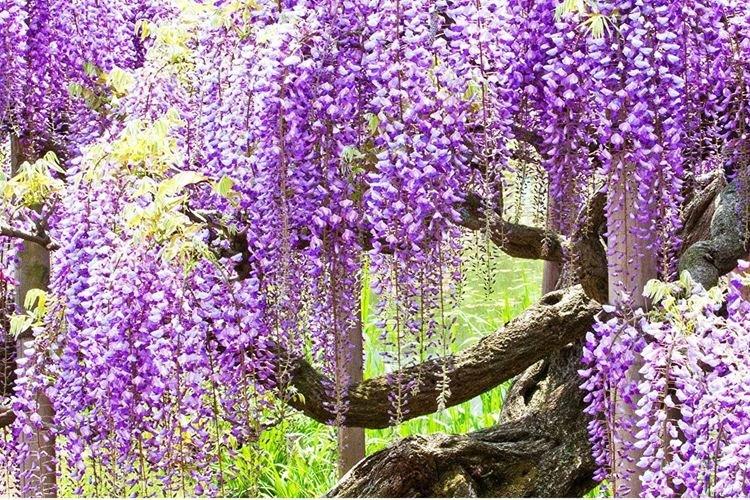

Chinese wisteria
A large woody liana quickly braids the most complex and large supports, therefore it is appreciated in landscape design. Chinese wisteria is thermophilic, but withstands short frosts down to -20 degrees. It is from this species that almost all decorative hybrids originated - Alba, Blue Sapphire, Plena, Sierra Madre.
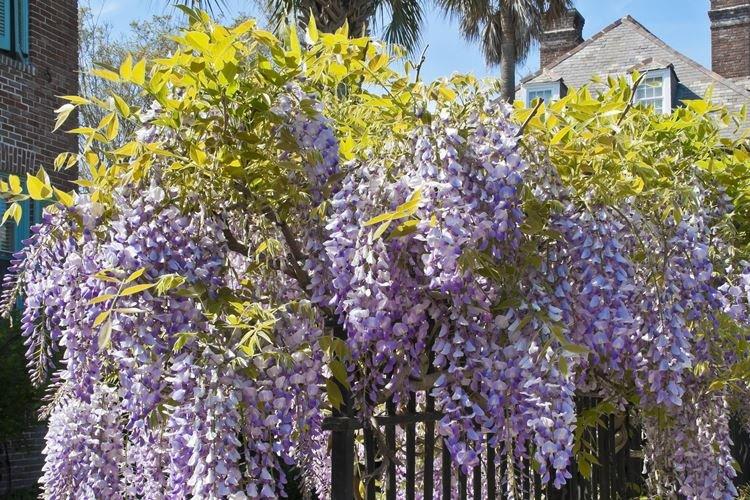

Wisteria care
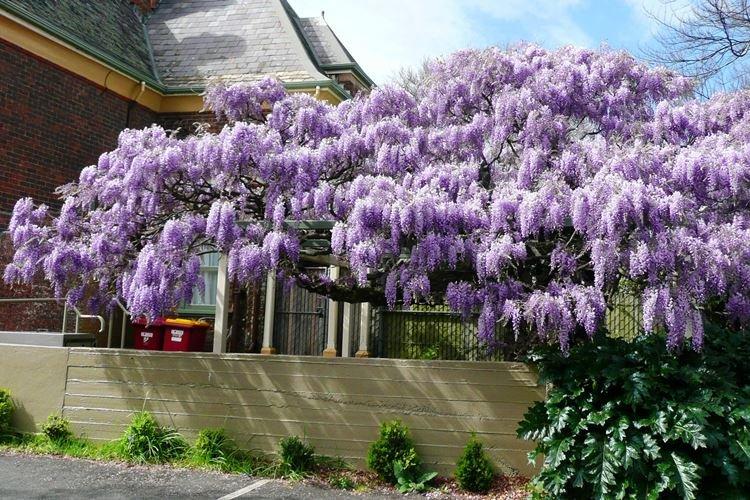
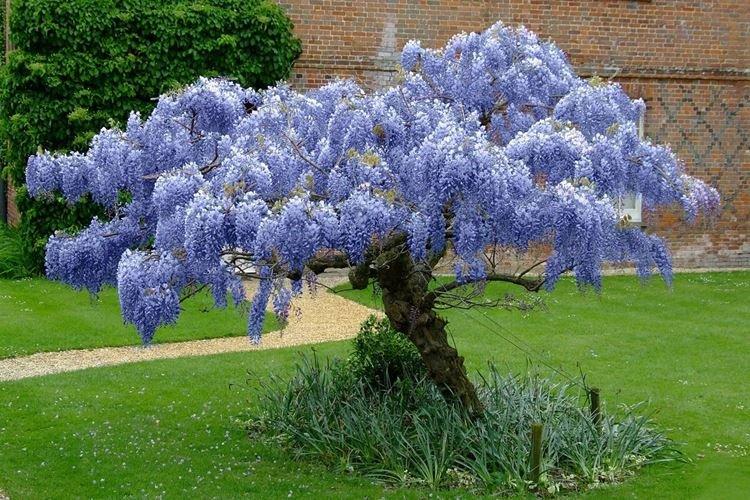
Wisteria came to us from warm regions, so it is heat that is the main condition for its maintenance. Landscape designers are very fond of wisteria, because it wonderfully decorates fences and gazebos. But you can grow liana in the house, in a fairly spacious container.
Temperature
In summer, wisteria feels great outdoors in the garden, but by winter, be sure to protect it from the cold. The root rosette is spud up high, and the whips are removed from the support, folded onto the near-trunk circle and covered with dry leaves. Indoor wisterias should hibernate in cold and dark - somewhere in the basement.
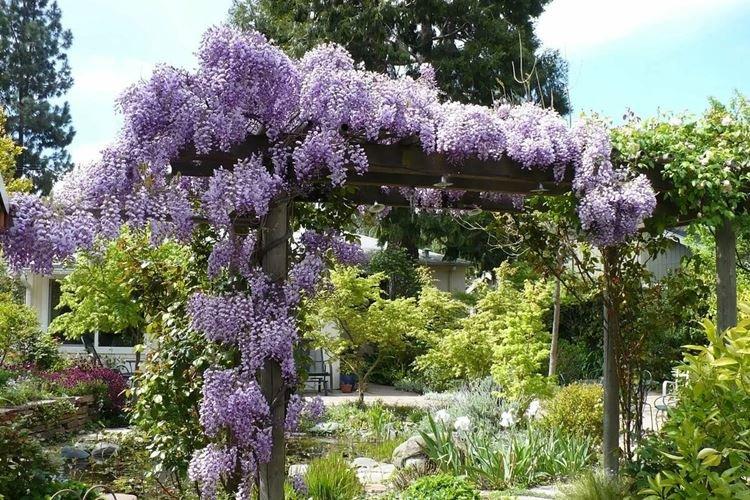

Lighting
Wisteria loves light and is one of those rare plants that need direct sunlight. In the garden, initially choose a bright, sunny place for planting, and if you grow wisteria at home, rearrange it in the summer on the southern windows or take it out to the balcony.
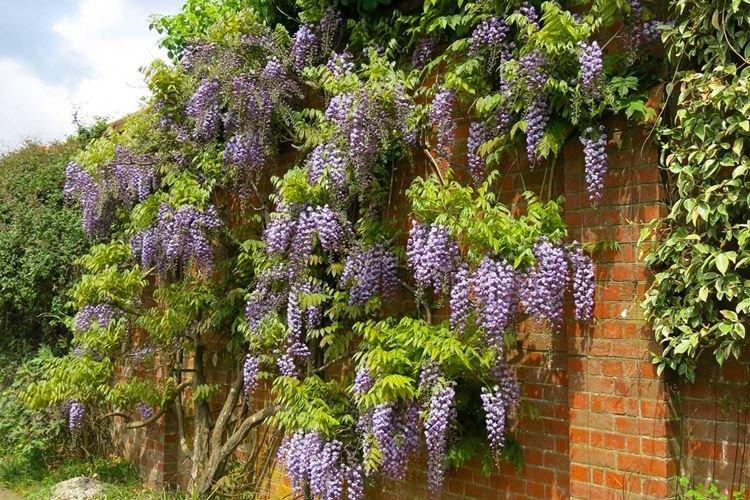

Watering
Wisteria can hardly tolerate excess moisture, so the main thing is not to pour it. The substrate should be only slightly wet, and in winter, watering is generally reduced to a minimum. In hot summer, the vine needs to be sprayed, but do it in the morning or evening, not under the sun.
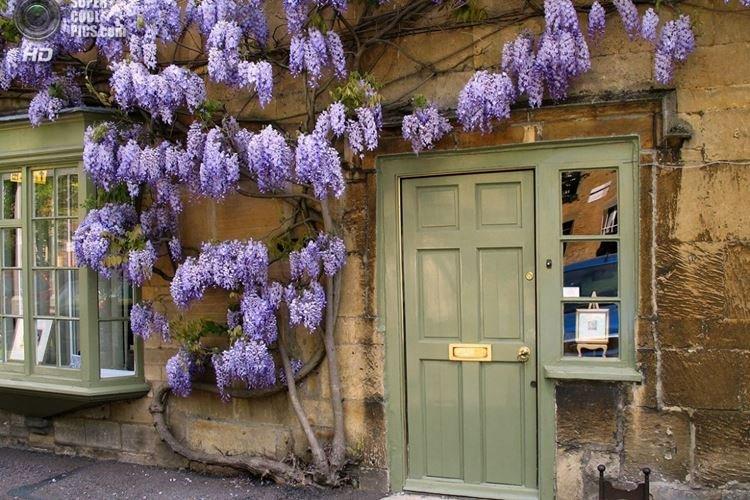

Soil and fertilizers
The plant needs nutritious saturated soil, so choose a soil with turf and humus. Feed regularly from March to September every two weeks. But there is also a plus: you do not have to be smart with combinations of minerals - complex fertilizers are suitable for her.
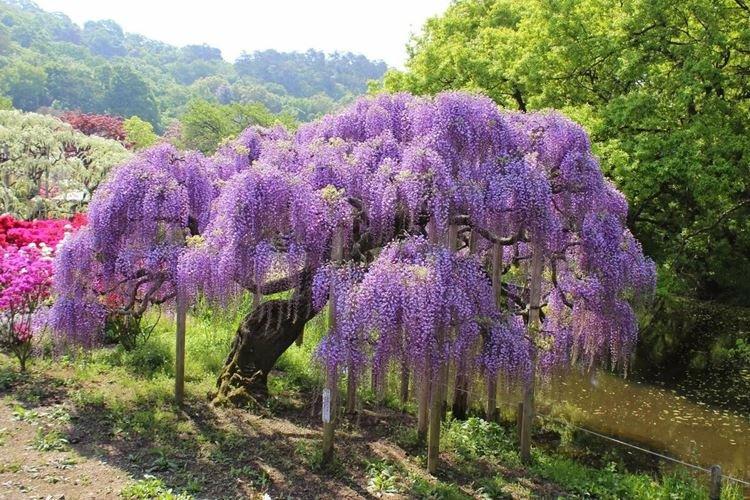

Transplant and reproduction
Wisteria is propagated by layering from the strongest annual shoots. Make an oblique cut and place the stem in a container of clay turf. It is best to detach it the next spring when it is firmly rooted.
Cutting and grafting are used as alternative methods, but they are not very effective.Growing wisteria from seeds is long and inconvenient - you need to keep the sprouts under the film in a dark place at 25 degrees for a month and a half.
Before planting, gradually harden the seedlings, but protect them from the wind. Wisteria can be planted in the ground only when the threat of frost has already passed, in a 60x60x60 pit along with mineral fertilizers. Young wisteria is transplanted every year, but adult large plants are transplanted as needed.

Pruning
Seasonal pruning is carried out to stimulate flowering and in order to thin out too dense lianas lianas. But wisteria can also be grown in the form of a trunk - then you need to constantly leave one of the most powerful shoots. Forming is carried out in the summer in two passes: at the beginning and at the end of the season as it grows.

Pest and disease control
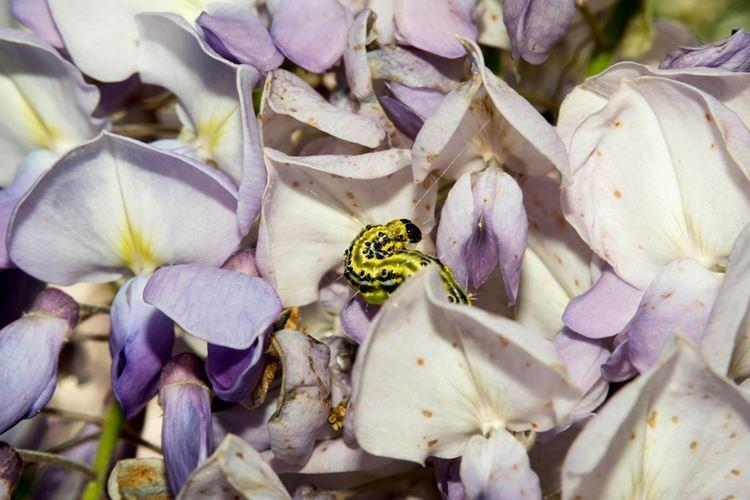
Wisteria is quite resistant to pests, but aphids and clover mites are unlikely to be avoided. For treatment, acaricides and insecticides are used prophylactically and as needed. The most common disease is leaf chlorosis, which usually occurs due to alkaline soil.

Wisteria - photo
All legends about the origin of wisteria are somehow connected with beauty and femininity. You can clearly see that this is not in vain, just by looking at our selection of photos!