If it were necessary to make the top of the most popular vegetables in the world, there would definitely be cucumbers. But even they are susceptible to infections and fungi. You cannot completely protect yourself from problems, but you can prepare in advance. Therefore, we have already collected a selection of the most common diseases of cucumbers with descriptions and photos, and also learned the best methods of treatment!
1. Ascochitis
The disease occurs everywhere: in the ground, greenhouses, young seedlings or adult beds. Gray spots are increasingly spreading over the surface of the leaves. On the stems, they acquire a brown tint, and sometimes they can secrete gum. The fruits are strewn with black dots, darken or completely mummified.
The fungus can be stored for months in old organic residues, so they must be removed. Do not water the beds with cold water and only use treated seed. Greenhouse soil should be steamed and disinfected with formalin every year. In the initial stages, spray the cucumber beds with Bordeaux liquid or copper sulfate with urea.
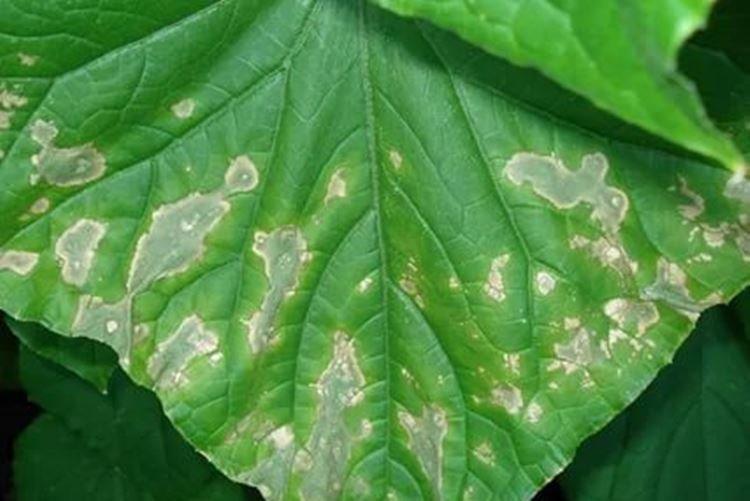

2. Mosaic
Almost all cultures suffer from a dangerous incurable virus. Cucumbers strike several varieties of mosaics, but the essence is the same - the plants are covered with chaotic spots that resemble a bizarre pattern. In later stages, they deform and wrinkle. The stems begin to crack until they burst along their entire length.
Most often, the disease enters the structure of the plant through wounds, so it is important to disinfect all instruments and sections. Destroy weeds in time and avoid pumpkin seeds. Treat the beds from aphids, which carry many diseases. Before planting, process the seeds thermally and chemically - with potassium permanganate or phosphates.
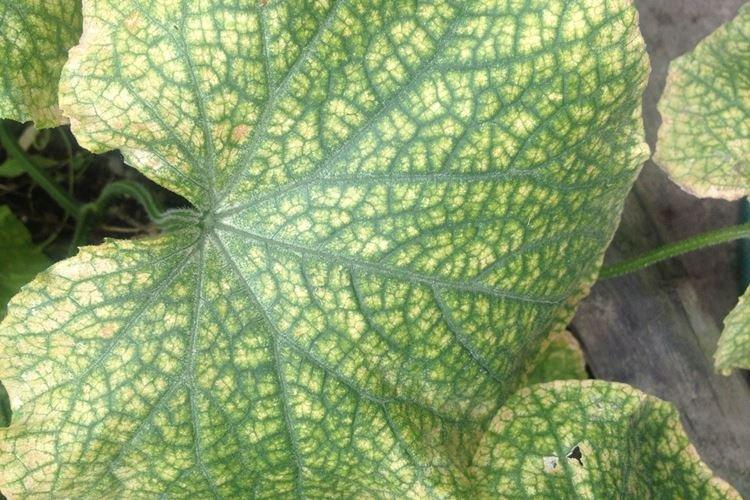

3. Fusarium
Fungal wilting develops rapidly with weakened seedlings immunity. First, the upper part withers, then the leaves turn yellow and the whips dry. In the future, cucumbers may dry out completely, and if the fruits are already formed, Fusarium destroys up to half of the crop.
Most often, the disease develops in greenhouses, so it is important to regularly and continuously ventilate the greenhouse. Inspect the leaves and roots periodically, and remove the affected plants immediately. The treatment uses chemicals like Previkura and its alternatives.
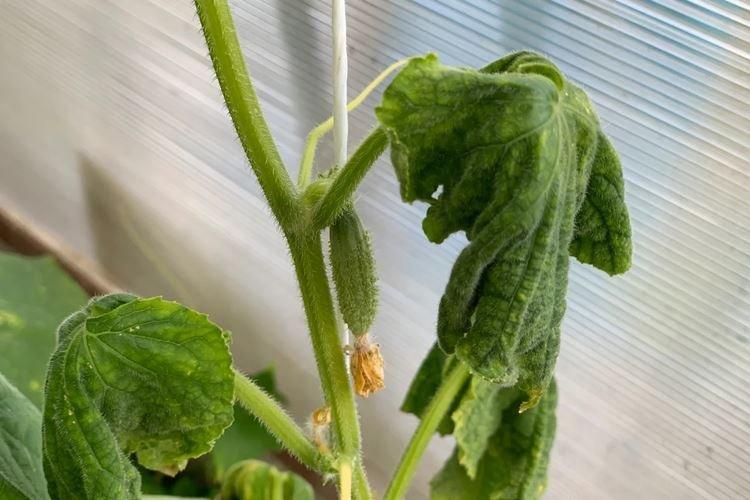

4. Bacteriosis
On hot, rainy days, angular spotting or bacteriosis thrives, which can kill more than 2/3 of the crop. All parts are covered with brown and oily spots. Their number is growing rapidly along with the scale, and in the last stages they turn into foci of necrosis.
Most often, the disease is transmitted through seeds even during planting, so they must be processed. In greenhouses, disinfect the frame, frames and all other elements, regularly ventilate and monitor the humidity. Fitolavin and similar fungicides help well for treatment.
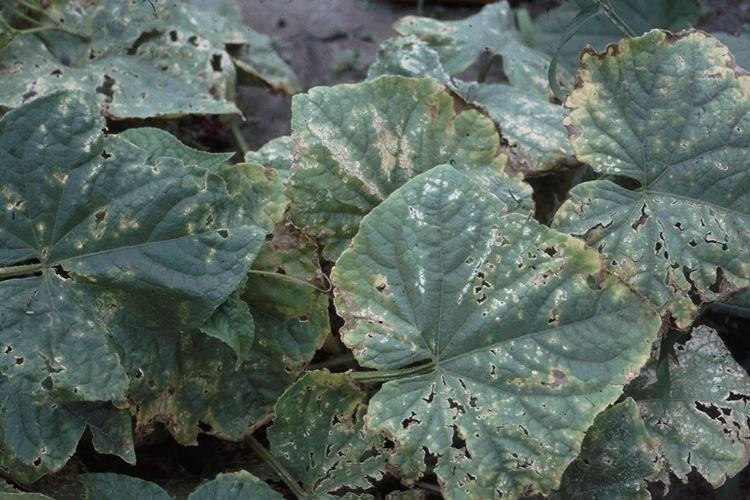

5. Powdery mildew
Whitish spots and plaque on the leaves appear after rains or a cold snap in summer. This is the same fungus that progresses and spreads rapidly. The spots darken, dry, the leaves are deformed, and the fruits lose moisture and taste.
In the initial stages, spraying cucumbers with a solution of liquid soap and baking soda may be enough. If this is not enough, use specialized preparations - Topaz, Novosil, Privent, Baktofit or their analogues. If there was already powdery mildew on the site, then choose varieties with increased immunity.
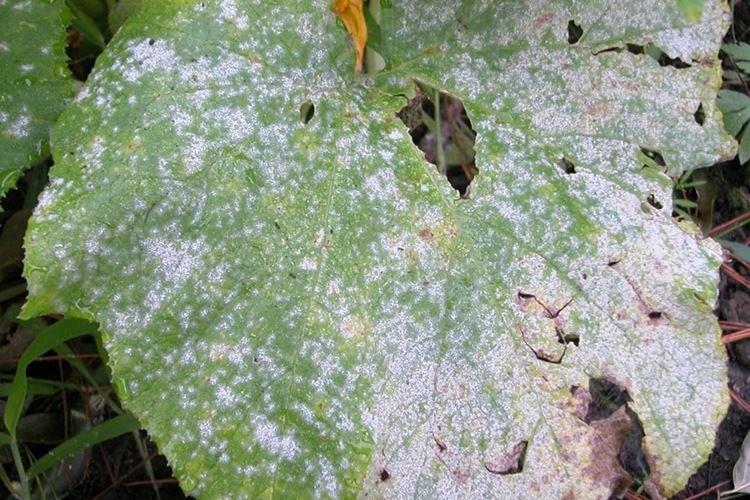

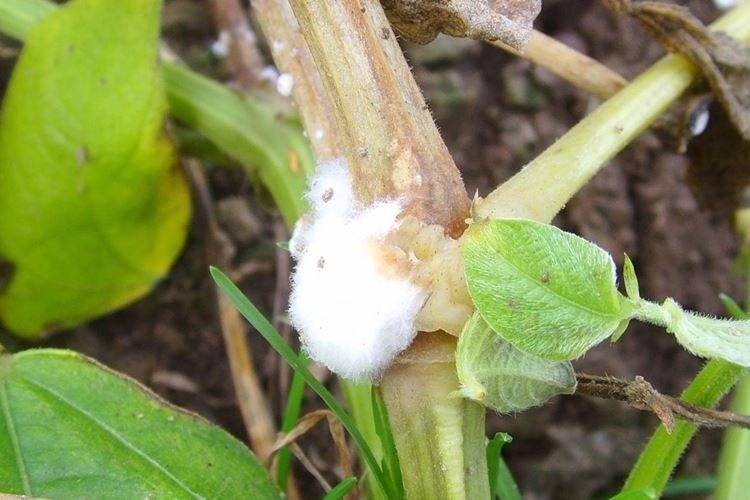
6. Sclerotinia
Shoots and leaves are covered with white formations, sometimes resembling pieces of cotton wool. Gradually, they darken, and the cucumbers are completely covered with white bloom.The fungus grows especially intensively on rainy days or in damp soil.
Maintain distances between plantings so that air can always circulate. Do not plant cucumbers in the same place, and remove plant debris regularly. Cut out all damaged areas to healthy tissues, treat with charcoal and feed the cucumbers with a warm solution of urea and zinc.

7. Cladosporium
Fungal spotting, popularly called "olive", is most often seen in the southern regions. Heat and humidity are ideal conditions for disease in young fruits. They are deformed and covered with a scattering of small spots, which over time surround the cucumbers with a net.
Remove weeds on time, disinfect gardening tools and the greenhouse, and keep an eye on moisture. Insects often carry the fungus, so routine insecticide spraying won't hurt. Also spray the cucumber beds with Bordeaux liquid or copper oxychloride up to 4 times a season.
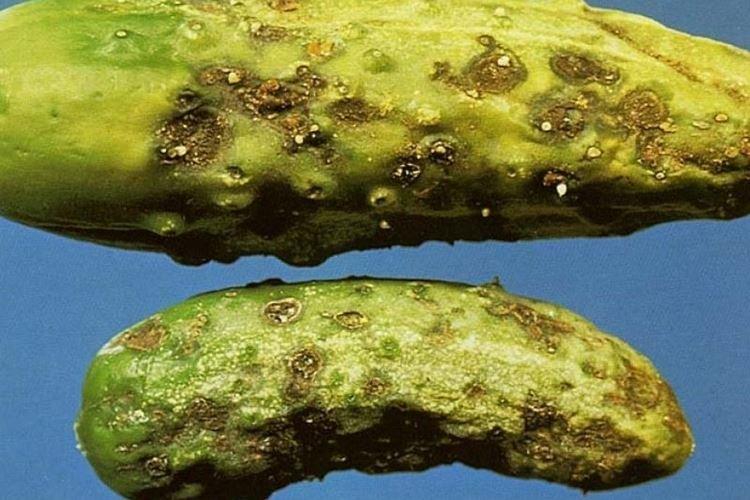
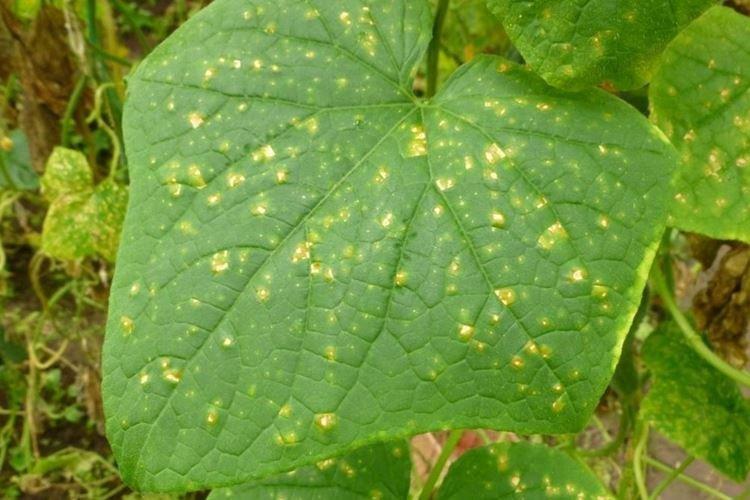
8. Peronosporosis
Pale yellow spots on the leaves begin to grow and darken, especially on wet days. Over time, the tissues die off, and a dark bloom appears on the back of the leaf plates. It is a downy mildew that loves high humidity and is carried by the wind.
At the first symptoms of the disease, immediately treat the cucumber beds with copper-containing fungicides or urea solution. Before planting, disinfect the seeds and soil, and then monitor the temperature and humidity conditions. If downy mildew has appeared by the end of the season, then just harvest and burn the plants.

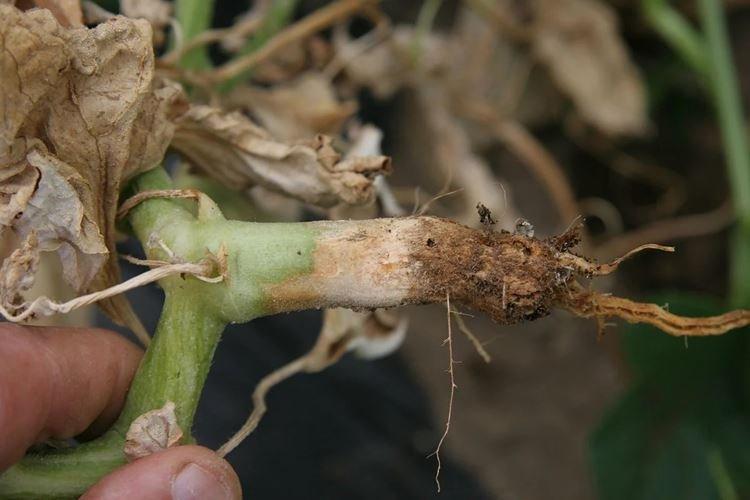
9. Root rot
Most often, rotting of the root system provokes an excess of moisture in combination with too dense soil. Less often - on the contrary, when the rhizome dries up from drought, and after that pathogens multiply on the damaged tissues. The damage to the rhizome gradually rises, the stem becomes thinner, weak, darkens or even becomes rotten.
Due to the fact that the reasons for the appearance of root rot are so contradictory, the main preventive rule is to observe agricultural techniques. Use only warm water for irrigation, dust the root part with chalk, sand or sawdust. If a disease is detected, remove the damaged cucumbers, reduce the frequency of watering and loosen the soil with bleach.