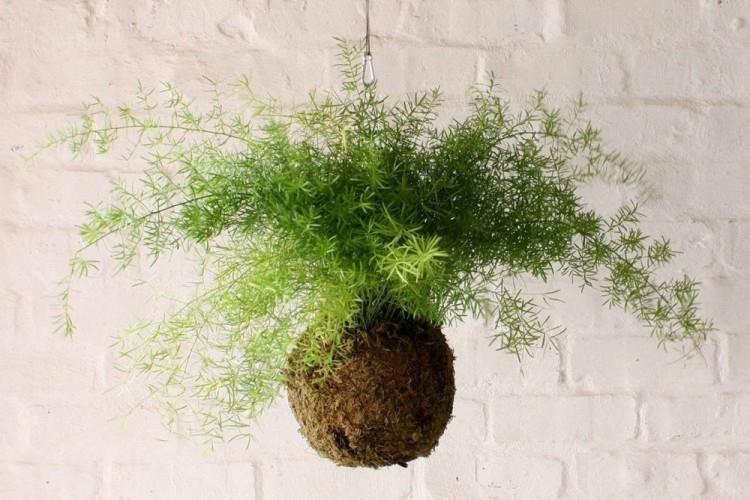
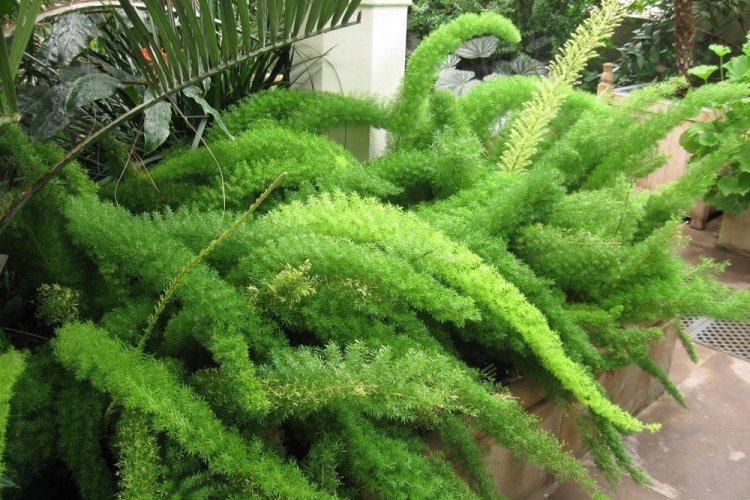
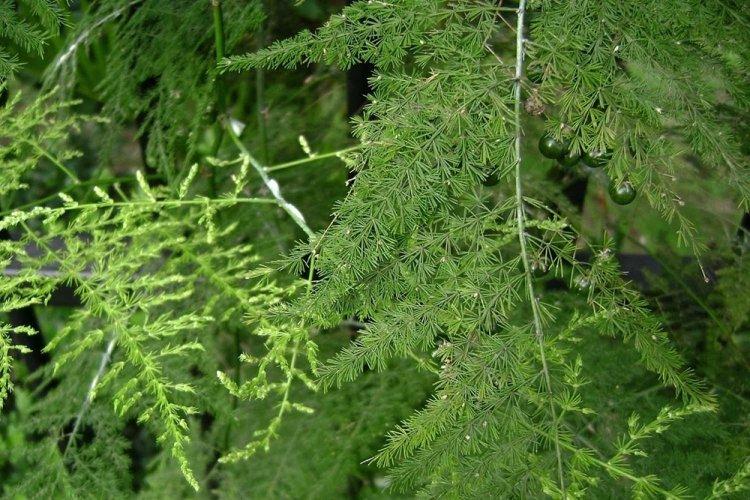
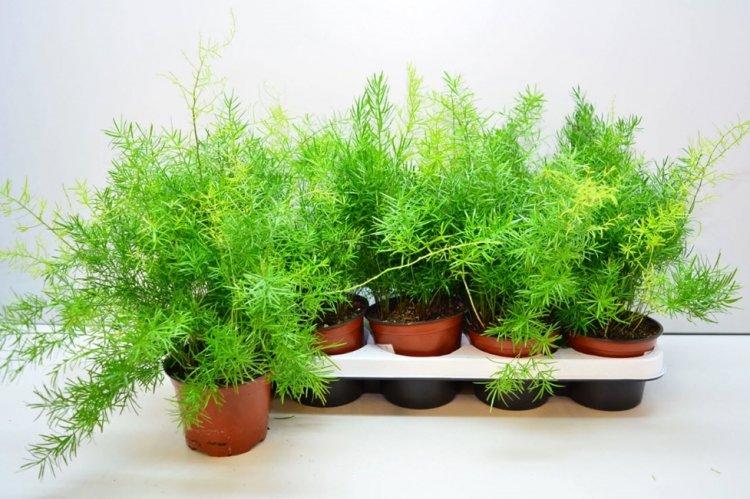
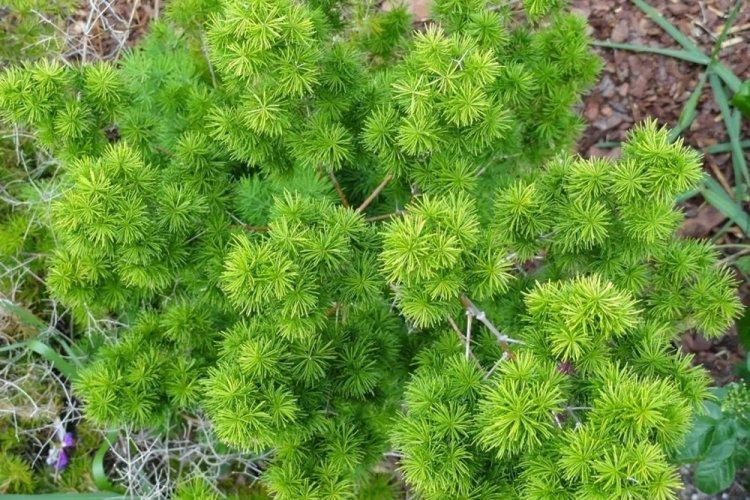
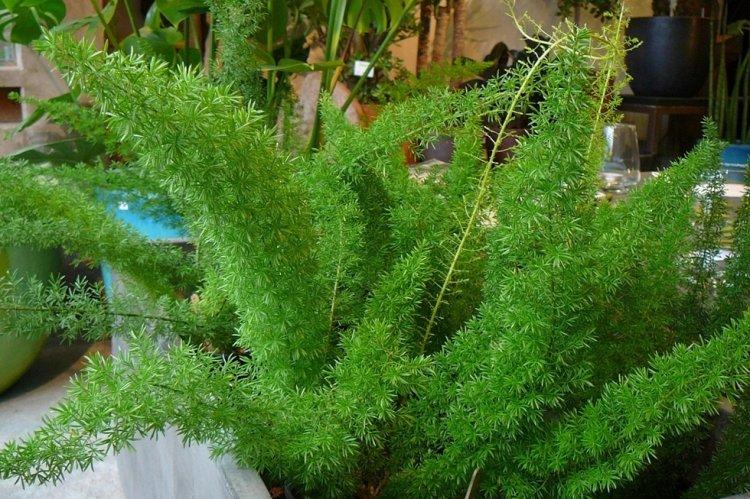
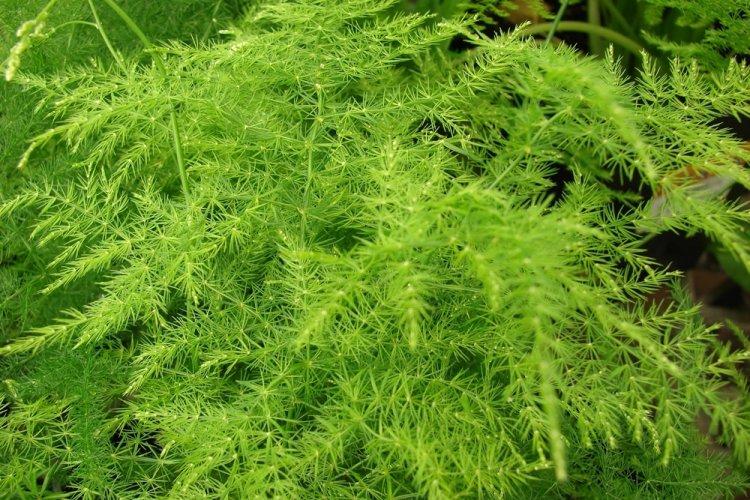
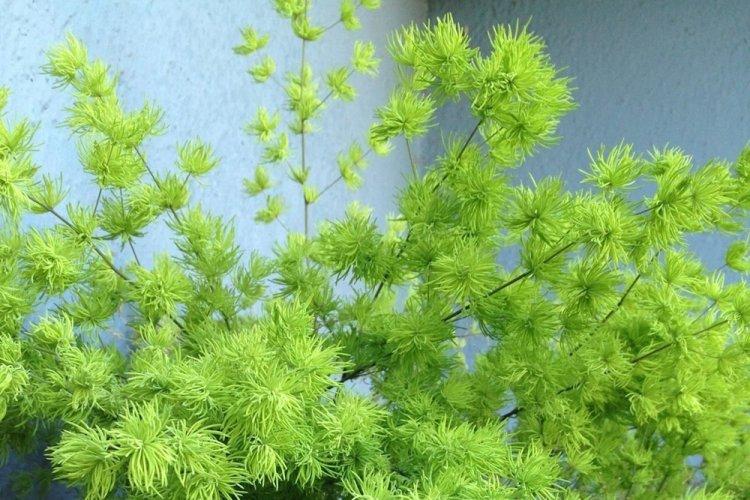
You probably know that asparagus is the real name for common asparagus. It would seem, how do indoor flowers relate to her? In fact, Asparagus is a whole family, and asparagus is a large and varied genus that has several hundred species! Let's tell you more!
general information
The genus of asparagus is distributed literally in all climatic zones and on all continents. Although it is most often found in Asia, Europe and Africa. In some latitudes, it is even grown on special plantations, but this applies to edible varieties.
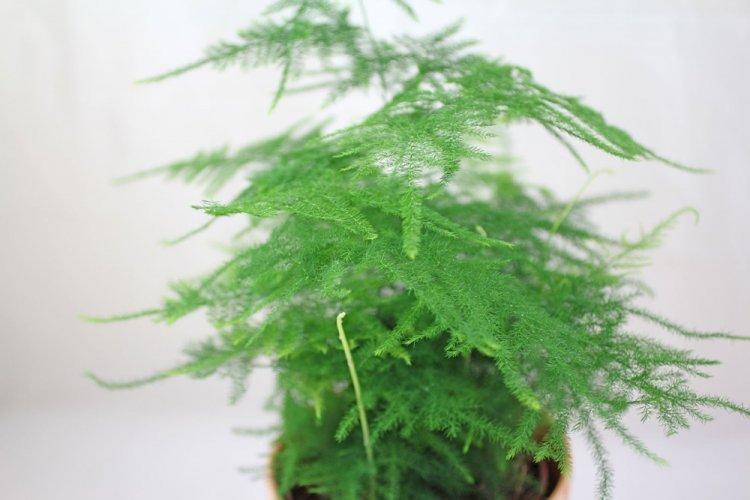
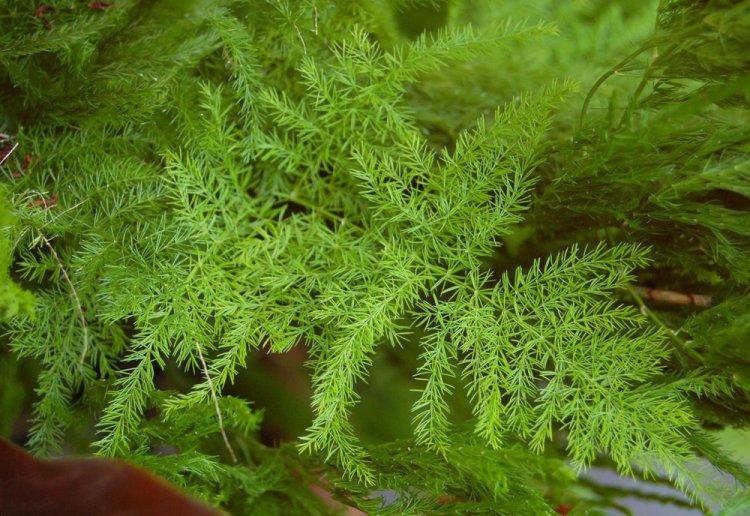
Asparagus is a perennial, but in shape it can be a shrub, liana, or herb. Instead of leaves on thin stems, the same thin and flexible shoots diverge. They resemble elongated needles and are called cladodes. In all external parameters, asparagus resembles a lily, but with a wide branched rhizome.
Asparagus blooms with pale small flowers, and then scarlet berries form. Moreover, the flowers are mono- and bisexual, even within the same bush. But keep in mind that it is almost impossible to achieve flowering on the windowsill at home.
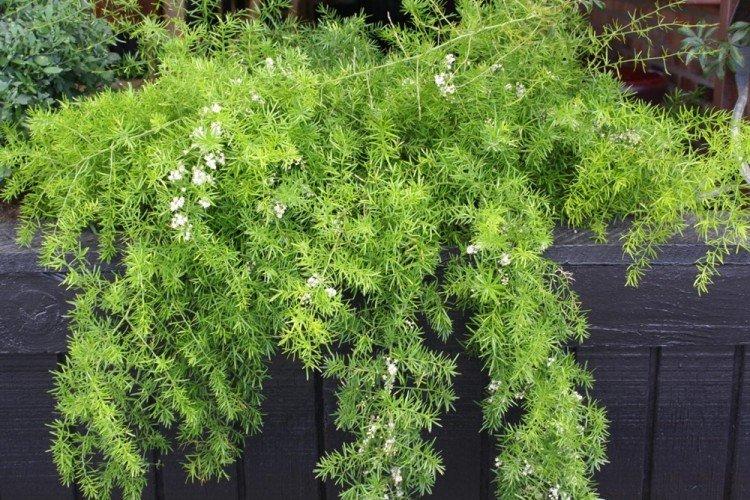

Asparagus species
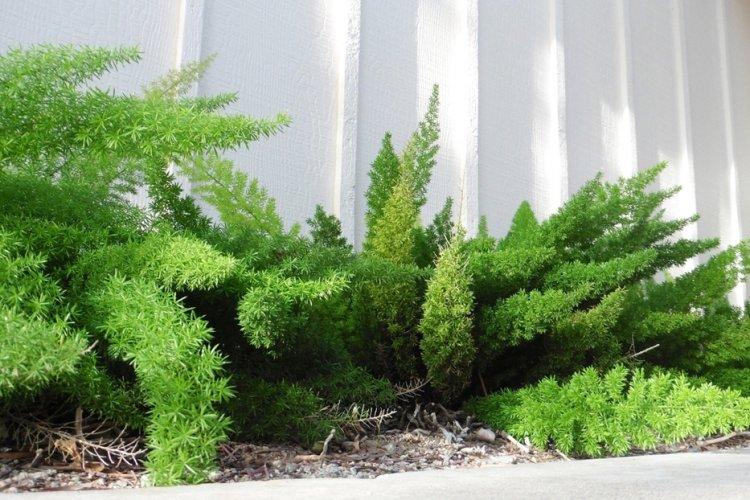
Hundreds of asparagus species differ markedly in their range and appearance. Among them there are edible varieties that are grown on an industrial scale. And there are decorative ones that adorn gardens, interiors and even bouquets or flower arrangements.
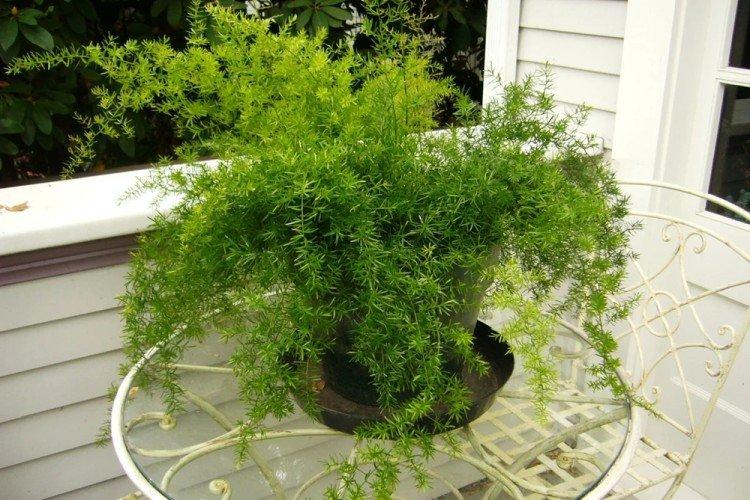
Feathery asparagus
It is a tropical African variety with highly branched vines. Small leaves resemble feathery scales in length of only half a centimeter. Thin cladodes stretch up to one and a half centimeters and grow in groups of up to twelve pieces. Outwardly, a separate shoot, due to its specific shape, resembles a fern leaf.
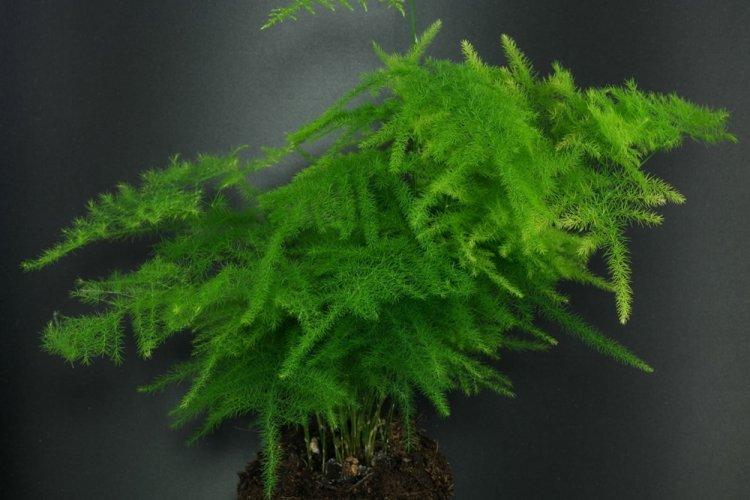

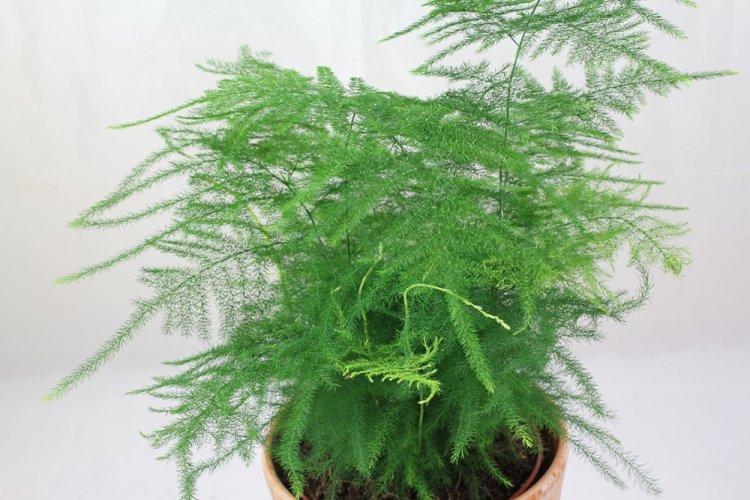
Racemose asparagus
It is a tall, beautiful and bright species that grows up to 2 meters. Claudias are also collected in groups and resemble spruce needles. The brushes of flowers are remarkable not so much for their decorative properties as for their delicate pleasant aroma.
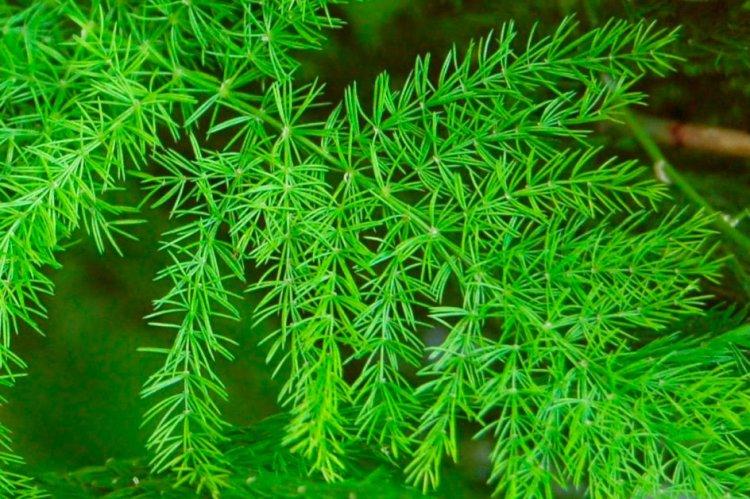

Sickle asparagus
The liana-like variety has a slightly succulent shape, especially during flowering. In nature, flexible creeping shoots stretch up to 15 meters, in a room - up to 4. Large long cladodes (up to 8 cm) push at an impressive distance from each other.
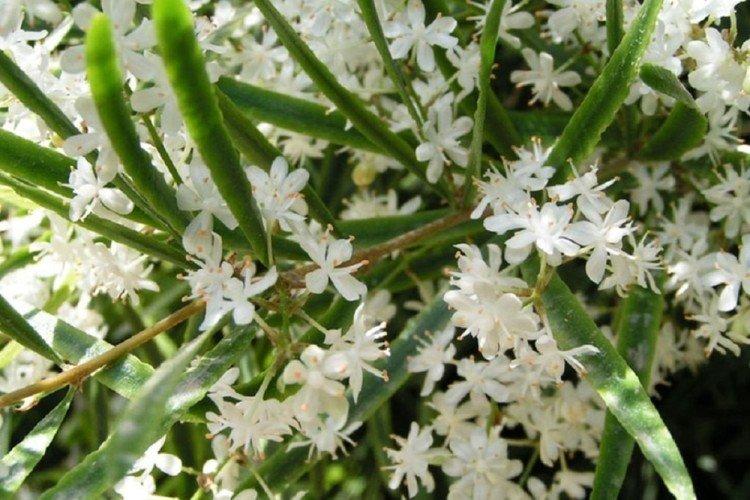

Asparagus Sprenger
This species is also called densely flowered, because in nature it blooms with abundant loose inflorescences of white or pink color. It is a creeping shrub native to the humid African mountains. Long stems up to one and a half meters do not stretch up, but spread along the ground.

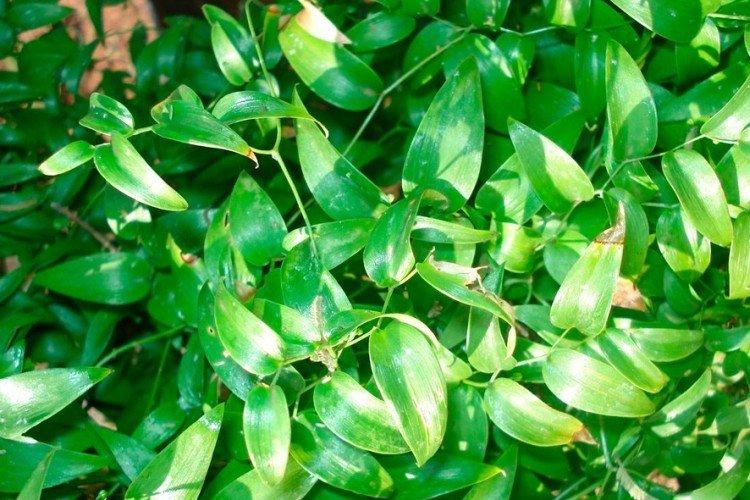
Asparagus asparagus
This is a rare variety in which cladodia do not resemble needles, but ordinary and rather large ovoid leaves. Asparagus asparagus is grown as ampelous, but if you want it to stretch upwards, it needs a strong support. An interesting feature of the bright orange-red fruits is their characteristic citrus scent.

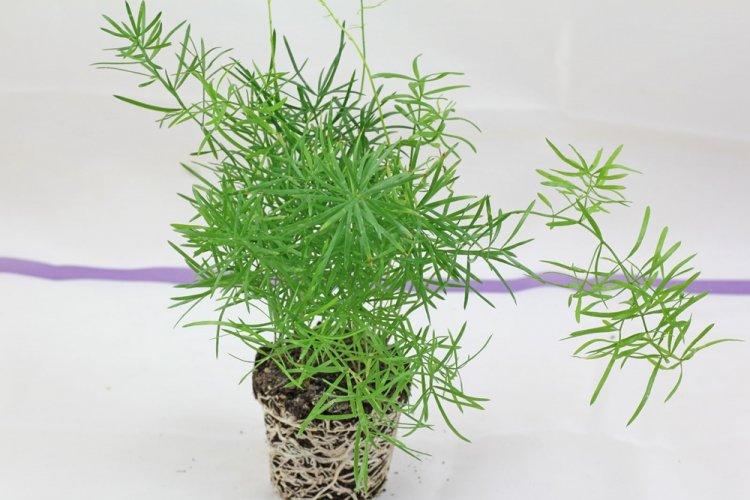
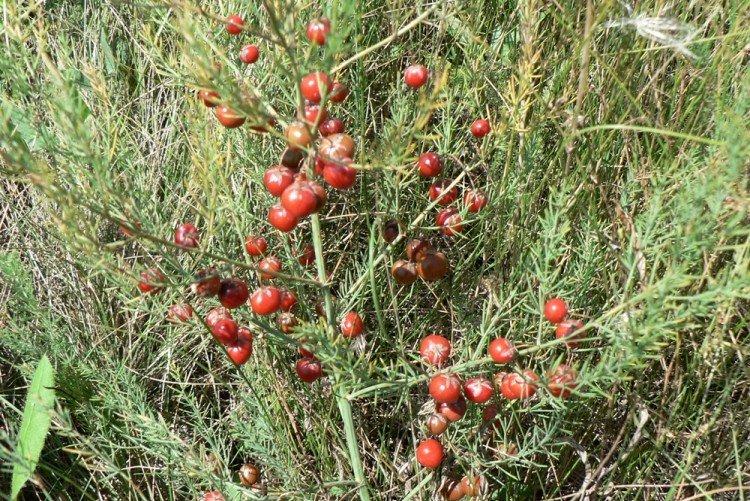
Medicinal asparagus
This is the most common species in temperate latitudes, which is also called common asparagus. Herbaceous shoots can be both compact and high - from 30 to 150 cm. Stems are smooth and densely covered with bundles of thin fibrous cladodia.

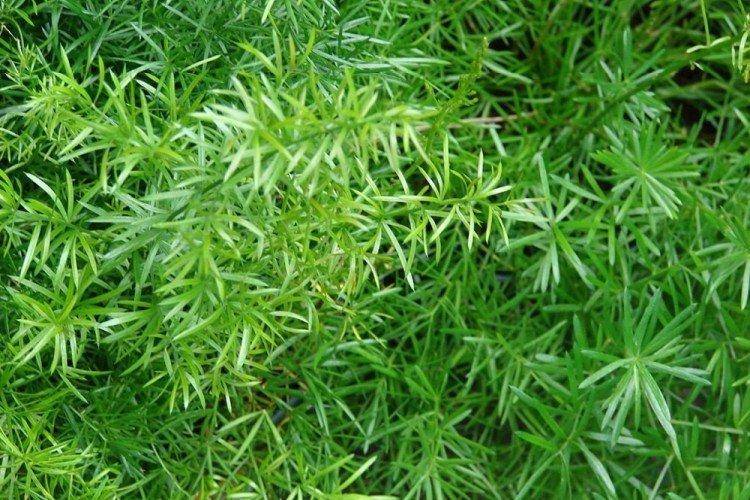
Asparagus Meyer
Ornamental shrub is often grown in gardens and plots because it is lush, voluminous and bright. Tall shoots stretch up to half a meter and are covered with small thin cladodia along the entire length. Each of them recalls either a racemose inflorescence, or just a fluffy brush.
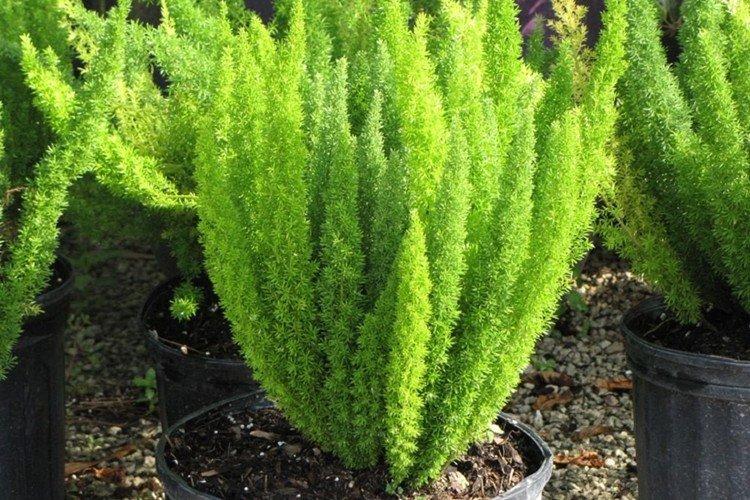

Pyramidal asparagus
Another beautiful ornamental variety, which stretches upward in neat shrubs from half to one and a half meters. It is soft, deep dark green in color and resembles a juniper. Claudia grow densely and in the same plane.

Asparagus care
Asparagus is completely unpretentious to any conditions, therefore it takes root in open ground and flowerpots. It easily tolerates winter frosts and reborns every year with warming. And all because the plant has a very powerful root system that stores enough resources.
Temperature
Asparagus will not kill either heat or frost in moderation, but they can affect its decorative properties. Make sure that in summer the temperature does not rise above 25 degrees. If a flowerpot hibernates in a warm room from 15 degrees, leaves can periodically fly around it - this is the norm. The main thing is to immediately remove all dried shoots so that they do not transfer resources and do not contribute to the development of diseases.

Lighting
Asparagus loves bright light and warmth, so feel free to take it to the east and west in your apartment. The plant does not tolerate direct rays, but this applies to almost all indoor flowers. Towards summer, take the flowerpot out into the fresh air, but start gradually, from several hours a day.

Watering
During the active season, water the asparagus every time the top layer dries. It is best to do this through a sump, and the water will not stagnate in an earthen coma. In cold weather, watering is reduced to a minimum: it is enough to make sure that the lump does not dry out completely.
Asparagus loves high humidity, so it can be sprayed with a spray bottle. Better to do this in the morning and evening, before it is too hot. You can add damp stones or moss to the pan, or use a humidifier.

Fertilizers and feeding
Asparagus is quite active and grows violently, therefore it requires regular feeding. During the peak season - weekly, in autumn - half as often. Fertilizers are needed even in winter, just even less often - after a month. Be sure to dilute the mixture so that they are weakly concentrated.

Transplant and reproduction
Until the shrub is 4-5 years old, it will have to be replanted regularly every spring. After that, you can cut the frequency in half or three times. Asparagus rhizome is developing rapidly, so in a year it will become cramped in its pot.
You can plant a new asparagus from seeds, but this method is not used among amateur flower growers - it is long and difficult. The easiest way is to split a large bush into a couple of parts when you transplant it. You can even shorten the roots a little to fit in the flowerpot.
Cuttings for propagation are also harvested from spring. Take several strong long stems about 10 cm from the bush and plant them in the sand. Then for a month and a half, they need to be placed in warmth under a film in a bright, sunny place. Do not forget to water and air the seedlings, and keep the temperature around 20-22 degrees. After that, the cuttings can be planted in flowerpots and transferred to normal daily care.

Pruning
Asparagus stems cannot be cut because they will no longer grow. Their number is laid in the root system even before the start of growth, and it does not increase over time. You will not do anything with this fact - this is the peculiarity of the plant.
Seasonal pruning is carried out when transplanting at the beginning of winter. Cut off any too old, sluggish and weak shoots, shoots without leaves and painful stems. Then the plant will direct all resources to the growth of the young, in order to bloom again in all its glory.

Pest and disease control
Asparagus rarely get sick, and in 99% of cases this is due to improper care. It sheds leaves due to too bright light or dry air. Aggressive direct light on a hot day can cause burns and yellow edges. Of the parasites, only the spider mite is found, from which standard insecticides or folk remedies will help.

Asparagus - photo
Asparagus in a room or garden is primarily a spectacular ornamental plant. In our latitudes, many do not know about it and, as a result, underestimate it. Completely in vain!